The water quality of printing and dyeing wastewater is complex, containing dyes, pulp, additives, oils, acids and bases, fiber impurities, sand substances, inorganic salts, etc. Pollutants can be divided into two categories based on their sources: one is the carryover from the fiber raw materials themselves, and the other is the pulp, oil agents, dyes, chemical additives, etc. used in the processing. The quality of printing and dyeing wastewater is closely related to factors such as fabric types, production materials, product types, and production processes. Overall, it has the following characteristics: (1) high chromaticity and organic matter content; (2) Significant changes in water quality and quantity; (3) Has strong biological toxicity. In addition to some pulp, additives, oils, acids and bases, fiber impurities, and inorganic salts, the nitro, amino compounds, benzene, and its homologues in the dye structure of printing and dyeing wastewater have strong biological toxicity. There are many production processes in printing and dyeing, and the nature of the wastewater generated in each process is different.
The country has issued and implemented the "Emission Standards for Water Pollutants in Textile Dyeing and Finishing Industry", which puts forward higher requirements for the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater. Moreover, with the increasingly strict management of water resources, improving the efficiency of water resource utilization is also an important task for the development of enterprises. The country has also issued the "Water Quality Standards for Recycled Water in Textile Dyeing and Finishing Industry" to guide the textile dyeing and finishing industry to strengthen the recycling and utilization of wastewater. With the increasing efforts in environmental protection and the improvement of emission standards in our country, it is necessary to deeply treat printing and dyeing wastewater. Firstly, it is necessary to achieve stable and compliant discharge after the improvement of emission standards. Secondly, it is necessary to meet the water quality requirements for resource utilization. Thirdly, it is necessary to minimize toxic organic pollutants to ensure environmental safety. This has significant practical significance for alleviating the water resource crisis and achieving sustainable development in the printing and dyeing industry.
The pollutants in the wastewater treated by conventional biochemical methods mainly include suspended solids, bacteria, difficult to biodegrade organic matter, and dissolved minerals that affect reuse. To further improve water quality, it is necessary to deeply treat the effluent after secondary or secondary enhanced treatment, remove the remaining pollutants from conventional biochemical treatment, and meet the new discharge standards or water quality requirements for reuse. The methods for advanced treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater at home and abroad include adsorption, biological, photochemical oxidation, electrochemical oxidation, ozone oxidation, membrane technology, and their combinations.
1. Advanced treatment process for conventional printing and dyeing wastewater
(1) Biological activated carbon
Biochar is a deep treatment method that combines activated carbon and biofilm technology, which has significant effects in decolorization and treatment of low concentration, difficult to degrade organic wastewater. PACT process (powder activated carbon activated sludge process) is a treatment process that is highly valued in the United States. As early as the 1970s, the US Environmental Protection Agency required industrial enterprises to adopt the BAT treatment process (the most economically effective control process). Against this backdrop, DuPont developed a technology to add powdered activated carbon to activated sludge systems, which is the PACT process. Biocarbon, on the one hand, due to its adsorption function, accumulates organic matter on the surface of carbon particles, which can increase the concentration of organic matter around the carbon particles and prolong the contact time between organic matter and microorganisms. On the other hand, activated carbon with adsorption properties can stimulate biological activity as a biological carrier. Microorganisms in the reactor have higher activity and can effectively metabolize difficult to degrade and adsorb organic matter.
(2) Aerated biological filter
Aerated biological filter (BAF) is a new type of biological treatment technology widely studied in recent years. It is a new type of biological membrane treatment technology that integrates physical adsorption, filtration, and biodegradation. It is filled with high specific surface area particle fillers in the bioreactor to provide a carrier for biofilm attachment. It can be used for the removal of organic matter and ammonia nitrogen, denitrification and other secondary and tertiary treatments of sewage. It has good development and application potential in the deep treatment and resource utilization of sewage. Due to the mechanical interception effect of the packing material and the adsorption effect of microorganisms and viscous substances generated during metabolism on the surface of the filter, the effluent SS is very low, generally not exceeding 10 mg/L. Periodic backwashing enables effective renewal of biofilms, which are thin and highly active. Under aerobic conditions, microbial membranes on granular filter media remove some COD and complete the nitrification of ammonia nitrogen. Even if the biological treatment system malfunctions, its physical adsorption and filtration can still ensure high-quality effluent in the short term.
(3) Photochemical oxidation
Photochemical oxidation can be divided into four types: photocatalytic oxidation, photo induced oxidation, photo induced oxidation, and photocatalytic oxidation. At present, the most widely researched and applied method is photocatalytic oxidation.
