What are the good methods for treating fluorine-containing wastewater on the market? How to achieve deep defluorination? This is a headache for many chemical plant owners. Here are some tips from Jiangsu Haipu's professional fluorine-containing wastewater treatment company?
Fluorine is a non-metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol F, and is one of the known elements with strong non-metallic properties.
The elemental form of fluorine is F2, which is a light yellow, highly toxic gas with strong corrosiveness and extremely active chemical properties. It is one of the highly oxidizing substances and can even react with some inert gases under certain conditions.

Fluorine is a pale yellow gas under standard conditions, a yellow liquid when liquefied, and a colorless liquid at -252 ℃.
Fluorine is present in the human body as well. In a normal adult human body, it contains about 2-3 grams, and the human body contains about 2.6g of fluorine.
It is mainly distributed in bones and teeth, where about 90% of fluoride is accumulated. The blood contains 0.04 to 0.4 micrograms per milliliter.
Fluoride, as an essential trace element in the human body, can not only prevent dental caries but also promote bone metabolism.
However, excessive intake of fluoride is also harmful to human health. Long term excessive intake of fluoride can lead to dental fluorosis. Due to the bone friendly properties of fluoride, it can also change the bone density of the human body, and in severe cases, lead to fluorosis.
The World Health Organization lists fluorine as the third largest pollutant absorbed by the human body that causes major diseases, after arsenic and nitrate.
Survey
In industry, wastewater discharged from industries such as fluorine-containing ore mining, metal smelting, aluminum processing, coking, glass, electronics, electroplating, fertilizers, and nongyao often contains high concentrations of fluoride.
In recent years, China's fluorine chemical industry has developed rapidly, and the fluorine chemical market is generally growing at a rate of 15-20%. In the long term, the fluorine chemical industry will also be one of the fastest-growing industries in the chemical industry.
However, the environmental threat posed by the rapid development of the fluorine chemical industry has become a major obstacle to its sustained growth.
On the one hand, due to the large amount of fluorine-containing wastewater generated during the manufacturing process of fluorine chemical products, it is easy to pollute water bodies, soil, and plants.
On the other hand, due to the fact that the vast majority of fluoride elements in wastewater treatment ultimately enter sludge, the fluoride content in sludge is relatively high. During storage, transportation, and disposal, it is easy to cause serious and widespread secondary pollution. Once this pollution of soil and groundwater is formed, it is extremely difficult to restore.
Current situation of fluorine-containing wastewater treatment
The commonly used fluorine-containing wastewater treatment technologies at home and abroad are roughly divided into:
1. Chemical precipitation method
Chemical precipitation is a commonly used method for treating fluorine-containing wastewater. It mainly involves adding a precipitant to the wastewater to convert fluoride ions into insoluble precipitates or form co precipitates through complexation. The solid-liquid separation process is used to remove fluoride ions.
2. Coagulation precipitation method
The coagulation precipitation method refers to adding substances with coagulation ability or chemical reaction with fluoride ions, such as aluminum salts, iron salts, etc., to high concentration fluorine-containing water as coagulants.
The principle is that coagulants form a large number of positively charged colloidal particles in water, adsorbing negatively charged fluoride ions in the water.
This method has the advantages of high efficiency, simple operation, and low power consumption, but it takes up a large area and the uncertainty of the dosage of chemicals, which can easily lead to secondary pollution of the water body.
3. Electrochemical method
(1) Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is an electrolytic method in which an aluminum or iron electrode serves as the anode. Under the action of a direct current electric field on the surface, it hydrolyzes into different forms of hydroxides with coagulation properties, adsorbing fluoride ions and fluoride complexes in water to remove fluoride ions.
The hydroxide produced by electrocoagulation has high activity and strong ability to remove fluoride ions.
(2) Electrodialysis
Electrodialysis, under the action of a direct current electric field, uses the potential difference as a driving force to allow fluoride ions and cations to flow through a selective ion exchange membrane towards the anode and cathode, respectively, thereby removing fluoride ions.
