Keywords: decolorization treatment of food wastewater; Food industry; High chromaticity wastewater
With the rapid development of the economy, the improvement of living standards, and the strengthening of industrialization, the pollution of the environment caused by the food production process has intensified, and the harm to human health has become increasingly common and serious. Especially, the wastewater discharged from the production process has the characteristics of high concentration of organic pollutants, high chromaticity, and large changes in water quality and quantity. The decolorization treatment of food wastewater is one of the most difficult industrial wastewater to treat. Especially chromaticity has always been a difficult and key point in the treatment of wastewater in the food industry.
The main source of high chromaticity wastewater in the food industry is: firstly, during the food production process, chemical reactions produce pigments, which eventually enter the wastewater, such as melanin produced by glucose oxidation during soy sauce fermentation. Secondly, during the production process, in order to achieve a good color of the food, edible coloring and dyes are added, such as caramel coloring artificially added during soy sauce blending and fruit green added during green bean production.
Current technology for decolorization treatment of food wastewater
From the current application of wastewater treatment technologies, effective methods for removing wastewater color include adsorption, coagulation, biological methods, membrane separation, chemical oxidation, and electrocoagulation.
1. Adsorption decolorization
Adsorption decolorization technology relies on the adsorption effect of adsorbents to remove chromaticity. The commonly used adsorbents include renewable adsorbents such as activated carbon and ion exchange fibers, as well as non renewable adsorbents such as various natural minerals (bentonite, diatomaceous earth), industrial waste (coal slag, fly ash), and natural waste (charcoal, sawdust). At present, adsorbents used for adsorption decolorization mainly rely on physical adsorption, but ion exchange fibers, modified bentonite, etc. also have chemical adsorption effects.
2. Flocculation decolorization
Coagulation decolorization is the process of using coagulants to precipitate color forming substances in wastewater for decolorization. Flocculation decolorization technology is a widely used decolorization technology with low investment cost, small equipment footprint, and large processing capacity.
3. Decolorization by oxidation method
Chemical oxidation decolorization refers to the use of oxidizing agents such as chlorine, ClO2, O3, H2O2, HClO4, and hypochlorite to break or alter the chemical structure of chromophores in wastewater under certain conditions, thereby achieving the purpose of wastewater decolorization. Oxidation methods include chemical oxidation, photocatalytic oxidation, and ultrasonic oxidation. Although the specific processes are different, the decolorization mechanism is the same. Chemical oxidation is currently a relatively mature method of research. Oxidants generally include Fenton reagent (Fe2+- H2O2), ozone, chlorine gas, sodium hypochlorite, etc.
4. Biological decolorization
Biological decolorization is the use of microbial enzymes to oxidize or reduce colored molecules, breaking their unsaturated bonds and chromophores to achieve decolorization.
5. Electrochemical decolorization
Electrochemical method purifies wastewater through electrode reactions. According to the electrode reaction mode, electrochemical methods can be divided into internal electrolysis, electrocoagulation and electrocoating, and electro oxidation. The most famous internal electrolysis method is the iron chip method.
6. Membrane separation method for decolorization
In the field of wastewater treatment, membrane separation is a technology that uses artificially synthesized or natural polymer films, driven by external energy or chemical potential differences, to selectively separate pollutants in water, thereby purifying wastewater.
Introduction to Haipu Technology
The wastewater decolorization and adsorption process developed by Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. removes the vast majority of colored substances in the wastewater by adsorption. The color of the adsorbed water can be reduced to transparency, ensuring subsequent discharge or reuse requirements.
When using Haipu's adsorption process for high chromaticity wastewater, the wastewater is pre filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, and then enters the adsorption tower for adsorption. The special adsorption material filled in the adsorption tower can adsorb the colored substances in the wastewater on the surface of the material, significantly reducing the chromaticity of the effluent. After adsorption saturation, specific desorption agents are used to desorb the adsorbent material, allowing it to regenerate, and this process is continuously repeated. The process flow of wastewater decolorization and adsorption treatment is shown in the following figure.
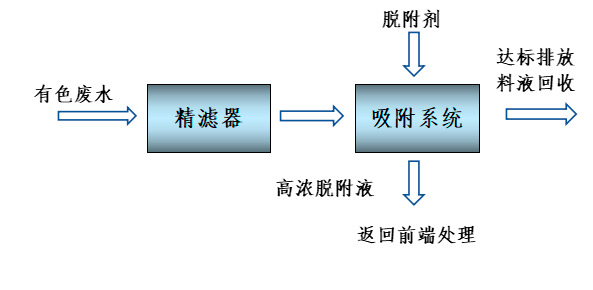
Figure 1 Wastewater decolorization process diagram
Case Introduction
This newly built wastewater decolorization and adsorption treatment facility has a total designed wastewater treatment capacity of 100m 3/d. The wastewater is high chromaticity wastewater from the factory, with deep color and high organic content, which cannot meet the stable production needs of the enterprise. Haipu has customized the process design for the wastewater, and the wastewater design indicators are shown in the table below.
Table 1 Wastewater Design Parameters Table
| Indicator | Water volume (m³/d) | Colour |
| Device water inlet | 100 | Brown red |
| Device effluent | ~100 | Canary yellow |
| Steam salt in the effluent |
| White |

Figure 2 Appearance of raw water (left) and effluent (right)
Haipu's customized adsorption process can deeply adsorb and remove organic matter from wastewater, reduce the color of the effluent, improve the stability and quality of the subsequent salt evaporation system, reduce the production and operation costs of the enterprise, and provide guarantee for stable production on site for customers.
Advantages of adsorption method
1. Deeply removing organic matter from wastewater, reducing the COD and chromaticity of adsorbed effluent, can ensure that the effluent meets the discharge standards or the operational requirements of subsequent processes;
2. Using specially modified adsorption materials, with large adsorption capacity, low equipment investment, and low operating costs;
3. The process flow is simple and can achieve full automation operation, making operation and maintenance convenient;
4. It can be arranged in multiple layers, with a small footprint and a short installation cycle.




 CN
CN




