In industrial production processes such as coal chemical, power, and petrochemical, a large amount of wastewater containing inorganic salts is generated. These wastewater have high salt content and belong to high salt wastewater. If such wastewater is directly discharged, it will damage the surrounding soil, increase the salt content of the water body, and waste mineral resources. Therefore, it is very important to study how to effectively treat this type of high salt wastewater.

The basic idea for treating high salt wastewater is to separate salt and water with low investment and operating costs, and recycle them separately. Although a simple evaporation process can be achieved, it consumes a lot of energy. In recent years, the application of some new technologies and processes has greatly reduced separation costs, leading to rapid development in the recycling and utilization technology of high salt wastewater.
1. Conventional treatment techniques for high salinity wastewater
Thermal concentration technology
Thermal concentration is a method of concentration using heating, mainly including multi-stage flash evaporation (MSF), multi effect evaporation (MED), and mechanical vapor recompression (MVR) technology. MSF is the earliest distillation technology applied, and due to its mature process and reliable operation, it has been widely used in seawater desalination worldwide. But there are disadvantages such as low thermodynamic efficiency, high energy consumption, severe equipment scaling and corrosion. MED operates several evaporators in series to maximize the utilization of steam heat and improve the efficiency of thermal energy utilization. MED has higher thermodynamic efficiency than MSF, but occupies a larger area. The thermodynamic efficiency of MED is directly proportional to its efficiency. Although increasing its efficiency can improve the system's economy and reduce operating costs, it will increase investment costs. MVR technology uses a compressor to compress the secondary steam generated in the evaporator, increasing its pressure, temperature, and enthalpy value, and then using it as heating steam, which has the advantages of small footprint and low operating costs. Compared to MED, it can compress and reuse all secondary steam, reducing the amount of steam used and thus being more energy-efficient.
Membrane separation technology
Membrane separation technology is driven by factors such as pressure difference, concentration difference, and potential difference, and is achieved through size exclusion, charge repulsion, and physicochemical interactions between solutes, solvents, and membranes. The main technologies used in desalination treatment of high salt wastewater are nanofiltration membrane (NF), electrodialysis (ED), and reverse osmosis membrane (RO). NF technology can remove the majority of easily scaling ions such as Ca2+, Mg2+, SO42-, etc. Therefore, desalination is the main application of nanofiltration technology, which can pretreat the inlet water of RO system to reduce the fouling of RO membrane by scaling ions. ED technology is a membrane separation technique that uses potential difference as a driving force and utilizes the selective permeability of ion exchange membranes to remove electrolytes from solutions. ED has high freshwater recovery rate, long membrane effective life, high operating temperature, and minimal membrane fouling, but cannot remove bacteria and microorganisms from the water. For economic reasons, compared to RO technology, ED technology is suitable for treating water bodies with salt concentrations ranging from 1000mg/L to 5000mg/L in small and medium-sized enterprises. RO technology has become quite mature as a desalination technology for seawater and brackish water. In recent years, with the increase of high salinity wastewater in industrial production, RO technology has also been widely used to concentrate various high salinity industrial wastewater. Usually, the desalination rate of RO is greater than 95%, and the water recovery rate is between 60% and 80%. Although RO separation technology has been widely used in industrial wastewater desalination and recovery, the increase in energy consumption and decrease in recovery rate caused by membrane fouling are still the main issues limiting the application of RO technology. High efficiency reverse osmosis (HERO) technology has been developed on the basis of conventional RO. Compared with conventional RO, HERO has no restrictions on the pollution density index of the influent, does not require a high investment pretreatment system, and operates at high pH values, greatly reducing the pollution of organic matter and microorganisms on the RO membrane.
Membrane distillation technology
Membrane distillation (MD) technology has been developed in the past 20 years and is a separation process driven by the vapor pressure difference on both sides of the membrane. It can be seen as a combination of membrane separation and distillation technology. The membrane used in MD technology is a hydrophobic microporous membrane. Under the drive of steam pressure difference, steam molecules on the high temperature side pass through the membrane and are condensed and recovered on the low temperature side. The solution on the high temperature side is concentrated. Compared with traditional distillation and membrane separation technologies, MD technology has mild operating conditions, a retention rate of up to 100%, strong pollution resistance, a wide range of energy sources, and strong adaptability to wastewater salt concentration. MD technology can be applied in fields such as freshwater production, heavy metal removal, and food industry, but currently the vast majority are still in the laboratory or small-scale factory testing stage, and industrialization is not yet mature. MD technology has broad application prospects for different types of saline wastewater. However, there is a phase transition process from liquid to vapor on the high-temperature side of MD technology, which consumes a large amount of thermal energy and reduces the efficiency of thermal energy utilization.
Direct desalination electro adsorption technology
