1 Overview of Coal Chemical Wastewater Treatment
The demand for coal chemical wastewater treatment is increasing in China, as the typical characteristics of China's energy situation are "rich in coal, poor in oil, and low in gas". Coal accounts for about 70% of China's primary energy consumption structure, far higher than the global average of about 30%. In the short term, China will continue to have a coal based energy consumption structure, and the abundant coal resources provide strong conditions for the development of China's coal chemical industry. With breakthroughs in key technologies such as coal to oil, coal to gas, and coal to olefins, China's coal chemical industry is shifting towards a new type of coal chemical industry dominated by petroleum substitute products.
However, the current demand for environmental protection and the shortage of water resources are becoming increasingly severe. How to treat industrial water treatment, especially coal chemical wastewater, is becoming more prominent. How to solve the zero emission requirement? Coal chemical projects have significant water consumption and wastewater discharge, and China's coal chemical projects are mainly located in northwest water scarce areas such as Inner Mongolia, Shanxi, Shaanxi, and Ningxia, with high requirements for water treatment. According to calculations, the proportion of water treatment investment in the total investment of coal chemical industry is generally between 3% and 8%. If calculated based on the newly added production capacity during the 12th Five Year Plan period, the total investment scale of new coal chemical industry from 2013 to 2016 is about 785-830 billion yuan, of which it is expected that coal to natural gas can form a total investment of about 2400-270 billion yuan, coal to olefins can form a total investment of about 2400-255 billion yuan, coal to oil can form a total investment of about 180 billion yuan, and coal to ethylene glycol can form an investment of about 30 billion yuan. Based on a total investment scale of 830 billion yuan and a 5% investment proportion in water treatment, it is estimated that the market share of water treatment in the coal chemical industry is about 42.5 billion yuan.
In recent years, with the increasing severity of environmental pollution, the growing scarcity of water resources in China, and the increasing national requirements for environmental protection, the application of "zero discharge industrial water treatment" technology has become increasingly widespread. The main design concept of this technology is to integrate various links in industrial water treatment, forming a closed loop system in each link of water treatment. The wastewater generated in the production process is deeply treated and reused to reduce the amount of water resources and maximize the utilization efficiency of water resources, achieving the goal of "water conservation and emission reduction". Industrial zero emission technology requires water treatment companies to provide personalized design solutions with high technical requirements. Zero emission technology can fundamentally achieve the effect of "saving water and reducing emissions", which is the future development direction of industrial water treatment.
2. Current situation and characteristics of coal chemical wastewater treatment
2.1 Characteristics of Coal Chemical Wastewater
The water quality of coal chemical wastewater fluctuates widely. During coal gasification, changes in coal quality, material balance, reaction temperature, pressure, etc. will inevitably lead to changes in wastewater quantity and quality, and will directly affect the end treatment and reuse of wastewater. For example, the COD fluctuation range of crushed coal pressurized gasification wastewater is generally more than 3 times; The COD fluctuation range of a coal direct liquefaction project can even reach more than 10 times. Coal chemical enterprises mainly discharge high concentration coal gas washing wastewater, which contains a large amount of toxic and harmful substances such as phenol, cyanide, oil, ammonia nitrogen, etc. The CODcr in comprehensive wastewater is generally around 5000mg/l, and the ammonia nitrogen is between 200-500mg/l. The organic pollutants contained in the wastewater include phenols, polycyclic aromatic compounds, and heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur. It is a typical industrial wastewater containing difficult to degrade organic compounds. The easily degradable organic compounds in wastewater are mainly phenolic compounds and benzene compounds; Arsenic, naphthalene, furan, and imidazole are biodegradable organic compounds; Difficult to degrade organic compounds mainly include arsenic, carbazole, biphenyl, triphenylene, etc
2.2 Current Status of Coal Chemical Wastewater Treatment
The basic process route for treating coal chemical wastewater follows the principle of "physical and chemical pretreatment+A/O biochemical treatment+physical and chemical deep treatment". The following is a brief introduction.
Common preprocessing methods include oil separation, air flotation, etc.
