During the dye production process, a large amount of pollutants are generated in processes such as sulfonation, nitration, diazotization, reduction, oxidation, and acid (salt) precipitation. The industry requires efficient printing and dyeing wastewater treatment processes. Technical personnel from Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. will explain in detail for you.
It is estimated that 90% of inorganic raw materials and 10% -30% of organic raw materials are transferred to water in dye production. The concentration of pollutants is high, and the composition of wastewater is complex, containing a large amount of organic matter and salts. It has the characteristics of high CODCr, deep color, and strong acidity and alkalinity, which has always been a difficult problem in wastewater treatment and has become one of the key sources of environmental pollution.
Current situation of dye wastewater treatment
The current situation and research progress of dye wastewater treatment at home and abroad. Dyes not only have specific colors, but also complex structures, mainly composed of polymer complexes, which are difficult to break. Their biodegradability is low, and most of them have potential toxicity. Their fate in the environment depends on many unknown factors.
In addition, dye production has the characteristics of multiple varieties, small batches, and fast updates, which makes it difficult to find effective treatment methods for dye wastewater. There are many treatment methods for dye wastewater, which will be briefly introduced below.
1.1 Membrane Separation Method
Membrane separation method is a general term for the selective permeation of certain components in liquids using special membranes. Commonly used membrane separation methods include dialysis, electrodialysis, ultrafiltration, and reverse osmosis.
Membrane technology can separate dye wastewater into concentrate and permeate. The concentrated solution can be used for dye recovery, and the permeate can also be reused for dye production.
This approach can achieve effective treatment of wastewater and prevent dye loss with drainage, without causing water pollution.
However, membrane separation technology has high processing costs due to concentration polarization, membrane fouling, and the high cost of membrane replacement, which seriously hinders the large-scale industrial application of membrane separation technology.
1.2 Extraction method
The essence of extraction is to use an extractant that is immiscible with water but can dissolve pollutants well, so that it can be fully mixed with wastewater and separated and extracted using the different distribution ratios of pollutants in water and solvents, thereby purifying wastewater.
The commonly used extraction methods include solution extraction, electrophoresis extraction, liquid membrane method, etc.
However, the extraction method has disadvantages in practical applications, such as high consumption of extractants, difficulty in separating extracts, high cost of treating one ton of water, and inability to continuously process large amounts of water.
1.3 Radiation method
Microwave radiation is a commonly used method for treating dye wastewater in radiation methods.
Microwave radiation is a new technology that emerged in the 1980s for the elimination of organic pollutants. Microwaves are located between infrared radiation and radio waves in the electromagnetic spectrum, and only affect polar molecules in liquids. They can cause high-speed rotation and collision of polar molecules, resulting in thermal effects that change the thermodynamic functions of the system, reduce the activation energy of reactions, and decrease the chemical activity of molecules.
In addition, microwaves also have non thermal effects, that is, in the microwave field, violent polar molecular oscillations can break chemical bonds and degrade pollutants.
But the main challenges of this technology are that the equipment used to generate high-energy particles is expensive, the technical requirements are high, and the energy consumption and energy utilization efficiency of this method are high; In addition, special protective measures are required to avoid the harm of radiation to the human body. Therefore, in order to put this law into operation, a lot of research and exploration work is needed.
1.4 Oxidation method
Oxidation method is also a commonly used method for treating dye containing wastewater, currently including high-temperature deep oxidation method, chemical oxidation method, and photocatalytic oxidation method. The application of photocatalytic oxidation technology in the field of dye wastewater treatment has good market prospects and economic benefits.
1.5 Coagulation method
Coagulation method is a commonly used method for wastewater treatment, mainly including coagulation sedimentation method and coagulation air flotation method.
However, the operating cost of this method is relatively high, with a large amount of sludge and difficulty in dehydration. The removal rate of hydrophilic dyes and other soluble N and P compounds in the water is poor, and new efficient coagulants need to be developed.
1.6 Biological methods
Generally speaking, physical and chemical treatment methods only concentrate and transfer pollutants, and the potential impact on the environment cannot be ignored. Biological methods, on the other hand, utilize pollutants as a nutrient source for microorganisms, and are an ideal means of reducing and harmless pollutants.
Biological methods are widely used in dye wastewater treatment, with advantages such as good treatment efficiency and low operating costs.
However, due to technical reasons, the operation of this law is unstable, its applicability is not wide, and it is greatly affected by external factors, which has limited its practical application to a certain extent.
1.7 Adsorption method
The adsorption method has a special position in the field of wastewater treatment due to its ability to selectively enrich certain compounds. Adsorption refers to the residual surface energy of molecules or atoms on a solid surface due to unbalanced forces. When certain substances collide with the solid surface, they are attracted by these unbalanced forces and remain on the solid surface.
The result of adsorption is the concentration of adsorbate on the adsorbent, and the surface energy of adsorption decreases.
Adsorption technology is the use of porous solids to adsorb one or several pollutants in wastewater, in order to recover or remove certain pollutants, and is also a method for purifying wastewater. Commonly used adsorbents in adsorption methods include activated carbon, resin, minerals, waste, etc.
There are two mechanisms for adsorption decolorization of dye wastewater: adsorption and ion exchange. The adsorption efficiency is influenced by many physical and chemical factors, such as the interaction between dye and adsorbent, the specific surface area of adsorbent, the particle size, temperature, pH value, and adsorption time of adsorbent.
