RO concentrated water treatment history
Reverse osmosis (RO) is the reverse process of forward osmosis. When external pressure is applied to the concentrated solution on one side of the reverse osmosis membrane, water molecules in the concentrated solution pass through the membrane and enter the dilute solution, which is the process of reverse osmosis. As reverse osmosis progresses, the concentrated solution continues to concentrate, causing membrane fouling and scaling of the reverse osmosis membrane. At this point, the maximum water production rate of the reverse osmosis membrane is reached, and the remaining concentrated solution cannot be further concentrated, becoming reverse osmosis concentrated wastewater (ROC).
Due to the fact that reverse osmosis technology can not only remove organic matter and ammonia nitrogen from wastewater, but also remove hardness and salts from wastewater, pure water can be obtained on the dilute solution side, and the treatment effect is very ideal. Therefore, reverse osmosis technology has been widely applied in the treatment of coking wastewater. However, the water production rate of reverse osmosis technology is only 70%~75%, which means that the remaining 25%~30% of reverse osmosis concentrated water cannot be effectively treated. Reverse osmosis concentrated water is the effluent after being concentrated through reverse osmosis technology. Therefore, the quality of concentrated water is closely related to the inlet water quality, pretreatment methods, etc. Due to concentration, pollutants in the water increase exponentially, resulting in high dissolved total solids (TDS) content, high conductivity, high organic matter content, poor biodegradability, and complex composition in reverse osmosis concentrated water.
With the gradual promotion and application of reverse osmosis technology, the amount of reverse osmosis concentrated water is also increasing. How to handle reverse osmosis concentrated water prudently and save water resources is becoming increasingly important. At present, the following methods are commonly used both domestically and internationally to dispose of concentrated reverse osmosis water:
One is direct or indirect discharge, which mainly involves discharging concentrated water directly into the ocean, surface water bodies, municipal sewage pipelines, or using deep well injection method to directly discharge into the underground at 1300-2000 meters, or using evaporation pond technology to naturally evaporate concentrated water. These processing methods are easy to operate and have low processing costs. But this method also has many unreasonable aspects. Due to the limitations of the pollutant carrying capacity of the ocean and surface water, direct discharge into the municipal sewage pipe network also needs to consider the corrosion phenomenon of concentrated water. Deep well injection also needs to consider the local hydrogeological conditions to prevent local groundwater pollution.
The second is comprehensive utilization, which can use reverse osmosis concentrated water for urban greening and road cleaning, and in industry, it can be used as dust removal water, ash and slag flushing water, etc. In the food and pharmaceutical industries, reverse osmosis concentrated water can be further concentrated to extract salts or certain chemical raw materials. For example, in production, the first stage reverse osmosis concentrated water is used as supplementary water for the cooling water of the generator set. Research has shown that long-term operation is stable and safe, reducing sewage discharge and improving economic benefits.
Coking RO concentrated water treatment technology
Due to the presence of many pollutants that pose significant risks to human health and the environment in concentrated water from coking reverse osmosis, direct or indirect discharge not only fails to meet the requirements of current environmental regulations but also poses significant potential hazards. The comprehensive utilization of concentrated water requires high water quality, and the amount of recycled water is relatively small compared to the production of concentrated water. So exploring the comprehensive treatment technology of reverse osmosis concentrated water, maximizing the reuse of concentrated water, and making reasonable and efficient use of the already decreasing water resources has become the focus of current research.
The main treatment technologies for reverse osmosis concentrated water can be summarized as physical methods, advanced oxidation methods, forward osmosis methods, and membrane distillation methods. Physical methods include coagulation precipitation method and activated carbon adsorption method.