There have been numerous reports on the use of photocatalytic oxidation for decolorization, degradation of organic matter, and improvement of biodegradability in printing and dyeing wastewater. Photocatalytic oxidation can effectively remove both biodegradable and non biodegradable COD from printing and dyeing wastewater, and has significant decolorization effects, high impact load resistance, and the ability to treat high concentration printing and dyeing wastewater. Due to its high efficiency and no secondary pollution, photocatalytic oxidation is a promising decolorization method.
(4) Ozone oxidation
Ozone oxidation method has complete reaction, fast speed, no secondary pollution, and can improve the biodegradability of high concentration and difficult to biodegrade printing and dyeing wastewater. However, using ozone oxidation alone to treat printing and dyeing wastewater has its limitations, as direct oxidation of ozone molecules has strong selectivity, slow speed, and low oxidation efficiency. In practical applications, various methods are often used to enhance the oxidation ability of ozone and increase its indirect oxidation ability. The commonly used method is to combine ozone with catalysts, ultrasound, activated carbon, or other technologies to improve its oxidation performance. Photocatalytic ozone oxidation mainly uses ultraviolet light (UV) as the energy source and ozone as the oxidant. It utilizes the hydroxyl radicals generated by the decomposition of ozone under UV action to enhance the oxidation ability of ozone and improve the effectiveness of ozone oxidation treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater. Ozone oxidation technology has high degradation efficiency and no secondary pollution, and has broad development and application prospects in the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater. At present, the processing cost still needs to be reduced. If the effluent can be reused in production, the economic and environmental benefits are considerable.
(5) Electrochemical technology
The mechanism of electrocatalytic oxidation treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater is to use electrolytic oxidation to destroy the molecular structure or existing state of pollutants. Electrocatalytic oxidation not only has good selectivity for the degradation of organic matter, but also has the advantages of small equipment, small footprint, easy operation, easy automation, convenient operation and management, and high degradation efficiency. It has become an effective process for the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater. The hydroxyl radicals generated by electrochemical processes can effectively degrade organic matter in dye wastewater. Chemical processes are generally carried out at room temperature and pressure, with high energy efficiency. They can be used alone or combined with other treatment methods. As a pretreatment, it can improve the biodegradability of wastewater. The traditional electrochemical method has disadvantages such as high energy consumption, high cost, and side reactions of oxygen and hydrogen evolution.
(6) Membrane separation technology
Membrane separation technology is an emerging high-efficiency separation, concentration, and purification technology, which has the advantages of high separation efficiency, simple process, convenient operation, easy control, and no pollution. The membrane technologies applied to the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater include microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, reverse osmosis, and their combinations. With the development of membrane technology, the application of membrane separation technology in the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater will also increase. At present, the main disadvantages of membrane separation technology in practical applications are high investment and operating costs, membrane fouling and blockage, requiring high-level pretreatment and regular chemical cleaning, and membrane fouling has become a bottleneck restricting the further application of membrane separation technology. Ultrafiltration membrane is usually used as a pretreatment process for reverse osmosis membrane, which can reduce the concentration of colloids and suspended solids in wastewater and reduce the pollution of reverse osmosis membrane. However, in long-term operation, ultrafiltration membranes used as pretreatment processes can also be contaminated. Membrane fouling can be divided into four types: microbial fouling, organic matter adsorption fouling, colloid and particle aggregation fouling, and inorganic salt precipitation fouling. The main problems in the practical application of membrane separation technology are how to control membrane fouling, reduce membrane pressure difference, improve membrane flux, and achieve longer membrane life.
2. Introduction to Haipu customized process:
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in Suzhou Industrial Park. It is a national high-tech enterprise that uses special adsorbents and catalysts as its core technology, supporting the development of application processes, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to solve related environmental problems for customers. Haipu's technical team won the Suzhou Industrial Park Leading Talent Award in 2013 and 2015, and the Gusu Leading Talent Award in 2015. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. was rated as a national high-tech enterprise twice in 2015 and 2018, and was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalytic Functional Nanomaterial Engineering Technology Research Center in 2018. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has a leading technological level in the treatment of adsorption materials. The supporting adsorption treatment process is efficient and stable, and has solved multiple environmental problems for many leading domestic enterprises in the industry.