(1) Activated carbon adsorption method
The high price of activated carbon limits its application. After use, activated carbon needs to be regenerated using two methods: high temperature and desorption treatment. Regeneration can result in a loss of 10-15% of activated carbon.
(2) Mineral and waste adsorption method
Many substances in nature have porous structures and good adsorption properties, which can be used to treat dye wastewater. Natural minerals mainly include various clays, ores, coal, etc., which are generally abundant in reserves. In China, there are also a large amount of waste such as slag, slag, coal slag, fly ash, etc., which are more cost-effective. Therefore, the application prospects of these inorganic adsorbents are relatively broad.
(3) Adsorbent adsorption method
In the late 20th century, with the successful development of structurally improved ion exchange resins, adsorption resins, and composite functional resins, resin adsorption methods were widely used in the treatment and resource utilization of chemical wastewater.
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has synthesized adsorbents with different physical and chemical properties for the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater, and achieved good treatment results. The adsorbents synthesized by the company can not only effectively remove COD in dye wastewater, but also remove indicators such as ammonia nitrogen in wastewater. The wastewater can be discharged continuously and stably in compliance with standards.
Industry customer demand
The characteristics of printing and dyeing wastewater determine that this type of wastewater cannot meet discharge standards through traditional treatment methods. Therefore, the adsorption method developed by Haipu functional materials can be used to treat this type of wastewater, in order to optimize the treatment effect and economic cost, which is a development direction in dye wastewater treatment.
The needs of dye wastewater treatment for enterprise customers include the following three points:
(1) Efficiently and stably remove COD, chromaticity, and other pollutants from wastewater to below discharge limits;
(2) Low investment cost, low operating cost, and convenient equipment operation and maintenance;
(3) Advanced and reliable technology, with no secondary pollution.
Haipu Functional Material Customization Process
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in Suzhou Industrial Park. It is a national high-tech enterprise that uses special adsorbents and catalysts as its core technology, supporting the development of application processes, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to solve related environmental problems for customers.
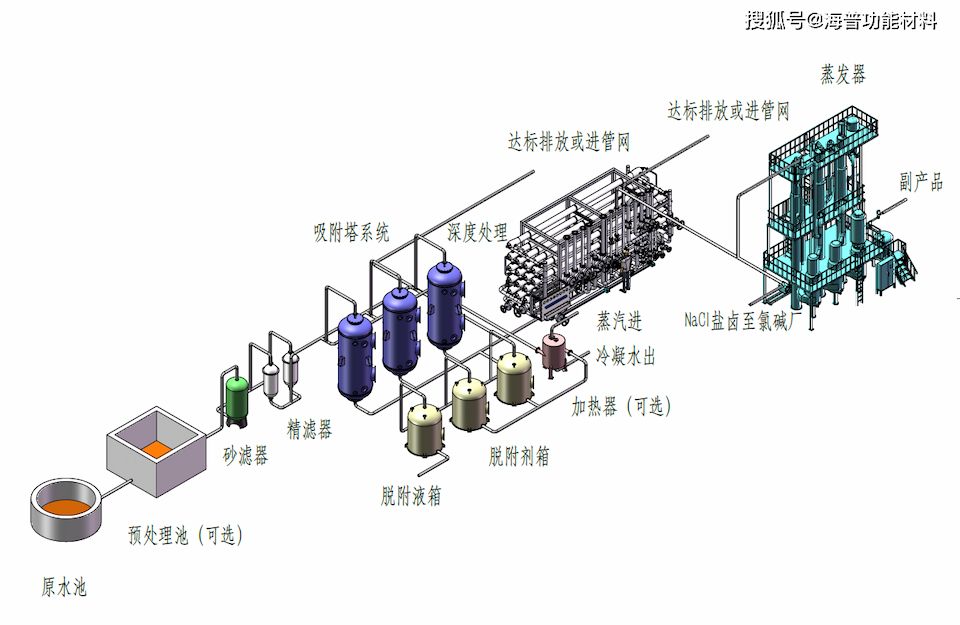
The principle of the Haipu adsorption process is to use the special adsorption materials developed by our company to selectively adsorb the components or substances to be removed. When the adsorption is saturated, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to regenerate. This process is continuously repeated. The conventional process diagram for treating wastewater by adsorption method is shown in Figure 4-1.
Process treatment effect
The use of adsorption technology to treat dye wastewater can effectively remove COD from the wastewater. The specific treatment data are shown in Tables 5-1 to 5-2.
| Raw water COD content | COD content in effluent | Compliance rate |
| 15600 mg/L | 400 mg/L | 97.40% |
| 15300 mg/L | 350 mg/L | 97.70% |
| 16000 mg/L | 420 mg/L | 97.30% |
Table 5-1 Wastewater Adsorption Data
A certain enterprise in Shandong requires that the COD content in the treated wastewater be less than 500mg/L. Experimental treatment results show that using adsorption treatment can stabilize the COD in the wastewater to be less than 500mg/L. While ensuring compliance with customer requirements, a certain safety margin is left, which can effectively prevent water quality fluctuations in the incoming wastewater from causing the effluent to not meet standards. The treatment effect is shown in the following figure.
The production process of this enterprise generates 100 tons of dye wastewater per day. After adsorption treatment, the COD in the wastewater can meet the discharge requirements. The enterprise has adopted the adsorbent and process package from Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd., and the adsorption system is currently running smoothly.




 CN
CN



