Midazoline, slightly soluble in cold water, easily soluble in organic solvents such as hot water, ethanol, butanone, DMF, and also soluble in cold alkaline solutions. Its main use is in the production of pesticide imidacloprid and as an intermediate in the synthesis of pesticide imidacloprid. Wastewater containing imidazolidine belongs to the category of difficult to biodegrade organic wastewater.
The characteristics of this type of organic wastewater mainly include the following:
(1) The composition of wastewater is complex, and the reaction materials are often solvents or cyclic compounds, which increases the difficulty of wastewater treatment.
(2) The wastewater contains a large amount of pollutants, mainly due to incomplete reaction of raw materials or the use of a large amount of solvents in production.
(3) There are many toxic and harmful substances, and there are many organic pollutants in fine chemical wastewater that are toxic and harmful to microorganisms, such as halogen compounds, nitro compounds, dispersants or surfactants with bactericidal effects, etc.
(4) There are many biologically recalcitrant substances, low BOD/COD, and poor biodegradability.
Below, Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials will provide a detailed introduction to the characteristics and treatment methods of imidazolidine wastewater treatment, hoping to be helpful to you.
1. Current situation and challenges in the treatment of recalcitrant organic wastewater:
In recent years, there has been some progress in the technology of treating high concentration and difficult to degrade organic wastewater. The main treatment methods include oxidation, physicochemical, biological, and concentration methods.
(1) Wet catalytic oxidation
Wet oxidation, also known as wet combustion, is an effective method for treating high concentration organic wastewater. Its basic principle is to introduce air under high temperature and pressure conditions to oxidize the organic pollutants in the wastewater. Decompose high molecular weight organic compounds into low molecular weight compounds, or completely oxidize and decompose them into CO2 and water.
Wet oxidation has the advantages of low secondary pollution, wide applicability, recyclable energy and useful materials, high treatment efficiency, and small equipment, and can be applied in the treatment of industrial wastewater. The disadvantage is that this method requires high temperature and pressure, thus requiring equipment that is resistant to high temperature, high pressure, and corrosion.
(2) Electrochemical catalytic oxidation
The basic principle of electrochemical oxidation method is to cause oxidation-reduction reactions of organic pollutants on the electrode, and the reaction degrades into carbon dioxide and water. The main functions are divided into two types: one is for the organic matter to be directly oxidized by the electrode, and the other is for the electrode to first react with water to produce hydroxyl radicals with strong oxidizing properties, and then the hydroxyl radicals react with the organic pollutants to achieve the purpose of degradation. This method occurs in water and does not require additional catalysts, effectively avoiding secondary pollution. It has the advantages of high treatment efficiency, easy operation, mild conditions, as well as coagulation and sterilization effects. The disadvantage is that the consumption of soluble electrode oxidation method electrodes is too high, the current efficiency is low, and the reactor efficiency is not high; Thoroughly decomposing organic matter in water using electrochemical methods requires high energy consumption and equipment costs.
(3) Fenton oxidation
Fenton reagent has strong oxidation ability, so Fenton oxidation method plays a huge role in the treatment of organic matter in wastewater. However, due to the presence of a large amount of Fe2+ions in the system, the utilization rate of H2O2 is not high, resulting in incomplete degradation of organic matter.
(4) Materialization method
Physical and chemical methods are often used as a pretreatment method in organic wastewater treatment, with the aim of recovering useful components from the wastewater, mainly by degrading difficult to degrade organic matter and improving biodegradability.
The commonly used physical and chemical techniques mainly include adsorption method, membrane treatment technology, etc. Adsorption method can be divided into physical adsorption and chemical adsorption based on the main principle of adsorption. Physical adsorption is achieved through intermolecular forces, while chemical adsorption is achieved through electron transfer to form chemical bonds or coordination compounds. There are many factors that affect the adsorption effect, including temperature, adsorbent structure, adsorbent dosage, and pollutant properties. Commonly used adsorbents in production applications include activated carbon, resin, polymer adsorbents, activated carbon fibers, etc. The advantages of adsorption method are small footprint, good treatment effect, low cost, and no secondary pollution. However, due to the limited adsorption capacity and weak regeneration ability of the adsorbent, these factors limit the practical application of this method.
Membrane separation technology mainly refers to the technical means of separating solutes and solvents in wastewater under the action of external energy through the selective action of membranes. Compared with conventional separation methods, membrane separation processes have the advantages of not polluting the environment, low energy consumption, high efficiency, and simple process. Membrane separation technology mainly includes ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, reverse osmosis, and electrodialysis.
(5) Concentration method
The concentration method is a technique that utilizes the low solubility of certain pollutants by evaporating most of the water to concentrate and separate the pollutants. Suitable for high concentration organic wastewater, the concentration method is easy to operate, the process is mature, and can achieve partial recovery of useful substances.
2. Industry customer demand:
The organic wastewater containing imidazolidine cannot be directly discharged through the above methods, so it is necessary to carry out deep treatment of the wastewater. The adsorption method developed by Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials can achieve the treatment effect. The needs of organic wastewater enterprise customers for wastewater treatment include the following three points:
(1) Efficiently and stably remove heavy metals from wastewater below emission limits;
(2) Low investment cost, low operating cost, and convenient equipment operation and maintenance;
(3) Advanced and reliable technology, with no secondary pollution.
3. Introduction to Haipu customized process:
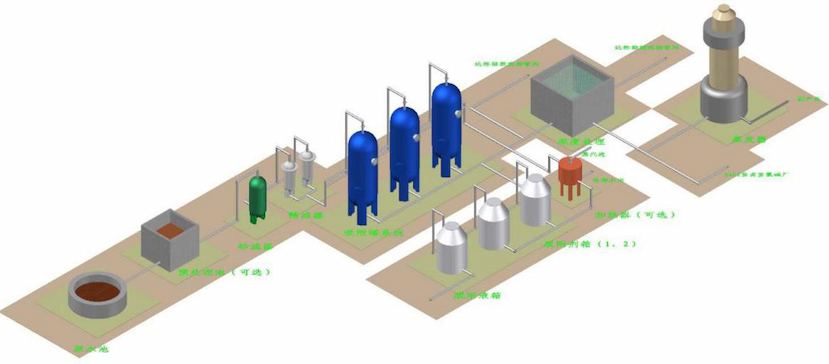
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in Suzhou Industrial Park. It is a company that uses special adsorbents and catalysts as its core technology, supporting the development of application processes, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to provide customers with solutions.
A national high-tech enterprise that solves relevant environmental problems. Haipu's technical team won the Suzhou Industrial Park Leading Talent Award in 2013 and 2015, and the Gusu Leading Talent Award in 2015. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. was rated as a national high-tech enterprise twice in 2015 and 2018, and was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalytic Functional Nanomaterial Engineering Technology Research Center in 2018. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has a leading technological level in the treatment of adsorption materials. The supporting adsorption treatment process is efficient and stable, and has solved multiple environmental problems for many leading domestic enterprises in the industry.
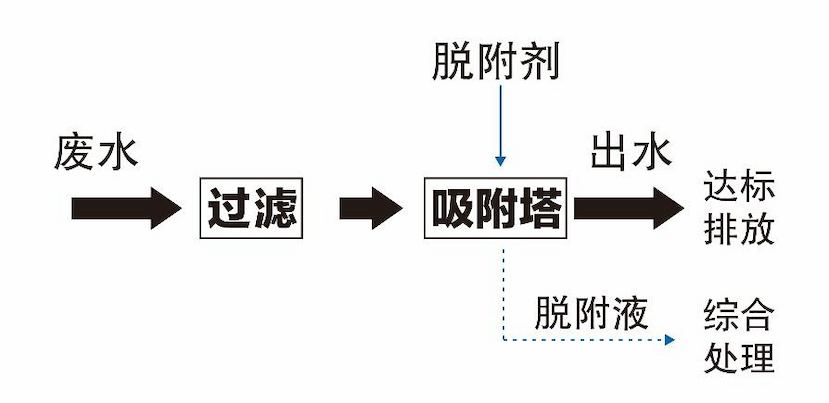
The principle of the Haipu adsorption process is to use the special adsorption materials developed by our company to selectively adsorb the components or substances to be removed. When the adsorption is saturated, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to be regenerated. This process is continuously repeated. The conventional process of treating wastewater by adsorption method is shown in the following figure.
Conventional process diagram for adsorption treatment of wastewater
When using Haipu's adsorption process to treat wastewater containing imidazolidine, the wastewater is pre filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, and then enters the adsorption tower for adsorption. The special adsorption material filled in the adsorption tower selectively adsorbs and enriches imidazolidine in the wastewater, reducing the concentration of imidazolidine in the adsorbed water. After adsorption saturation, the adsorbent material is subjected to desorption treatment to regenerate and resume adsorption, and this process is continuously repeated.
Adsorption treatment process of imidazolidine wastewater
4. Process treatment effect:
Adsorption technology is used to treat wastewater containing imidazolidine. Experiments have shown that using special adsorbents for adsorption can effectively reduce the concentration of imidazolidine in wastewater. The specific treatment data is shown in the table below:
| Indicator | Midazolane (mg/L) | Nitroguanidine effluent (mg/L) |
| Absorb incoming water | 5097 | 2087 |
| Adsorbed water 1 | 831 | 1867 |
| Adsorbed water 2 | 871 | 1411 |
| Adsorbed water 3 | 910 | 1495 |
After adsorption treatment, the experimental treatment effect of wastewater from a certain enterprise in Shandong showed that the removal rate of imidazolidines in the wastewater reached over 80% using adsorption treatment, and also had a certain removal effect on dichlorosalicylic acid and toluene. While ensuring compliance with customer requirements, a certain safety margin was left, which can effectively prevent water quality fluctuations in the incoming wastewater from causing effluent to fail to meet standards.

