Preface
Glyphosate ammonium, also known as glyphosate, is a non selective foliar spraying organic phosphorus herbicide with the characteristics of high efficiency, low toxicity, and broad spectrum. In 1979, it was first synthesized and developed by Hoechst Chemical Company in the Federal Republic of Germany (later under Bayer). Glyphosate ammonium has an endogenous effect, which can inhibit the synthesis of glutamate amide synthase, leading to nitrogen metabolism disorders, excessive accumulation of ammonia, and chloroplast disintegration in plants, thereby inhibiting photosynthesis and ultimately leading to plant death. Glyphosate ammonium has strong herbicidal activity and has control effects on more than 40 families of plants, including monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous, annual and perennial, herbaceous and shrub plants. It is currently an ideal herbicide for genetically modified crops due to its safety, high activity, wide weed killing spectrum, and low pesticide damage. Its application prospects are very broad.
Glyphosate ammonium is a broad-spectrum contact herbicide with weak systemic absorption. Unlike glyphosate, Glyphosate ammonium first kills leaves and can be transmitted through plant transpiration in the xylem. Its quick acting ability is between that of glyphosate and paraquat.
Table 1 Comparison of Glyphosate, Glyphosate Ammonium and Paraquat
| Glyphosate | Glufosinate-ammonium | Paraquat |
| Principle | Glycine like compounds inhibit enolpyruvate synthase and inhibit protein synthesis | Phosphoric acid, ammonium contact kill, inhibits glutamine synthesis | Quaternary ammonium salt herbicides. The active ingredients have a strong destructive power on the chloroplast membrane, causing rapid cessation of photosynthesis and chlorophyll synthesis |
| Mode of action | Internal absorption and conduction type spectral herbicide, which is transmitted to the underground through stems and leaves, has a strong ability to damage the underground tissues of deep rooted weeds | Non selective conductive herbicide | Quick acting contact killing herbicide |
| Effective time | 7-10 days | 3 days | 1-2 days |
| Crop impact | If the medicine drifts, it will kill crops | Only produce drug spots at the contact area, with little impact on crops | Only affects crop stems and leaves |
| Sowing after medication | It takes 20-30 days after the medication to sow and transplant | Sow and transplant within 1-4 days after medication | Sowing and transplanting can be done at any time after pesticide application |
With the widespread use of herbicides, the problem of environmental pollution and wastewater treatment has become increasingly serious. Currently, the treatment methods for glyphosate containing phosphorus wastewater mainly include biochemical methods, advanced oxidation methods, adsorption methods, and combustion methods, among which biochemical methods are the main ones. The incineration method requires thickening and consumes a huge amount of energy, which can cause serious secondary pollution during the incineration process, making it less feasible.
1. Biological law
The biodegradation of organic compounds is common in water treatment applications in China. In the process of biodegradation of glyphosate, microbial metabolism leads to the breakdown of glyphosate into smaller molecules, and the enzymes involved in biodegradation usually only produce harmless molecules. Therefore, choosing biological methods to degrade organic pollutants is ecologically effective. However, biological methods generally require a long decomposition time and suitable microbial growth conditions to achieve the desired effect. Most studies use glyphosate as a phosphorus source, and rarely use glyphosate as a nitrogen or carbon source. However, in the growth and metabolism of microorganisms, their demand for carbon sources is much higher than that for nitrogen or phosphorus sources. Therefore, microorganisms using glyphosate as a carbon source can achieve a more efficient removal process.
2. Advanced oxidation method
Photocatalytic oxidation is increasingly being studied as an efficient method for removing glyphosate ammonium. Photocatalytic oxidation has been increasingly studied as an efficient method for removing glyphosate. Among them, TiO2, due to its band gap of 3.2 eV, can only utilize 4% of solar radiation, which has led researchers to constantly seek other photocatalysts. In recent years, bismuth tungstate has received considerable attention in the photodegradation of organic pollutants due to its stability, chemical inertness, and excellent photocatalytic activity. However, the combination of photo generated electrons and holes also limits the photocatalytic activity of bismuth tungstate. The traditional Fenton process has disadvantages such as continuous loss of oxidants and iron ions, solid mud formation, reagent handling, and high costs and risks of transportation and storage. The electric Fenton process solves these problems. Compared to other advanced oxidation methods, electrochemistry not only provides higher energy efficiency, but also does not add chemicals. Nowadays, when the concentration of glyphosate is less than 200mg/L, electrochemical oxidation can fully achieve mineralization.
Zhao Zehua et al. used graphite plate as the anode and stainless steel plate as the cathode of a three-dimensional electrocatalytic device, and activated carbon particles as the particle electrode for the reaction. They studied the effect of three-dimensional electrocatalytic oxidation technology on the treatment of glyphosate pesticide wastewater; And the influence of factors such as current density, electrode spacing, electrolysis time, initial concentration, pH value, and particle electrode dosage on its treatment effect was investigated. The experimental results showed that under the conditions of initial wastewater concentration of 300mg · L ^ -1, reaction time of 90min, electrode spacing of 4cm, pH value of 5, current density of 31.5mA · cm-2, and particle electrode dosage of 3.08g · L ^ -1, the COD removal rate of wastewater was 83.48%. Three dimensional electrocatalytic oxidation technology improves charge transfer efficiency by reducing particle spacing; The improvement of current efficiency also significantly enhances the treatment efficiency of wastewater.