Coagulation precipitation method:
It is a traditional water treatment method widely used. The coagulation and sedimentation treatment process includes several parts: dosing, mixing, reaction, and precipitation separation. Firstly, dosing. The preparation and dosing methods of coagulants can be divided into two types: dry dosing and wet dosing. Dry dosing refers to directly adding chemicals into the water being treated. Dry process addition has high labor intensity, difficult to control the dosage, and high requirements for mixing machinery and equipment. Currently, this method is rarely used domestically. Wet dosing refers to first preparing a solution of a certain concentration of chemicals and then adding it to the treated wastewater. The wet dosing process is easy to control and has good uniformity of dosing. Equipment such as metering pumps, water jets, and siphon quantitative dosing can be used for dosing. After further mixing, when the drug is added to the sewage, it undergoes hydrolysis and produces heterocharged colloids that come into contact with colloids and suspended solids in the water to form small flocs (commonly known as alum flowers). The mixing process is completed within approximately 10-30 seconds. Mixing requires stirring power, which can be used in two ways: hydraulic stirring and mechanical stirring. Hydraulic stirring commonly uses methods such as pipeline, perforated plate, and vortex mixing; Mechanical systems can use devices such as variable speed mixing and water pump mixing tanks. At the reaction stage, when the mixing is completed in the mixing reaction equipment, small flocs have already been produced in the water, but they have not yet reached the natural settling particle size. The task of the reaction equipment is to gradually coagulate the small flocs into large flocs for precipitation. After adding chemicals, mixing, and reacting, the wastewater in the final sedimentation stage completes the flocculation process and enters the sedimentation tank for sludge water separation. The sedimentation tank can adopt various forms of results such as horizontal flow, radial flow, vertical flow, and inclined plate. The disadvantage is that maintenance and management are difficult, and it is generally suitable for primary or secondary sedimentation tanks in sewage treatment plants. Moreover, the COD removal effect is poor and new solid waste is generated.
Activated carbon adsorption method:
It has the advantages of simple operation and significant effects, and is also widely used in the field of wastewater treatment. Research has shown that using granular activated carbon (GAC) and powdered activated carbon (PAC) to compare the removal rates of COD in reverse osmosis concentrated water are 88% and 95%, respectively. The disadvantage of granular activated carbon is that it has a short service life under severe pollution.
Advanced oxidation method:
The principle is to utilize various existing and external conditions to generate functional groups with strong oxidizing ability in wastewater, so as to oxidize and decompose organic matter in water. The use of advanced oxidation methods for influent can only remove organic matter from the water, with low removal efficiency for hardness ions and salts, and strict requirements for content and type. The universality is poor, and the requirements for permeable membranes are also quite strict. At present, further exploration of suitable membrane materials and driving fluids is needed.
Positive osmosis method:
The principle is to use a liquid with a higher concentration than reverse osmosis concentrated water as the driving liquid (usually an easily separable ammonium solution), and the water molecules in the concentrated water will spontaneously diffuse through the forward osmosis membrane to the driving liquid side, thereby achieving concentration of concentrated water. Studies have shown that using a 5mol/L sugar solution as the driving liquid and forward osmosis technology to treat concentrated salt water can intercept 99% of the salt in concentrated water at a temperature of 50'C and a water production flux of 8.21kg/(m² · h). After a long period of treatment (18h), the average water production rate is 76%. However, there are also many problems, such as the long-term accumulation of solutes and dissolved substances in the reactor, which leads to a continuous decrease in osmotic pressure difference and affects membrane flux. In addition, the energy consumption is high and the membrane fouling is severe, and the low molecular weight fouling rejection is low.
Membrane distillation technology:
The new technology developed in recent years combines membrane technology and evaporation technology, and the mass transfer driving force is the vapor pressure difference on both sides of the membrane. A pilot test was conducted on the reverse osmosis concentrated water of a thermal power plant in Inner Mongolia using membrane distillation technology, and the test results were very good. However, membrane distillation does not have significant advantages in investment and operating costs, even when there is waste heat utilization in the factory area. The summary result is that firstly, the cost of membrane materials is relatively high, and the system investment is also high. Currently, it can only be applied to certain specific demand systems. Secondly, the operating cost of the system is relatively high. Although it can utilize waste heat, solar energy, geothermal energy, etc., and the process can also be made into four effect, five effect, etc., the operating cost is still a disadvantage at present. Thirdly, inorganic scaling and organic pollution in the system still constrain the promotion of membrane distillation technology.