Processing rendering, from left to right are raw water and adsorbed effluent, respectively
From the above figure, it can be seen that the raw water is yellow, the adsorbed water is colorless and transparent, and the imidazolidine in the wastewater is almost completely removed. Experiments have shown that using special adsorbents for adsorption can effectively reduce the concentration of imidazolidine in wastewater.
5. Core advantages of craftsmanship:
At present, the treatment methods for organic wastewater containing imidazolidine have their own shortcomings in terms of treatment efficiency and operating costs. The adsorption method can effectively remove imidazolidine from wastewater below the discharge limit, making it an economical and effective method for treating imidazolidine organic wastewater. Its advantages include the following points.
(1) Stable compliance with emission standards or returning to production lines can effectively alleviate the environmental pressure on enterprises.
(2) Conduct experiments on the sampling samples of wastewater generated on the enterprise site, based on technology, and design adsorption processes based on experiments. The matching degree between wastewater and processes is 100%.
(3) The equipment occupies less land, has a compact structure, and requires less investment in civil engineering and equipment; The desorption agent is applied multiple times and concentrated step by step, resulting in high drug utilization and low operating costs.
(4) It can be implemented in module component form, flexibly adjusted according to production capacity, and easy to install.
(5) Advanced and mature technology, no secondary pollution, strong technical support, and rich engineering application experience.
6. Similar on-site project images

Pre-treatment of 500 tons/day heterocyclic wastewater and resource utilization of 350 tons/day benzoic acid wastewater in a certain chemical industry




 CN
CN