Due to the excessive amount of oil, it can affect the effectiveness of subsequent biochemical treatment. The role of air flotation method for coal chemical wastewater pretreatment is to remove the oil and recycle it for reuse. In addition, it also plays a role in pre aeration.
For pre treated coal chemical wastewater, both domestically and internationally, anaerobic and aerobic biological methods (A/O process) are generally used for treatment. However, due to the presence of polycyclic and heterocyclic compounds in coal chemical wastewater, the COD index in the effluent treated by aerobic biological methods is difficult to stably meet the standard.
In order to solve the above problems, some new treatment methods have emerged in recent years, such as PACT method, carrier fluidized bed biofilm method (CBR), anaerobic biological method, anaerobic aerobic biological method, etc.
1) Improved aerobic biological method
(1) PACT method
The PACT method involves adding activated carbon powder to the activated sludge aeration tank, utilizing the adsorption of organic matter and dissolved oxygen by activated carbon powder to provide food for microbial growth, thereby accelerating the oxidation and decomposition ability of organic matter. Activated carbon is regenerated by wet air oxidation method.
(2) Carrier fluidized bed biofilm method (CBR)
CBR is actually a biological fluidized bed technology based on special structured fillers. This technology combines biofilm method with activated sludge method in the same biological treatment unit. By adding special carrier fillers to the activated sludge tank, microorganisms attach and grow on the surface of suspended fillers, forming a certain thickness of microbial film layer. The attached microorganisms can achieve a high biomass, so the biological concentration in the reaction tank is 2-4 times that of the suspended growth activated sludge process, reaching 8-12 g/L, and the degradation efficiency is also doubled as a result. The uniquely designed packing material floats with the water flow in the reaction tank under the disturbance of air blowing aeration, driving the attached and growing microbial community to fully contact the pollutants and oxygen in the water. The pollutants enter the biofilm through adsorption and diffusion, and are degraded by microorganisms, resulting in high degradation efficiency of the overall system.
Due to the attachment growth mode of microorganisms (different from the suspended growth of activated sludge), the microorganisms on the surface of the fluidized bed carrier have a long sludge age (20-40 days), which is very conducive to the proliferation of autotrophic microorganisms such as slow growing nitrifying bacteria. There are a large number of nitrifying bacteria breeding on the surface of the packing material, so the system has a strong ability to remove ammonia nitrogen through nitrification. The simultaneous attachment growth mode is beneficial for the natural selection of other special bacterial communities, which can effectively degrade characteristic pollutants in coal gasification wastewater, especially some difficult to degrade pollutants, thereby obtaining lower effluent COD concentration. CBR technology can be applied to the treatment of high concentration coal chemical wastewater, as well as to subsequent deep treatment and reuse units.
2) Anaerobic biological method
A technology called Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Bed (UASB) is used to treat coal chemical wastewater. The reactor used in this law is G. from the Netherlands Lettinga was successfully developed in 1977. Wastewater flows from bottom to top through a reactor with a sludge layer at the bottom, where most of the organic matter is converted by microorganisms into CH4 and CO2 in the upper part of the reactor. Equipped with a three-phase separator to separate gas, liquid, and solid phases. In addition, activated carbon anaerobic expanded bed technology has also been used to treat coal chemical wastewater, which can effectively remove phenolic and heterocyclic compounds from the wastewater.
3) Anaerobic aerobic combined biological method
The use of aerobic or anaerobic technology alone to treat coal chemical wastewater cannot achieve satisfactory results, and the combined biological treatment of anaerobic and aerobic is gradually receiving attention from researchers. After anaerobic acidification treatment, the biodegradation performance of organic matter in coal chemical wastewater is significantly improved, resulting in a CODcr removal rate of over 90% in subsequent aerobic biological treatment. The removal rates of the more difficult to degrade organic compounds naphthalene, quinoline, and pyridine are 67%, 55%, and 70%, respectively, while the removal rate of these organic compounds in general aerobic treatment is less than 20%. The use of anaerobic fixed membrane aerobic biological method to treat coal chemical wastewater has also achieved satisfactory results.
