Preface
The issue of water resources is becoming increasingly prominent and has become one of the most focused problems in the world. Especially the urgent need to treat fluorine-containing wastewater, the water use efficiency of most industrial enterprises in China is not scientific, resulting in an increasing amount of fluorine-containing wastewater discharge, which further deepens the dilemma of water resource shortage. Haipu is committed to the research and development of fluorine-containing wastewater treatment processes and has rich project experience in fluorine-containing wastewater treatment.
In recent years, the application of membrane technology in industrial wastewater treatment has become increasingly widespread. The popularization of the synergistic dual membrane (microfiltration/ultrafiltration reverse osmosis) technology using physicochemical biochemical methods has provided a new approach for the resource utilization and sustainable reuse of wastewater. Among them, the reverse osmosis method can convert about 75% of the effluent from the secondary sedimentation tank into regenerated water, but there are still about 25% of the concentrated reverse osmosis water that needs to be treated in a timely manner. This is because the water contains a large amount of difficult to degrade soluble small molecule organic matter, such as intermediate products such as dyes and surfactants, biological metabolites, and concentrated inorganic salts.
Compared with traditional water treatment processes, reverse osmosis water treatment technology is one of the most effective ways to obtain clean water. At the same time, it has the characteristics of easy operation, small footprint, and economic efficiency, and has been widely used in various fields such as seawater and brackish water desalination, urban and industrial water treatment, pure water and ultrapure water preparation, industrial wastewater treatment, food processing, and aerospace. In recent years, reverse osmosis water treatment technology has been the most successful, rapidly developing, and widely popularized membrane technology in China, generating enormous economic and social benefits. At the same time, it also leads to an increase in the production of concentrated reverse osmosis water. The water quality of various types of reverse osmosis concentrated water is complex and intricate, which not only brings new challenges to researchers in the field of environment, but also poses potential hazards to the ecological environment. Concentrated water not only contains organic pollutants, but also accumulates chloride ions, sulfate ions, and fluoride ions.
Fluorine is one of the most widely distributed elements in the world, with the strongest electronegativity and activity. It can interact with almost all elements, so fluorine mostly exists in the form of compounds and does not exist as elemental fluorine. Fluoride is an essential element for the human body, mainly ingested in trace amounts through water and food, with an absorption rate of 80% to 97%. Trace amounts of fluoride are crucial for the growth of teeth and bones in the human body. However, if the fluoride content exceeds the standard, it will cause a series of problems. According to the regulations of the World Health Organization (WHO), the fluoride content in drinking water should not exceed 1.5mg/L. In China, the fluoride content in drinking water must be less than 1.0mg/L. Long term consumption of drinking water below 0.3mg/L can lead to dental caries in children and osteoporosis and fragility in the elderly. Excessive intake of fluoride can affect the normal metabolism of proteins, vitamins, minerals, and carbohydrates in the human body. When the fluoride content in drinking water is 1.5-2.0mg/L, infants and young children may suffer from spotted enamel teeth, and even tooth defects and loss; When the fluoride content in drinking water is 3-6mg/L, adults may experience fluorosis, functional impairment, and even paralysis. High doses of fluoride can even affect the endocrine function of the thyroid, gonads, and pituitary gland, and in severe cases, endanger life. If fluoride containing wastewater is directly discharged into nature without professional treatment, it will also cause serious ecological pollution, leading to local fluoride exceeding standards and directly threatening human life and health.
Fluorine chemical industry is a highly polluting and dangerous industry, and fluorine-containing wastewater can corrode equipment, accelerate equipment depreciation rate, and increase the economic burden on enterprises. According to the Comprehensive Wastewater Discharge Standard (GB 8978-1996), the secondary discharge standard for fluoride in industrial wastewater needs to be less than 10mg/L. Therefore, addressing the issue of fluorine-containing wastewater, achieving clean production, and pursuing a green and environmentally friendly path are challenges for the fluorine chemical industry.
1. Sources of Fluorinated Industrial Wastewater
The fluoride content in surface water in our country mainly comes from groundwater and human production activities. Fluorine containing minerals are constantly washed away and weathered, leading to an increase in fluoride content due to diffusion in local water bodies; Fluorine chemical industry is an important branch of new chemical materials in China. Fluorine chemical materials are important materials in industries such as military, metallurgy, aerospace, optics, and automobiles, and occupy an irreplaceable strategic position in future industrial production. In modern industry, industries such as the application of hydrofluoric acid, steel production, electrolytic refining of aluminum, production of sulfur fertilizers and sulfuric acid, smelting of rare earth metals and non-ferrous metals, and reprocessing of fluorides inevitably produce a certain amount of fluorine-containing wastewater. At present, the discharge of fluorine-containing wastewater in some areas continues to increase, and at the same time, it has not been well treated, resulting in many areas becoming high fluoride areas, and fluoride poisoning phenomena occur from time to time. Therefore, it is urgent to find a high-speed and effective fluorine-containing wastewater treatment process to address the problems of long treatment process, high treatment cost, difficult filtration, and difficult recovery and treatment of fluoride resources.