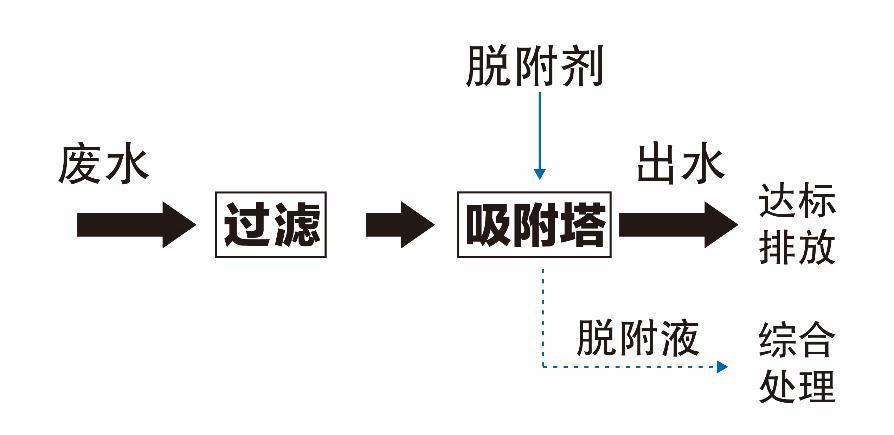
The principle of the Haipu adsorption process is to use the special adsorption materials developed by our company to selectively adsorb the components or substances to be removed. When the adsorption is saturated, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to be regenerated. This process is continuously repeated. The conventional process of treating wastewater by adsorption method is shown in the following figure.
Conventional process diagram for adsorption treatment of wastewater
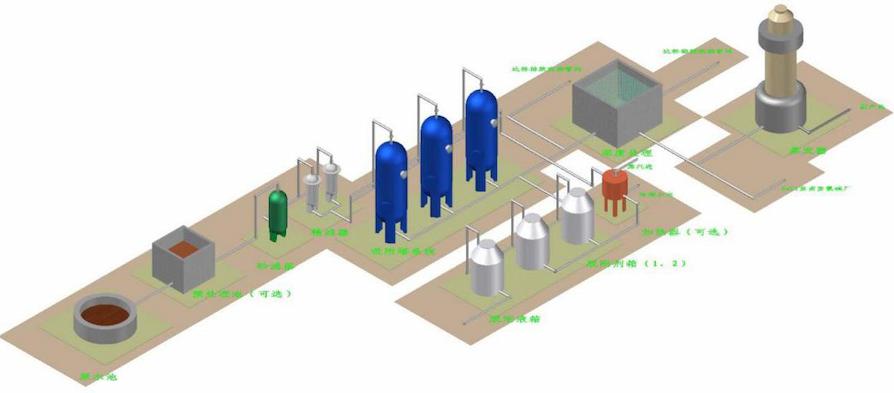
When using Haipu's adsorption process to treat printing and dyeing wastewater, the wastewater is pre filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, and then enters the adsorption tower for adsorption. The special adsorption material filled in the adsorption tower selectively adsorbs and enriches COD in the wastewater into the adsorption material, reducing the COD concentration in the adsorbed water. After adsorption saturation, the adsorbent material is subjected to desorption treatment to regenerate and resume adsorption, and this process is continuously repeated.
Advanced treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater - adsorption treatment process flow
4. Process treatment effect
Adsorption technology is used to treat printing and dyeing wastewater. Experiments have shown that the use of special adsorbents can effectively reduce COD concentration in wastewater. The specific treatment data is shown in the table below:
| Indicator | COD(mg/L) |
| Adsorbed water | 46 |
| Adsorbed water | 4.4 |
| Adsorbed water | 8.4 |
| Adsorbed water | 7.52 |
After adsorption treatment, the experimental treatment effect of wastewater from a printing and dyeing enterprise in Jiangsu showed that the COD removal rate in the wastewater reached over 80% using adsorption treatment, meeting customer requirements.

Processing rendering, from left to right are raw water and adsorbed effluent, respectively
From the above figure and table, it can be seen that the raw water and effluent are colorless and transparent, and the COD in the wastewater is reduced to below 10mg/L. Experiments have shown that using special adsorbents for adsorption can effectively reduce the COD concentration in wastewater.
5. Core advantages of craftsmanship:
At present, the advanced treatment methods for printing and dyeing wastewater have their own shortcomings in terms of treatment efficiency and operating costs. The adsorption method can effectively remove COD from printing and dyeing wastewater below the discharge limit, making it an economical and effective method for deep extraction of printing and dyeing wastewater. Its advantages include the following:
(1) Stable compliance with emission standards or returning to production lines can effectively alleviate the environmental pressure on enterprises.
(2) Conduct experiments on the sampling samples of wastewater generated on the enterprise site, based on technology, and design adsorption processes based on experiments. The matching degree between wastewater and processes is 100%.
(3) The equipment occupies less land, has a compact structure, and requires less investment in civil engineering and equipment; The desorption agent is applied multiple times and concentrated step by step, resulting in high drug utilization and low operating costs.
(4) It can be implemented in module component form, flexibly adjusted according to production capacity, and easy to install.
(5) Advanced and mature technology, no secondary pollution, strong technical support, and rich engineering application experience.




 CN
CN