Advanced treatment of coal chemical wastewater
After biochemical treatment, the concentration of CODcr, ammonia nitrogen, and other pollutants in the effluent of coal chemical wastewater has greatly decreased. However, due to the presence of recalcitrant organic matter, the COD, chromaticity, and other indicators of the effluent have not yet reached the discharge standards. Therefore, the effluent after biochemical treatment still needs further treatment.
The main methods for deep processing include coagulation precipitation, immobilized biotechnology, adsorption catalytic oxidation, and reverse osmosis membrane treatment technologies.
1) Coagulation sedimentation
The precipitation method is a process that utilizes the settling property of suspended solids in water to sink under the action of gravity, in order to achieve solid-liquid separation. The purpose is to remove suspended organic matter in order to reduce the organic load of subsequent biological treatments.
In production, coagulants such as aluminum salts, iron salts, polyaluminum, polyiron, and polyacrylamide are usually added to enhance the precipitation effect. The influencing factors of this method include the pH of the wastewater, the type and dosage of coagulants, etc.
2) Fixed Biotechnology
Fixed biotechnology is a new technology developed in recent years, which can selectively immobilize dominant bacterial strains and treat wastewater containing recalcitrant organic toxins in a targeted manner. The domesticated dominant bacterial strains have a degradation ability 2-5 times higher than that of ordinary sludge for quinoline, isoquinoline, and pyridine, and the degradation efficiency of the dominant bacterial strains is higher. After 8 hours of treatment, quinoline, isoquinoline, and pyridine can be degraded by more than 90%.
3) Advanced oxidation technology
Due to the complexity and diversity of organic compounds in coal chemical wastewater, the majority of which are difficult to degrade, such as phenols, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The presence of these difficult to degrade organic compounds seriously affects the effectiveness of subsequent biochemical treatments. Advanced oxidation technology generates a large amount of free radicals in wastewater, which can non selectively degrade organic pollutants into carbon dioxide and water. Advanced oxidation technologies can be divided into homogeneous catalytic oxidation, photocatalytic oxidation, multiphase wet catalytic oxidation, and other catalytic oxidation methods. Catalytic oxidation method can be applied in the early stage of coal chemical wastewater treatment process to remove some COD and enhance the biodegradability of wastewater, but it has the problems of high consumption and uneconomical operation. Therefore, the application of this technology in subsequent deep treatment units can achieve better economic and degradation effects.
4) Adsorption method
In the late 20th century, with the successful development of structurally improved ion exchange resins, adsorption resins, and composite functional resins, resin adsorption methods were widely used in the treatment and resource utilization of chemical wastewater. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has synthesized adsorbents with different physical and chemical properties to treat coal chemical wastewater, and has achieved good treatment results. The adsorbents synthesized by the company can not only effectively remove COD from coal chemical wastewater, but also remove color and other indicators from the wastewater. The wastewater can be discharged stably and meet the standard.
3. Industry customer demand
The characteristics of coal chemical wastewater determine that it cannot be reused and discharged through traditional biochemical treatment methods. Therefore, the adsorption method developed by Haipu functional materials can be used to treat this type of wastewater, in order to achieve the optimization of treatment effect and economic cost, which is a development direction in dye wastewater treatment.
The needs of coal chemical wastewater enterprise customers for wastewater treatment include the following three points:
(1) Efficiently and stably remove COD, chromaticity, and other pollutants from wastewater below the discharge limit;
(2) Low investment cost, low operating cost, and convenient equipment operation and maintenance;
(3) Advanced and reliable technology, with no secondary pollution.
4. Introduction to Haipu Customized Process
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in Suzhou Industrial Park. It is a national high-tech enterprise that uses special adsorbents and catalysts as its core technology, supporting the development of application processes, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to solve related environmental problems for customers. Haipu's technical team won the Suzhou Industrial Park Leading Talent Award in 2013 and 2015, and the Gusu Leading Talent Award in 2015. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. was rated as a national high-tech enterprise twice in 2015 and 2018, and was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalytic Functional Nanomaterial Engineering Technology Research Center in 2018. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has a leading technological level in the treatment of adsorption materials. The supporting adsorption treatment process is efficient and stable, and has solved multiple environmental problems for many leading domestic enterprises in the industry.