Electro adsorption desalination technology (EST) utilizes the electrochemical properties of charged electrode surfaces to remove ions and decompose organic matter from water. This technology adopts a new concept of water treatment, which has unique advantages in treatment efficiency, adaptability, energy consumption, operation and maintenance, and environmental friendliness. Compared with distillation, RO and other technologies, EST technology uses electrostatic action instead of extracting ions from water through high temperature and high pressure, resulting in relatively lower energy consumption. Compared with RO technology, EST system has a smaller discharge of concentrated water and does not contain membrane components, so it has lower requirements for inlet water quality. EST technology does not require the addition of any chemicals for electrode material regeneration, and the discharged water does not contain any new secondary pollutants. However, EST technology is suitable for treating water with conductivity less than 5000 μ S/cm, and the desalination rate is not very high. Therefore, according to the requirements of recycled water quality, EST technology can be combined with other desalination technologies to reduce overall operating costs. If EST technology is used to pretreat the inlet water of the RO device in the HERO system, it can improve the system's water production rate and outlet water quality, extend the service life of the membrane, and reduce operating costs. At present, EST technology still has shortcomings such as low electrode adsorption capacity, high cost, and poor reusability. Therefore, improving the performance of electrode materials and optimizing the electro adsorption model will promote the maturity of EST technology.
Concentrated liquid treatment technology
When using thermal distillation or membrane separation technology to concentrate saline wastewater, a small amount of higher concentration concentrate will be produced. If the concentrated solution can be further processed to minimize or even achieve zero emissions of the final waste, it will achieve both economic and environmental benefits. The concentrated liquid produced during hot distillation and EST processes comes from raw water, and direct crystallization or drying technology can be selected to achieve zero emissions depending on the degree of pollution. The composition of membrane filtration concentrate is complex, so its treatment is the key to achieving zero wastewater discharge. The treatment of membrane filtration concentrate should be achieved in two steps. Firstly, adsorption, advanced oxidation, biochemistry and other methods are used to degrade the organic matter in it. Then, the membrane filtration concentrate is subjected to deep desalination to improve the overall water production rate. At present, the main desalination methods for membrane filtration concentrate include membrane distillation (MD), forward osmosis (FO), and eutectic freeze crystallization (EFC). As mentioned earlier, MD technology can treat high concentration waste liquids (close to saturation), so combining MD technology with crystallization technology to treat concentrated liquids can basically achieve zero emissions. FO technology is a membrane separation process driven by permeation, which utilizes the permeation gradient on both sides of a semi permeable membrane to make water flow from the concentrated liquid (low osmotic pressure) side to the driving liquid (high osmotic pressure) side. This process does not require external pressure, so energy consumption is relatively low. FO technology can process concentrated solutions with high TDS mass concentration (>70000mg/L), and the degree of membrane fouling is lower than that of pressure driven membrane separation technology. EFC technology achieves the separation of ice and salt by lowering the temperature of the concentrated solution to a low melting point. The separated ice is washed and dissolved to obtain pure water. The crystallized salt is mixed with the mother liquor and the crystallization process is repeated.
2. Introduction to Haipu customized process:
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in Suzhou Industrial Park. It is a national high-tech enterprise that uses special adsorption materials and catalysts as its core technology, supporting the development of application processes, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to solve related environmental problems for customers. At present, the current situation of environmental protection in China is that 70-80% of environmental protection/technology (or environmental protection companies) have only solved 30% of environmental problems, and the remaining 70% are environmental problems that urgently need new materials and technologies to thoroughly solve, in order to achieve sustainable development in various industries and the Chinese Dream of clear water and blue sky. Haipu Company is positioned for the research and industrialization of new materials and technologies, providing cost-effective green and environmental protection solutions to safeguard the sustainable development of the industry and customers.
The Haipu technology team is led by Dr. Cai Jianguo and consists of several PhDs and masters who have worked in well-known foreign companies and research institutions such as Dow Chemical, General Electric, Novartis, Nanjing University, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Dr. Cai Jianguo, a technology leader, is skilled in the research and industrialization of adsorption and catalytic functional nanomaterials. He has worked for Rohm and Haas in the United States, Dow Chemical in the United States, and the National Engineering Technology Research Center for Organic Toxic Pollution Control and Resource Utilization, engaged in the research and industrialization of new materials related to green chemistry and environmental protection. He has been responsible for the entire process of research and industrialization of multiple functional material projects, from small-scale research and pilot scale up to 10000 ton level application trials. In 2010, he won the Dow Chemical Technology Innovation Award. We have over 40 national invention patents, 1 US invention patent, and 10 utility model patents. The technical team led by Dr. Cai won the 7th Suzhou Industrial Park Leading Talent Award in 2013, the Gusu Leading Talent Award in 2015, the 9th Suzhou Industrial Park Leading Talent Award in 2015, and was awarded the National High tech Enterprise twice in 2015 and 2018. In 2018, it won the Jiangsu Provincial Education Teaching and Research Achievement Award, and was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalytic Functional Nanomaterial Engineering Technology Research Center.
As a provider of green environmental protection solutions, Haipu focuses on the research and development of separation and catalytic functional new materials, as well as the development of supporting processes. Through technological innovation, Haipu has solved relevant environmental problems for many leading domestic enterprises in the industry.
The relevant certificates are shown in the following figure:


Part of the wastewater in the chemical industry has high salt content and contains a large amount of organic matter. The color of the salt evaporated products in the wastewater is high, and it must be treated as hazardous waste, which incurs high treatment costs. The treatment of high concentration organic wastewater seriously affects the normal production of enterprises. From the perspective of clean production, Haipu Company adopts a special adsorbent adsorption and concentration method to selectively adsorb and recover organic matter in wastewater. While recovering organic products, the COD of the wastewater is greatly reduced. After adsorption treatment, the wastewater is evaporated and the evaporated salt is white, and the salt can be disposed of as solid waste, solving the problem of high color and high treatment cost of enterprise wastewater evaporation.
Process diagram for adsorption treatment of wastewater
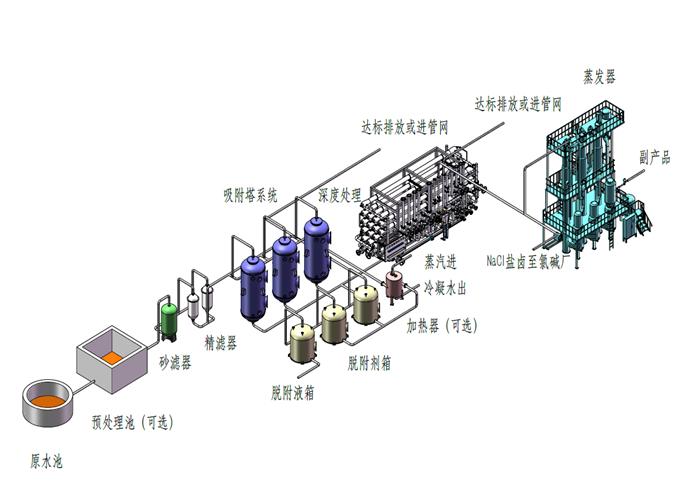
Process flowchart
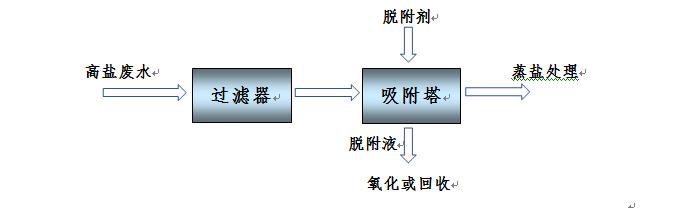
Scope of application
Treatment of high salt wastewater decolorization or salt evaporation white color
advantage
1. Reduce the COD of the adsorbed effluent, turn the evaporated salt in the adsorbed effluent white, and convert the evaporated waste salt from hazardous waste to solid waste, greatly reducing the treatment cost of the enterprise;
2. Remove organic compounds in wastewater that are difficult to biodegrade or have high chromaticity, improve the stability of the subsequent salt evaporation system, and reduce the risk of blockage in the salt evaporation device;
3. High salt mother liquor wastewater can desorb and recover products from the mother liquor, solving the problem of salt evaporation color and recovering products, which has significant economic benefits;
4. The equipment has low operating costs, high degree of automation, and simple operation.
Wastewater adsorption treatment data
Case 1 Adsorption of inlet and outlet water data
| Water volume(m³/d) | Raw water COD(mg/L) | Effluent COD(mg/L) | Salt content |
|
| 200 | 8790 | <1500 | ~10% |

Figure 1 Appearance of Adsorbed Inlet Water (left) and Adsorbed Outlet Water (right)