Industry customer demand:
Coking wastewater has always been recognized as difficult to treat in the industry. Currently, deep membrane filtration and reuse systems are used, which solves the problem of wastewater reuse but brings new challenges, mainly focusing on concentrated water treatment using nanofiltration and reverse osmosis. Especially for reverse osmosis concentrated water, it is often accompanied by unfavorable factors such as high COD, high chloride ions, high fluoride ions, high total nitrogen, and high total cyanide.
Wastewater treatment needs to meet the following requirements:
Efficiently and stably remove COD from RO concentrated water.
Low investment cost, low operating cost, and convenient equipment operation and maintenance.
Advanced and reliable technology, with no secondary pollution.
Introduction to Haipu customized process
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in Suzhou Industrial Park. It is a national high-tech enterprise that uses special adsorbents and catalysts as its core technology, supporting the development of application processes, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to solve related environmental problems for customers. Haipu's technical team won the Suzhou Industrial Park Leading Talent Award in 2013 and 2015, and the Gusu Leading Talent Award in 2015. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. was rated as a national high-tech enterprise twice in 2015 and 2018, and was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalytic Functional Nanomaterial Engineering Technology Research Center in 2018. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has a leading technological level in the treatment of adsorption materials. The supporting adsorption treatment process is efficient and stable, and has solved multiple environmental problems for many leading domestic enterprises in the industry.
The principle of the Haipu adsorption process is to use the special adsorption materials developed by our company to selectively adsorb the components or substances to be removed. When the adsorption is saturated, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to be regenerated. This process is continuously repeated. The conventional process of treating wastewater by adsorption method is shown in the following figure.
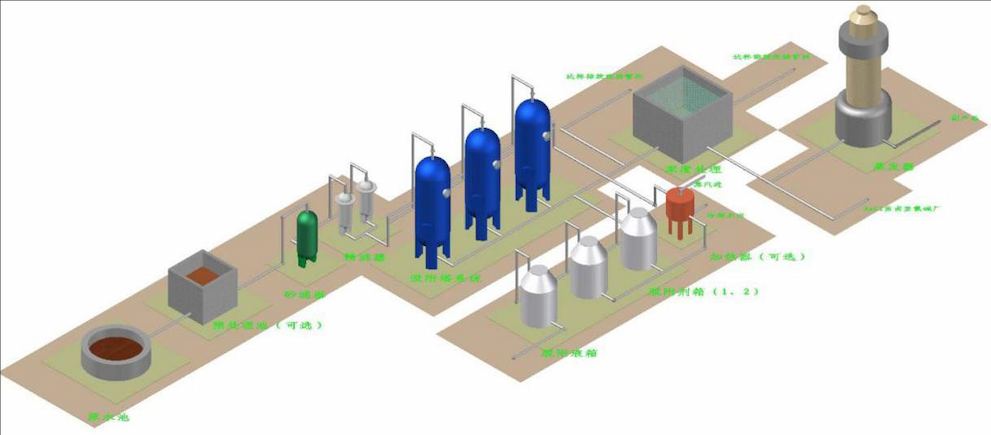
Conventional process diagram for adsorption treatment of wastewater
Case Introduction
The total design treatment capacity of this newly built wastewater adsorption treatment facility is 400m3/d. The wastewater is high COD wastewater, which does not meet the discharge requirements and affects the stable production of the enterprise. Haipu has customized the process design for the wastewater, and the wastewater treatment effect is shown in the table below.
Table 1 Wastewater adsorption treatment
| COD content(mg/L) | Water volume(m³/d) |
|
| Absorb incoming water | 784 | 400 |
| Adsorbed water | 232 | 400 |

Figure 1 In order, it is adsorption inlet water and adsorption outlet water
From the experimental results, it can be seen that the filtered water from the raw water is treated with a special adsorbent and the effluent is colorless, with a COD removal efficiency of up to 70%. Meet the customer's requirements.
Advantages of adsorption method:
1. Deeply remove COD from wastewater;
2. Using specially modified adsorption materials, with large adsorption capacity, low equipment investment, and low operating costs;
3. The process flow is simple and can achieve full automation operation, making operation and maintenance convenient.
4. It can be arranged in multiple layers, with a small footprint and a short installation cycle.




 CN
CN