The principle of the Haipu adsorption process is to use the special adsorption materials developed by our company to selectively adsorb the components or substances to be removed. When the adsorption is saturated, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to regenerate. This process is continuously repeated. The conventional process diagram for treating wastewater by adsorption method is shown in Figure 4-1.
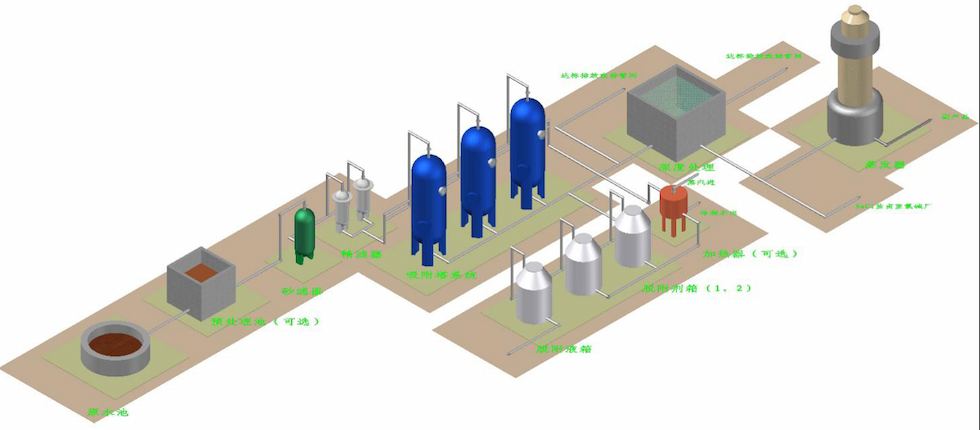
Figure 4-1 Conventional process diagram for adsorption treatment of wastewater
When using Haipu's adsorption process to treat coal chemical wastewater, the wastewater is pre filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, and then enters the adsorption tower for adsorption. The special adsorption material filled in the adsorption tower can adsorb organic matter in the wastewater on the surface of the material, ensuring that the effluent COD and other indicators continue to meet the discharge standards. After adsorption saturation, first use a dilute alkaline solution to desorb the organic matter on the adsorbent material, and transfer the organic matter into the desorption solution. Then, rinse the residual alkaline solution on the surface of the adsorbent material with a small amount of soft water, and evaporate or treat the desorption solution. The washing solution contains trace amounts of adsorbed substances and can be used as dilution water for dilute alkali. The adsorbed effluent is wastewater with COD lower than the discharge limit, which can be directly discharged or reused in the front-end production line. The adsorption treatment process flow of coal chemical wastewater is shown in Figure 4-2.
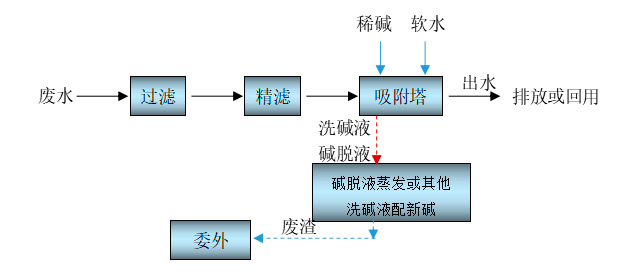
Figure 4-2 Adsorption treatment process flow of coal chemical wastewater
5. Process treatment effect
The use of adsorption technology to treat coal chemical wastewater can effectively remove COD and chromaticity from the wastewater. The specific treatment data are shown in Tables 5-1 to 5-2.
Table 5-1 Adsorption COD removal data for coal chemical wastewater treatment
| Raw water COD content | COD content in effluent | Compliance rate |
| 178 mg/L | 35mg/L | 100% |
| 150mg/L | 28 mg/L | 100% |
| 188mg/L | 40 mg/L | 100% |
A certain enterprise in Shanxi requires that the COD content in the treated wastewater should be less than 50mg/L, and the color should be colorless and transparent. The experimental treatment effect shows that using adsorption treatment can stabilize the COD in the wastewater to be less than 50mg/L. While ensuring that the customer's requirements are met, a certain safety margin is left, which can effectively prevent the water quality fluctuation of the incoming wastewater from causing the effluent to not meet the standard. The treatment effect is shown in the following figure.
