Adsorption Material
- Chelating Resins
- Strong Base Anion Exchange Resins
- Weak Base Anion Exchange Resins
- Strong Acid Cation Exchange Resins
- Weak Acid Cation Exchange Resins
- Hybrid Resins
- Macroporous Adsorption Resins
- Mixed Bed Resins
- Salt Lake Resource Extraction Adsorbents
- Lithium Battery Recycling Resins
- Hydrometallurgy Resins
- Nuclear Grade Resins
- Plant Extraction Resins
- Water Treatment Resins
- Gas Adsorption Resins
- Chemical Industry Resins
- Fruit/Vegetable Juice Resins
- HP686——Copper removal resin
- HPB119——Boron removal resin
- HP2000——Aluminum-Loaded Fluoride Removal Resin
- HPU3——Uranium Extraction Resin
- KF420——Copper, Zinc, Cobalt Removal Resin
- HP115——Rhenium Extraction Resin
- HP380——Molybdenum Extraction Resin
- HP1053——Vanadium Extraction Resin
- HP1042——Tungsten Extraction Resin
- HPC116——Polysilicon Disproportionation Catalytic Resin
- HPC118——Polysilicon Disproportionation Catalytic Resin
- HPC211——Polysilicon Disproportionation Catalytic Resin
- HP705——Deep Heavy Metal Removal Resin
- HP709——Cobalt/Nickel Removal Resin
- HP606——Heavy Metal Removal Resin
- HPN201-Nuclear Power Plant Waste Purification Resin
- HPN202-Nuclear Power Plant Waste Purification Resin
- HPN203-Nuclear Power Plant Waste Purification Resin
- HUC800——Regenerable Polishing Mixed Bed Resin
- HUA70——Regenerable Polishing Mixed Bed Resin
- HP160 -- Aluminum-Based Lithium Adsorption
- HPL900——Titanium-Based Lithium Adsorbent (Salt Lake Brine/Precipitated Lithium Mother Liquor)
- HPY408——Rubidium/Cesium Extraction Resin
- HP560——Arsenic/Phosphorus/Antimony Removal Resin
- HP268——Organic Matter Removal Resin
- HP706——Advanced Calcium/Magnesium Removal Resin
- HPC001——Cobalt Extraction Resin
- HP5600——Phosphorus Removal Resin
- HP409——Germanium Extraction Adsorbent
- HP4040——Calcium/Magnesium Removal Resin
- HP686——Copper removal resin
- HP605——Iron Removal Resin
- HP707——Lead/Zinc Removal Resin
- KF380——Heavy Metal Adsorbent
- HPN609——Plutonium Extraction Resin
- HPN341——Plutonium Extraction Resin
- HPN606——Plutonium Extraction Resin
- HPN383H——Boron-Silicon Separation Resin
- HPN1053——Uranium Extraction Resin
- HPN705——Uranium Extraction Resin
- HPN340——Uranium Extraction Resin
- HPN507——Cesium Extraction Resin
- HPN403——Cesium Extraction Resin
- HPN408——Cesium Extraction Resin
- HPN4010——Strontium Extraction Resin
- HPN4080——Strontium Extraction Resin
- HPN4900——Radioactive Anion Removal Resin
- HPN119——Radioactive Anion Removal Resin
- KFN340——Radioactive Anion Removal Resin
- KFN380——Radioactive Anion Removal Resin
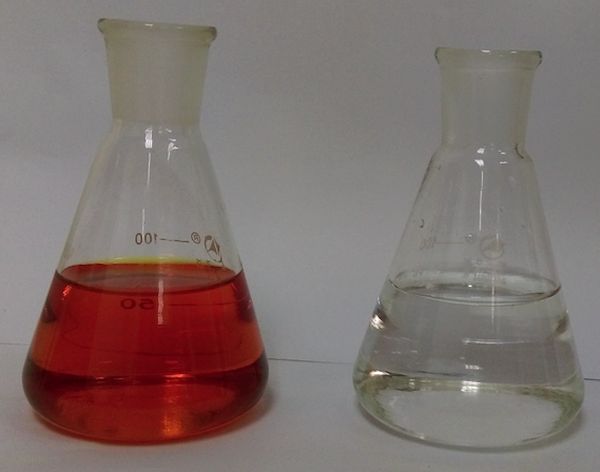
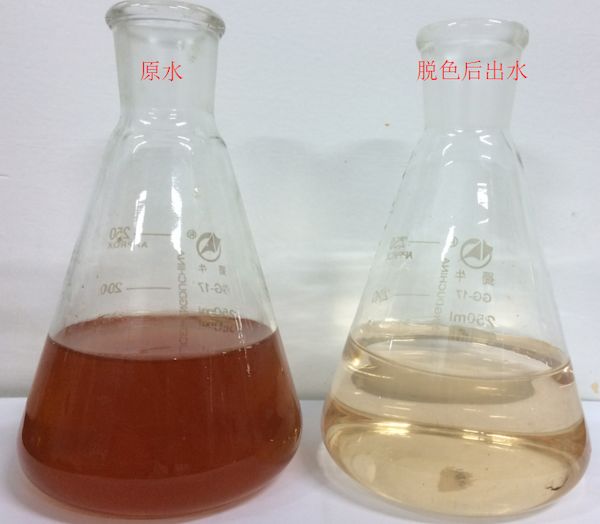
- HP388——Decolorization and COD Removal Resin
- HP1048——Deep Heavy Metal Removal Resin
- HP1050——Oil/TOC Removal Resins
- HDV336——Aromatic Hydrocarbon Removal Resin
- HDV330——Ester/Ether Removal Resin
- HDV536——Halogenated Hydrocarbon Removal Resin
- HPC137——CO2 Capture Adsorbent
Synthesis and Purification Materials
Membrane Material
WHAT ARE YOU LOOKING FOR?
 CN
CN