2. Fluoride removal process for treating fluorine-containing wastewater
The composition of fluorine-containing industrial wastewater is very complex. The fluoride entering the water mainly exists in the form of HF and fluorosilicates, as well as various other pollutants (organic matter, inorganic salts, etc.), which pose great difficulties to the treatment process. It is necessary to reduce COD to 75mg/L through primary treatment, and then undergo secondary treatment to make the fluorine-containing wastewater meet the discharge standard (fluoride content less than 10mg/L). There have been a lot of studies on the fluoride removal process from fluorine-containing wastewater, mainly including ion exchange method, membrane separation method (electrodialysis and reverse osmosis), adsorption method, and precipitation method (chemical precipitation and coagulation precipitation). For industrial grade treatment processes, adsorption and precipitation methods are mainly used to meet emission standards, with less application of other methods. However, there are still many researchers striving to overcome the problems of low fluoride removal efficiency and high treatment costs.
2.1 Ion exchange defluorination process
The principle of ion exchange method for fluoride removal is to use certain anions contained in the resin to exchange a considerable amount of fluoride ions, thereby adsorbing and capturing fluoride ions in wastewater, achieving fluoride removal from wastewater.
The advantages of ion exchange resin method are convenient process, easy operation, and recyclability. However, due to the high production and regeneration costs of resin, the problem of secondary pollution is difficult to solve, and other harmful ions may appear in the treated wastewater, which limits its industrialization process.
2.2 Membrane Separation Process for Fluoride Removal
Membrane separation method is to separate the fluoride ions in the solution through a semi permeable membrane under different pressure differentials and external forces, thereby achieving the removal of fluoride from wastewater. Both electrodialysis and reverse osmosis belong to membrane separation methods and are widely used in the industrial field today.
2.2.1 Electrodialysis method for fluoride removal
Electrodialysis was first used to desalinate seawater, utilizing an external direct current to direct the migration of cations and anions through an ion exchange membrane made of ion exchange resin. The use of electrodialysis for fluoride removal does not require the addition of foreign drugs. It not only has a good fluoride removal effect, but also reduces the salt content of wastewater, which has unparalleled advantages compared to other methods. However, while removing fluoride from drinking water, this method also removes other beneficial minerals. People should be alert to the polarization phenomenon that occurs during the fluoride removal process and constantly change the anode and cathode to maintain the stability of the fluoride removal work.
2.2.2 Fluoride removal by reverse osmosis method
The reason why the reverse osmosis method for fluoride removal is called reverse osmosis is because it is opposite to the direction of natural osmosis, and also uses the principle of osmotic pressure difference of the solution to intercept fluoride ions through the selective permeability of the semi permeable membrane, allowing water molecules to pass through. It belongs to the category of physical filtration. This method is easy to operate, thoroughly removes fluoride, does not take up space, and is also one of the most advanced technologies today. However, reverse osmosis membranes are expensive and prone to clogging and pollution, resulting in high maintenance costs and additional economic burdens for enterprises, making it difficult to systematically remove fluorine on an industrial scale. In short, membrane separation method has the advantages of simple operating environment (can be carried out under normal temperature and pressure), small footprint, and low energy consumption. However, membrane modules themselves are expensive, have weak resistance to temperature and pH changes, and the membrane separation process is prone to contamination. Therefore, pre-treatment processes must be set up, which leads to high operating and maintenance costs and increases the operating costs of enterprises.
2.3 Adsorption based defluorination process
Adsorption method for fluoride removal refers to using the functional groups of the adsorbent itself to promote ion exchange of fluoride ions, or relying on physical adsorption or chemical reactions to attach fluoride ions to the adsorbent, thereby achieving the purpose of fluoride removal. The adsorbent itself is renewable, which can restore its adsorption capacity and achieve recycling. At present, most of them are used to treat drinking water, and less are used to treat high concentration fluorine-containing wastewater. The main adsorbents currently used include aluminum containing adsorbents (activated alumina, molecular sieves, bauxite, polyaluminum salts, etc.); Natural polymer adsorbents (chitosan adsorbents, functional fiber adsorbents, tea iron adsorbents, etc.); Other adsorbents (activated carbon, activated magnesium oxide, zeolite, bone charcoal, etc.). Among them, activated alumina is currently the most commonly used adsorbent. The advantage of adsorption method is that the raw materials are easy to obtain, the price is affordable, and excellent performance adsorption materials can be obtained. After defluorination treatment, the effluent water quality is stable. The disadvantage is that in order to avoid cost increase, fluorine-containing wastewater needs to be pretreated, and the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent is limited. The capacity of the regenerated adsorbent will also be reduced to a certain extent, and the regeneration process is cumbersome, which may cause secondary pollution and other problems.