3. Adsorption method
The adsorption method is widely used in the field of wastewater treatment due to its advantages such as single tube design and non toxicity. For decades, many people have used different materials to adsorb and remove glyphosate from water environments. Most adsorbents use biochar, such as activated carbon, which has low cost, high aromaticity, and porous structure, which can improve removal efficiency. In addition, chemical modification methods can effectively modify the surface properties of biochar to achieve higher adsorption performance, such as using thiourea modified feces to prepare biochar that increases the apparent adsorption capacity.
Adsorption method is an effective alternative treatment method for glyphosate, but it also has some drawbacks, such as the lack of selectivity of the adsorbent for glyphosate. Therefore, when there are many other pollutants in the wastewater and their concentration is higher than that of glyphosate, even if glyphosate has good affinity with certain adsorbents, it is difficult to use adsorption as the main treatment technology. Only when the concentration of other pollutants in the wastewater is not high but the concentration of glyphosate is high, adsorption is beneficial for removing glyphosate, and further research is needed for the treatment of the residue after adsorption.
The Haipu adsorption+RRP process (wastewater resource utilization) can selectively adsorb and enrich the effective components in glyphosate wastewater, and achieve the recovery and utilization of effective components through desorption process. The treated wastewater can be discharged to meet the standard through biochemical treatment.
3.1 Haipu Customized Processing Technology
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is committed to the research and industrialization of high-performance adsorbents and catalytic products. Through years of independent research and development, we have leading professional expertise in ion exchange technology, adsorption technology, and hybrid technology of nano inorganic materials. We have achieved a series of adsorption and catalytic products, which have been successfully applied in the fields of environmental protection and resource recycling. Haipu, with its independently developed series of high-performance adsorbents and catalytic products as its core, combined with independent and open process technology, has become a professional solution provider in the fields of environmental protection and source recycling.
Haipu adsorption+process core special adsorption materials can selectively adsorb glyphosate in wastewater, achieving efficient adsorption and complete desorption of glyphosate. The content of glyphosate in the desorbed wastewater is greatly reduced, and glyphosate is adsorbed and recovered, returned to the production process for use, achieving the resource utilization of wastewater.
When using Haipu's adsorption process to treat wastewater containing glyphosate, the wastewater is pre filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, and then enters the adsorption tower for adsorption. The special adsorption material filled in the adsorption tower can adsorb glyphosate in the wastewater on the surface of the material. After adsorption saturation, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to regenerate. This process continues in a continuous cycle. The process flow of wastewater adsorption treatment is shown in the following figure.
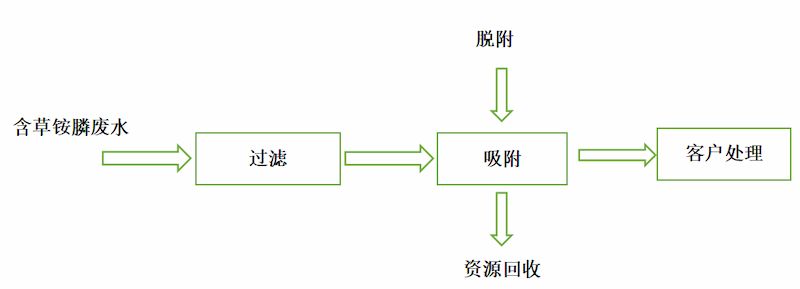
Figure 1 Process Flow Diagram
3.2 Technical advantages
The Haipu adsorption+RRP process (wastewater resource utilization) can efficiently remove substances such as glyphosate from wastewater, with a high removal rate. The adsorbed water can be treated biochemically to meet the standard or according to the needs of the enterprise;
Recyclable glyphosate in wastewater can improve resource utilization and increase the economic benefits of enterprises;
Low equipment investment, low operating costs, advanced and reliable technology, and no secondary pollution;
Modular component form, high degree of automation, and simple operation.
4. Summary
In the above methods, the adsorption method does not damage the structure of glyphosate. If the concentration of glyphosate in the wastewater is high, the adsorption method can be used before (or after) other treatment processes to reduce the final concentration of glyphosate; Both biological and oxidative methods can damage the glufosinate molecules and produce by-products during the treatment process, which can affect the efficiency of glufosinate molecule treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the degradation pathway of glyphosate in the process of biological or oxidative treatment. The advantage of these processes is that they can oxidize glyphosate and most of its by-products. In order to reduce costs, it is more reasonable to use adsorption to first reduce pollution concentration, and then use biological or oxidation methods for treatment.




 CN
CN