The production process of this enterprise generates 500 tons of coal chemical biochemical wastewater per hour. After adsorption treatment, the COD in the wastewater can meet the requirements of reuse standards. The enterprise has adopted the adsorbent and process package from Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. Currently, the adsorption system is running smoothly.
6. Core advantages of craftsmanship
At present, the treatment methods for coal chemical wastewater have their own shortcomings in terms of treatment efficiency and operating costs.
The precipitation method usually adds coagulants such as aluminum salts, iron salts, polyaluminum, polyiron, and polyacrylamide to enhance the precipitation effect. The influencing factors of this method include the pH of the wastewater, the type and dosage of coagulants, etc. It is difficult to achieve stable and standard discharge.
Fixed biotechnology requires high domestication of bacteria and relatively poor ability to adapt to changes in water quality.
Advanced oxidation technologies can be divided into homogeneous catalytic oxidation, photocatalytic oxidation, multiphase wet catalytic oxidation, and other catalytic oxidation methods. But this law has the problems of high consumption and uneconomical operation.
The adsorption method can effectively remove organic matter from dye wastewater below the discharge limit, with simple operation and high degree of automation, making it an economical and effective method for treating coal chemical wastewater. The advantages of adsorption method are as follows:
(1) Stable and compliant emissions can effectively alleviate the environmental pressure on enterprises;
(2) Conduct experiments on sampling samples of wastewater generated on the enterprise site, based on technology, and design adsorption processes based on experiments. The matching degree between wastewater and processes is 100%;
(3) The equipment occupies less land, has a compact structure, and requires less investment in civil engineering and equipment; The desorption agent is applied multiple times and concentrated step by step, resulting in high drug utilization and low operating costs;
(4) It can be implemented in module component form, flexibly adjusted according to production capacity, and easy to install;
(5) Advanced and mature technology, no secondary pollution, strong technical support, and rich engineering application experience.
7. Case Introduction
500 t/d dye wastewater treatment project of a coal chemical enterprise in Shanxi Province
The company uses our adsorption process to treat the dye wastewater generated during its production process. Experiments have shown that the COD content in the wastewater has decreased from 180mg/L to below 50mg/L. The treated wastewater has a particularly low COD content and can be directly discharged or reused, solving the problem of production constraints for enterprises and reducing their environmental pressure.
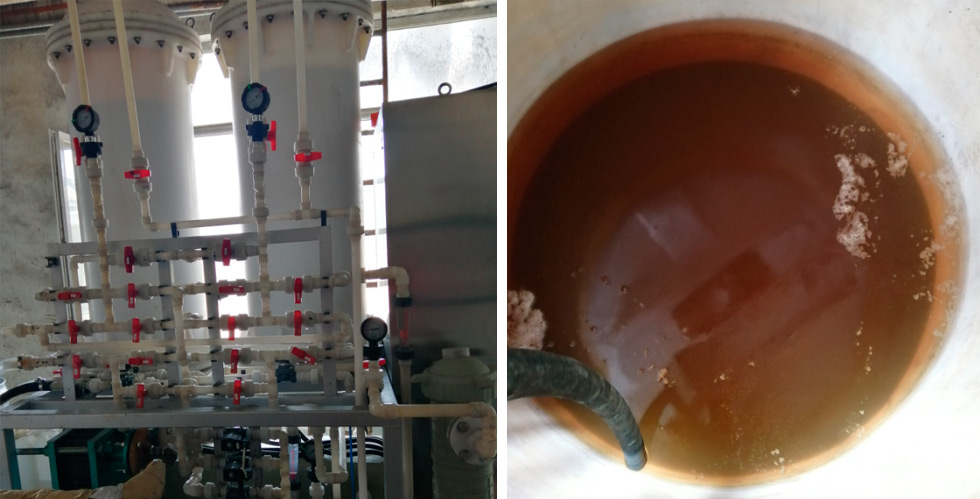

Figure 7-1 On site application of adsorption tower




 CN
CN





