The general form of nitrogen in nature is NO3-. After water pollution, ammonia nitrogen is formed, with some existing in the form of free ammonia and others in the form of ions, mainly depending on the pH of the solution. Ammonia nitrogen wastewater can lead to a decrease in dissolved oxygen in water and an increase in harmful substances, posing a threat to the safety of aquatic animals and indirectly damaging human health through the food chain. Therefore, removing ammonia nitrogen from water is an effective solution to address eutrophication and promote health.
1. Wastewater treatment methods:
The main treatment methods for ammonia nitrogen wastewater currently used in industry include blow off, chemical precipitation, adsorption, ion exchange, and membrane separation., The advantages and disadvantages of each process are compared as follows:
| Processing technology | Advantage | Shortcoming |
| Blow off method | It is highly effective in treating high concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater, with a simple equipment structure, easy operation, mature technology, and high removal rate. | The energy consumption is high, and the ammonia blown out needs further absorption and treatment, which can easily cause secondary pollution. The low-temperature effect is significantly reduced, and the pH value of the wastewater needs to be adjusted back after blowing off. |
| Chemical precipitation method | The process is simple, the footprint is small, the reaction speed is fast, the recovery rate is high, and the ammonia nitrogen obtained by precipitation can be recycled. | Incomplete removal of ammonia nitrogen and high dosage of chemicals result in high costs. |
| Adsorption method | Simple art, easy operation, fast response, energy-saving and efficient, high recovery and utilization rate of ammonia. | The adsorption method requires the addition of special treatment agents and the installation of specific equipment, resulting in higher treatment costs than the precipitation method. |
| Ion exchange method | Low investment, simple process, small footprint, not affected by temperature. | Resin is prone to wear and tear, requiring frequent regeneration and backwashing, complex operation, and high cost. The original solution needs to be pre treated. |
| Membrane separation method | Stable effect, fast start-up, easy operation, high recovery rate of ammonia nitrogen, and the membrane can be regenerated and reused repeatedly. | Pre treatment of the original solution is required to treat high concentrations of ammonia nitrogen, and the membrane requires frequent regeneration and water washing, resulting in increased costs. |
2. Introduction to Haipu customized process:
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in Suzhou Industrial Park. It is a company that uses special adsorbents and catalysts as its core technology, supporting the development of application processes, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to provide customers with solutions.
A national high-tech enterprise that solves relevant environmental problems. Haipu's technical team won the Suzhou Industrial Park Leading Talent Award in 2013 and 2015, and the Gusu Leading Talent Award in 2015. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. was rated as a national high-tech enterprise twice in 2015 and 2018, and was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalytic Functional Nanomaterial Engineering Technology Research Center in 2018. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has a leading technological level in the treatment of adsorption materials. The supporting adsorption treatment process is efficient and stable, and has solved multiple environmental problems for many leading domestic enterprises in the industry.
The principle of the Haipu adsorption process is to use the special adsorption materials developed by our company to selectively adsorb the components or substances to be removed. When the adsorption is saturated, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to be regenerated. This process is continuously repeated. The conventional process of treating wastewater by adsorption method is shown in the following figure.
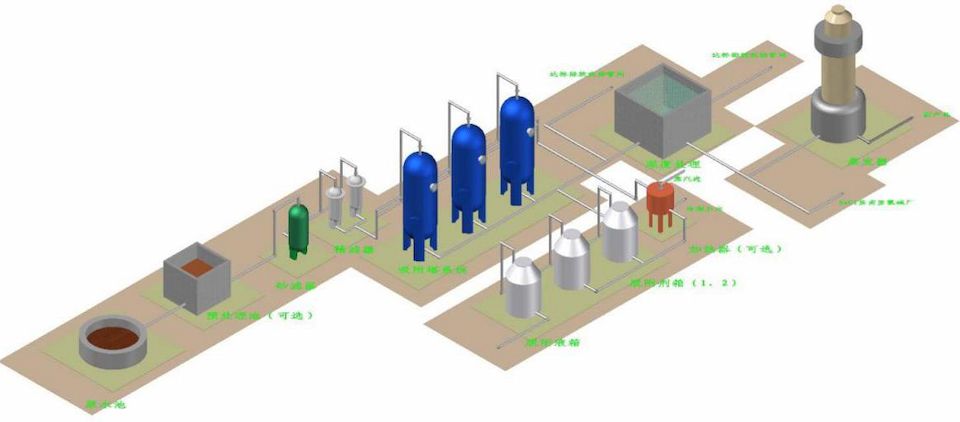
Conventional process diagram for adsorption treatment of wastewater
When using Haipu's adsorption process to treat fluorine-containing wastewater, the wastewater is pre filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, and then enters the adsorption tower for adsorption. The special adsorption material filled in the adsorption tower selectively adsorbs and enriches fluorine in the wastewater, reducing the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the adsorbed water. After adsorption saturation, the adsorbent material is subjected to desorption treatment to regenerate and resume adsorption, and this process is continuously repeated.
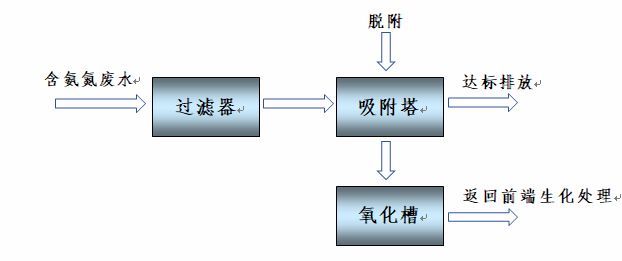
Process flowchart
3. Case Introduction
This newly built fluoride removal wastewater adsorption treatment facility has a total designed wastewater treatment capacity of 120m3/d. It uses adsorption technology to treat fluoride containing wastewater. Experiments have shown that using special adsorbents for adsorption can effectively reduce the fluoride concentration in wastewater. The specific treatment data is shown in the table below:
| Indicator | Water volume (t/d) | Ammonia nitrogen (mg/L) |
| Absorb incoming water | 120 | 223 |
| Adsorbed water 1 | 120 | 4.62 |

Processing rendering, from left to right are raw water and adsorbed effluent, respectively
The adsorption process customized by Haipu can deeply adsorb and remove ammonia nitrogen from wastewater. The ammonia nitrogen content in the adsorbed water is much lower than the customer's requirement (<25mg/L). As can be seen from the figure, most of the ammonia nitrogen in the wastewater is adsorbed and removed, and the ammonia nitrogen is transferred to a small amount of desorption solution. After oxidation, the desorption solution can be directly returned to the front-end biochemical system, meeting the customer's discharge requirements without generating secondary pollution, ensuring the normal operation of the enterprise.
4. Advantages of adsorption method for fluoride removal:
Efficiently remove ammonia nitrogen substances from wastewater with high removal efficiency, and strictly control the ammonia nitrogen content in the effluent (effluent ammonia nitrogen content<15mg/L);
Deep treatment of biochemical wastewater with high concentration ratio, solving the problem of low concentration wastewater treatment;
Low design investment, low operating costs, advanced technology, and no secondary pollution;
The process flow is simple, reliable, and occupies a small area.




 CN
CN