Figure 2 Effect diagram of evaporation recovery of sodium chloride

Figure 3 Salt steaming effect before (left) and after (right) on-site renovation
3. High salt wastewater treatment plan for a chemical unit
Explanation of Adsorption Principle
The basic principle of our company's processing technology is to utilize the adsorption performance of special adsorption materials to adsorb and enrich aniline in wastewater into the adsorption material. After adsorption saturation, the adsorption material is desorbed to regenerate and resume adsorption, and this process is continuously repeated.
| Index | Water volume(t/d) | Aniline(mg/L) | COD(mg/L) | Colour | Remarks |
| Absorb incoming water | 200 | 98.1 | 2500 | Reddish brown |
|
| Adsorbed water | 200 | <10 | <1000SS | Canary yellow |
|
| Oxidation effluent | 200 | <10 |
| Water clear | Evaporation treatment |
| High concentration desorption solution | ~1.33 | / |
|
| Return to front-end process processing |
| High concentration water washing solution | ~1.33 | / |
|
|
|
Note: The designed running time is 24 hours per day.
Process treatment effect
Our company conducted multiple batches of adsorption and desorption experiments on the sampled wastewater on site. The specific experimental results and comparison chart before and after treatment are as follows:
Table 3-1 Adsorption inlet and outlet water data
| Project | Raw water aniline(mg/L) | Aniline in effluent(mg/L) |
| 1 | 98.1 | 3.3 |
| 2 | 98.1 | 4.2 |
| 3 | 98.1 | 3.6 |

Figure 3-1 Appearance of Raw Water (left), Adsorbed Water (middle), and Oxidized Water (right)
Technological process
The process flow is shown in Figure 3-2. After the wastewater is filtered and treated by the customer, it is first finely filtered to intercept suspended solids and fine particles, preventing impurities from entering
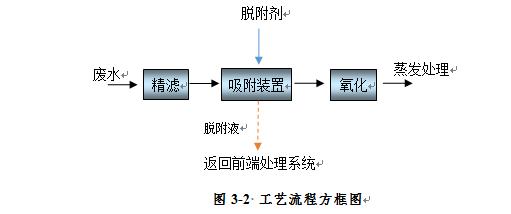
In adsorbent materials, it affects the adsorption performance. The filtered wastewater is then sent to an adsorption tower equipped with special adsorption materials for adsorption. After adsorption saturation, the adsorption materials are subjected to desorption and regeneration treatment. The regenerated adsorption materials can be reused, and the adsorbed water is evaporated for treatment. The high concentration desorption solution can be used in the customer's front-end treatment system.
Adsorption operation instructions
To ensure the continuous and stable operation of the device, and to ensure the effectiveness of the device's water output, the adsorption device adopts a 3 tower 2 series 1 desorption operation mode. Among them, 2 towers are connected in series at the beginning and end to adsorb the water output, and 1 tower is rotated for desorption. During desorption switching, the original first tower is desorbed, and the original tail tower is transformed into the first tower and then reconnected with the desorbed tower (used as the tail tower) to adsorb the water output. The illustrated process is shown in the figure below, where each adsorption tower rotates its roles in the order of arrows during different operating periods.
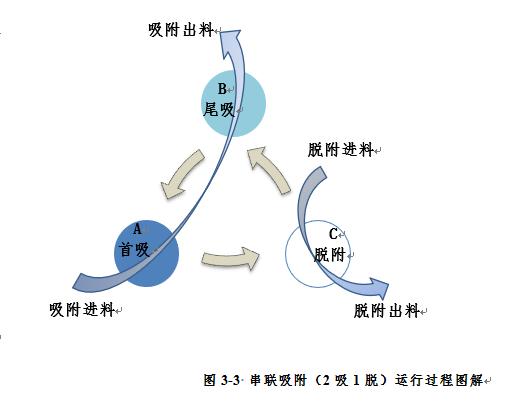
Figure 3-3 Schematic diagram of the operation process of series adsorption (2 adsorption and 1 desorption)
Process equipment and pipeline design
Selection of equipment and pipelines
Considering the water quality characteristics and desorption process requirements of the wastewater to be treated, and taking into account technical and economic considerations as well as construction convenience, the key equipment adsorption tower is made of steel lined PTFE material, and the pipeline system is mainly made of SUS304/carbon steel lined PP.
Device layout plan
The adsorption device equipment can be arranged entirely on the ground, or the three-dimensional layout of the frame structure can be used to reduce the footprint (the adsorption tower and filtration equipment can be placed on the upper layer, and the storage tanks and pumps can be placed on the lower layer), depending on the specific situation of the enterprise. According to the layout plan, it is estimated that the adsorption system will require a land area of approximately 260m².




 CN
CN













