China is a major producer of chemical raw materials, especially in the production capacity and output of fermented drugs, which are ranked first in the world; The production process of active pharmaceutical ingredients generates a large amount of "three wastes", with complex waste components and serious pollution hazards, which in turn increases the environmental pressure on pharmaceutical companies. Pharmaceutical companies are constantly being required to limit production or suspend production for rectification due to non-compliance with environmental standards. The treatment of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the three wastes has attracted much attention.
The production process of chemically synthesized drugs mainly starts with chemical raw materials as reactants. Through chemical synthesis, intermediate drugs are synthesized, and their drug structures are modified to obtain the target product. Then, the final product is obtained through major processes such as deprotection, extraction, refining, and drying. Pharmaceutical companies choose a variety of solvents based on the different types of pharmaceuticals, such as ethanol, isopropanol, acetone, dichloromethane, dichloroethane, etc. The organic waste gas generated by the volatilization of various solvents is generated during the extraction and refining processes, solvent distillation recovery, transportation, and storage. Due to the requirement of cleanliness, most pharmaceutical companies have closed workshops and discharge organic solvents in an organized manner. Pharmaceutical companies have made solvent recycling a major part of their production processes during their operations. After extracting the active ingredients, solvents are generally recovered through distillation towers. The types of exhaust gases generated are generally relatively single, but they have high concentrations, strong odors, and are generally flammable and explosive gases with high risks. They have become one of the key focuses of air pollution control. Common pharmaceutical waste gas treatment processes include low-temperature condensation, pyrolysis, membrane separation, and activated carbon adsorption.
Low temperature condensation method is a process that utilizes the characteristic of the saturation vapor pressure of organic pollutants decreasing with temperature to lower the exhaust gas temperature below the boiling point of the pollutants, transforming them from a gaseous state to a liquid state. This process has a good recovery effect on high concentration organic waste gas, but if the condensation is not thorough, there will still be high concentration waste gas discharged, which is generally used as a pre-treatment process for waste gas treatment.
The pyrolysis method can be divided into direct combustion method and catalytic combustion method. The direct combustion method burns the combustible components in the exhaust gas directly as fuel, but the calorific value of the exhaust gas concentration is generally not sufficient to maintain its own combustion, and auxiliary fuel needs to be added for combustion. Mostly used as the ultimate measure for pharmaceutical waste gas treatment. Catalytic combustion method utilizes the catalytic effect of a catalyst to convert large organic molecules in exhaust gas into harmless substances or substances that are easier to separate and remove from the airflow. The catalyst price for this process is relatively high, the process conditions are strict, and the treatment effect is unstable.
The basic principle of membrane separation method is to use a polymer membrane with selective permeability for organic waste gas, which allows organic matter to permeate through the polymer membrane under a certain pressure and be enriched. The gas with removed organic components is left in the permeate side discharge system. This process is simple and has low energy consumption. But at the same time, the investment cost is high and there are few applicable types.
The activated carbon (fiber) adsorption method utilizes the adsorption properties of porous carbon to separate and adsorb organic components from exhaust gas, and the treated exhaust gas is discharged. Activated carbon is regenerated and utilized by adsorption saturation and desorption. The adsorption effect of activated carbon in this process is greatly affected by moisture, and the adsorption performance decreases significantly after multiple regenerations; Frequent replacement of activated carbon is required, and the replaced activated carbon is hazardous waste with high processing costs.
In response to the current problems in pharmaceutical waste gas treatment, Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has developed an HDV type polymer nano adsorbent that can adsorb and remove organic components from waste gas. After adsorption saturation, the nano adsorbent is desorbed and regenerated using thermal desorption, and organic vapor can be condensed and recovered. The specific process is as follows:
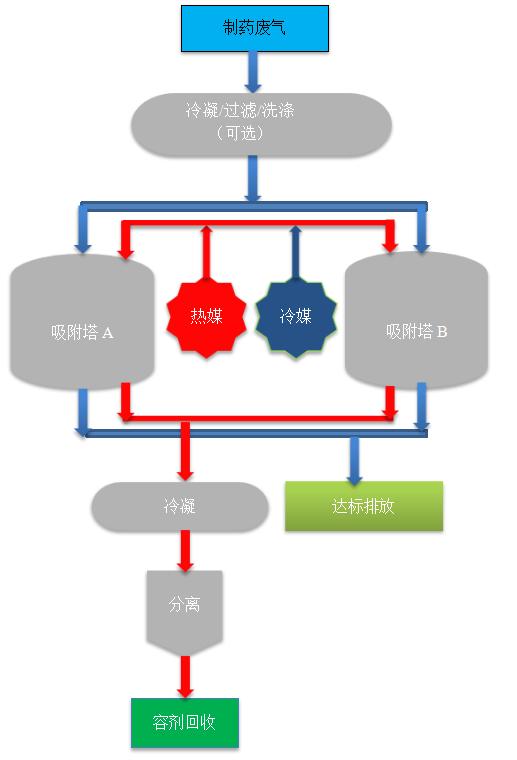
Specific process description: Pharmaceutical waste gas is first extracted by vacuum pump/fan/compressor, and then pre condensed/washed (optional). The condensed and liquefied oil is received in a storage tank, and the uncondensed organic components are transferred to an adsorption tower containing nano adsorbents for adsorption and enrichment. The exhaust gas can be discharged in compliance with standards after adsorption. After the adsorbent is saturated, low-pressure steam (or hot nitrogen) is introduced into the adsorption tower for stripping. The blown organic vapor is then condensed and liquefied, and allowed to settle and separate into layers, allowing for the separation and recovery of organic solvents. The temperature of the nano adsorbent after thermal desorption is relatively high. After cooling to room temperature with clean air, it can be reused for adsorption. The adsorption tower is usually equipped with two units, one for adsorption and one for desorption as a backup. For high concentration exhaust gases, two or more units can also be configured.
This process can achieve a removal rate of over 99% for organic components in pharmaceutical waste gas and has been validated on multiple project sites.
Advantages of HDV type nano adsorbent:
1. Controllable pore structure and high pore volume;
2. It has good physical and chemical stability, is resistant to acid, alkali, and organic solvents, has high thermal stability and mechanical strength, and is wear-resistant;
3. The surface exhibits high hydrophobicity, and humidity has no effect on adsorption performance;
4. Easy to regenerate and stable adsorption performance;
5. No hazardous waste is generated without the need for replacement.
In summary, the comparison of various processing methods is shown in the following table:




 CN
CN