2.4 Precipitation method for fluoride removal process
2.4.1 Chemical precipitation method for fluoride removal
Chemical precipitation method for fluoride removal refers to the process of adding a precipitant to fluorine-containing wastewater, causing a chemical reaction between fluoride ions and the precipitant to form insoluble fluorine-containing precipitates or fluorine-containing complexes, followed by liquid-solid separation to achieve the goal of removal. The chemical precipitation method is widely used and suitable for treating high concentration fluorine-containing wastewater. The solubility product constant K sp of fluoride and calcium, CaF2 is only 2.7 × 10-11, indicating that the fluoride removal effect of calcium salts is very good. At the same time, calcium salts are relatively inexpensive, so the calcium salt precipitation method is the most commonly used method for fluoride removal. When the wastewater contains a certain amount of sodium chloride, potassium chloride, and sodium sulfate, the solubility of calcium fluoride in water will increase, reducing the effectiveness of fluoride removal. The chemical precipitation method has good fluoride removal effect, simple operation, and low cost. However, attention should be paid to the solubility of calcium fluoride and secondary pollution issues.
2.4.2 Fluorination removal by coagulation precipitation method
The coagulation precipitation method for fluoride removal refers to adding coagulants to fluorine-containing wastewater, using coagulants to chelate fluoride to produce precipitation, or using coagulants to produce adsorption after hydrolysis reaction to coagulate or precipitate fluoride, and then removing it from the wastewater through sedimentation filtration. This method is suitable for large-scale treatment of fluorine-containing wastewater. Commonly used inorganic coagulants include aluminum chloride, ferrous sulfate, polyaluminum chloride, polymeric iron sulfate, etc; The commonly used organic coagulant is acrylamide (PAM). The coagulation sedimentation method has a simple process, easy operation, space saving, and low investment. However, the operating temperature, acidity, settling time, stirring intensity, and Cl -, SO2- ions can all have significant interference with the defluorination effect. When treating wastewater with high fluoride content, it can increase the amount of coagulant input and increase treatment costs. Therefore, coagulation method is generally used for treating low concentration fluorine-containing wastewater that fails to meet the standard after calcium salt treatment.
3. Introduction to Haipu Process
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in the beautiful Suzhou Industrial Park and is a high-tech enterprise dedicated to the research and development of high-performance adsorbents, catalysts, and process applications. Jiangsu Haipu is committed to providing internationally leading products, technologies, and overall solutions for industries such as environmental protection, resource regeneration, new energy, chemical and pharmaceutical, food, and printing and dyeing.
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has a leading technological level in the treatment of adsorption materials. The supporting adsorption treatment process is efficient and stable, and has solved multiple environmental problems for many leading domestic enterprises in the industry.
The principle of the Haipu adsorption process is to use the special adsorption materials developed by our company to selectively adsorb the components or substances to be removed. When the adsorption is saturated, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to regenerate. This process continues in a loop.
When using Haipu's adsorption process to treat fluorine-containing wastewater, the wastewater is pre filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, and then enters the adsorption tower for adsorption. The special adsorption material filled in the adsorption tower selectively adsorbs and enriches fluorine in the wastewater, reducing the fluoride concentration in the adsorbed water. After adsorption saturation, the adsorbent material is subjected to desorption treatment to regenerate and resume adsorption, and this process is continuously repeated. The process flow is as follows:
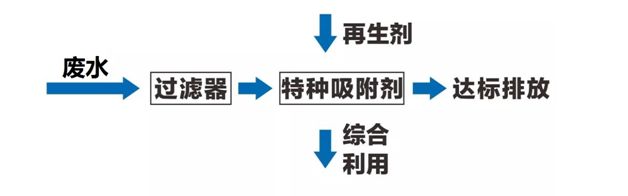
Figure 1 Process Flow Diagram
4. Haipu cases
After being treated with the Haipu adsorption process, the fluoride content in the 600t/d fluorine-containing washing water of a certain enterprise in Shandong was greatly reduced, and no other metal ions or impurity ions affecting reuse were introduced. The removal rate reached over 90%.
| Index | Fluorine/ppm |
| Inlet | 28.8 |
| Effluent | 1.33 |
| Removal rate | 95.30% |

Figure 2 Appearance of effluent (left) and raw water (right)
From the above figure and table, it can be seen that the filtered water of the raw water is treated with a special adsorbent and the effluent is colorless. The fluoride in the wastewater is almost completely removed. The experiment proves that using a special adsorbent for adsorption can effectively reduce the fluoride concentration in the wastewater.




 CN
CN