This method does not require the addition of chemical agents and solves the problems of fluoride and salt removal simultaneously. However, due to the fact that the treatment system consists of multiple parts, the investment is large, the management is complex, and the energy consumption is high, which limits the wide application of this method
4. Membrane separation method
Nanofiltration membrane is a membrane separation technology that emerged in the 1990s, named after the nanoscale pore size of the membrane
Nanofiltration is a novel membrane separation process driven by pressure, which falls between reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration. This method is particularly suitable for separating small molecule organic compounds and can fill the gaps left by ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis
Capable of intercepting small organic molecules and allowing salt to pass through, requiring much lower external pressure than reverse osmosis membranes
Although nanofiltration membranes require low external pressure and minimal membrane fouling, the initial investment cost is high. Additionally, a certain amount of concentrated water is still produced, which requires subsequent treatment and hinders their further promotion and application;
Introduction to Haipu Customized Process
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in Suzhou Industrial Park. It is a national high-tech enterprise that uses special adsorbents and catalysts as its core technology, supporting the development of application processes, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to solve related environmental problems for customers
The principle of the Haipu adsorption process is to use the special adsorption materials developed by our company to selectively adsorb the components or substances to be removed. When the adsorption is saturated, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to be regenerated. This process continues in a continuous cycle
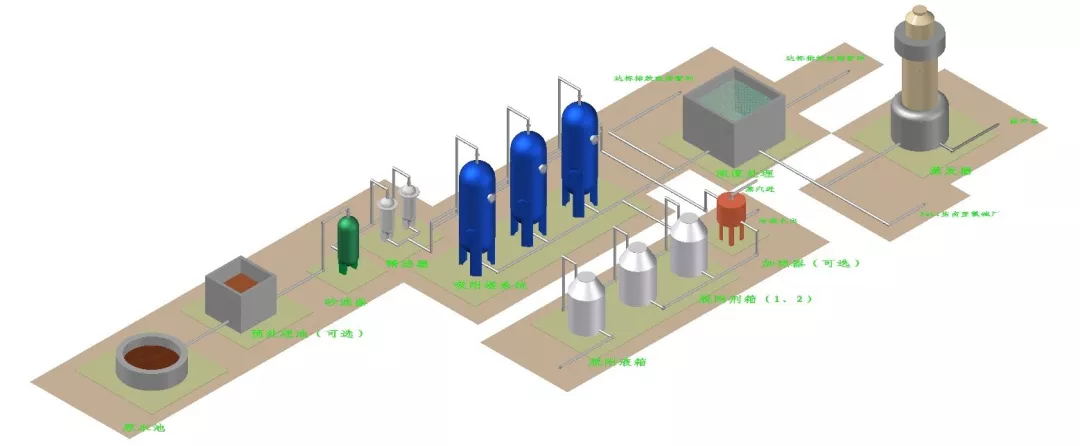
Conventional process diagram for adsorption treatment of wastewater
The following figure shows the adsorption treatment process flow of fluorine-containing wastewater
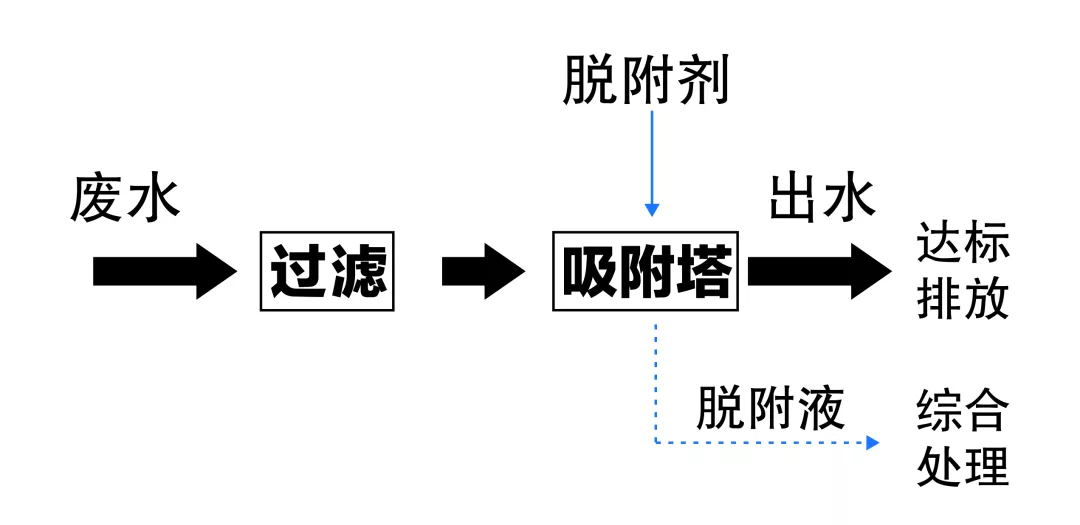
Process treatment effect
Using adsorption technology to treat fluorine-containing wastewater can effectively remove fluoride ions from the wastewater.
A mining enterprise produces groundwater with a fluoride content of about 1.4 mg/L during the process of mining ore. The enterprise requires that the fluoride content in the treated wastewater be less than 0.5 mg/L. Experimental treatment results show that using adsorption treatment can stabilize the removal rate of fluoride ions in the wastewater at over 92%, and the fluoride content in the effluent can be controlled below 0.5 mg/L. While ensuring that the customer's requirements are met, a certain safety margin is left to effectively prevent water quality fluctuations in the incoming wastewater from causing the effluent to not meet the standard.
| Raw Water Fluoride Content | Treated Water Fluoride Content | Removal Rate |
| 1.4mg/L | 0.04mg/L | 97.14% |
| 1.4mg/L | 0.10mg/L | 92.86% |
| 1.4mg/L | 0.08mg/L | 94.28% |
A company produces wastewater with a fluoride content of around 300 mg/L. It is required that the fluoride content in the treated wastewater be less than 10.0 mg/L. The experiment uses adsorption method to treat the wastewater, and the fluoride ion removal rate in the wastewater is stable at over 96%. The fluoride content in the effluent is less than 10.0 mg/L.
| Raw Water Fluoride Content | Treated Water Fluoride Content | Removal Rate |
| 300mg/L | 9.1mg/L | 96.97% |
| 300mg/L | 9.5mg/L | 96.83% |
| 300mg/L | 9.4mg/L | 96.87% |
A company produces 100 tons/day of wastewater with a pH of 9.5 and a fluoride content of 10.5mg/L during the production process. The treatment requirement is ≤ 1mg/L. Therefore, our company uses a special nano adsorbent to adsorb and separate fluoride ions in drinking water. The fluoride content after adsorption treatment is significantly reduced, which meets the customer's treatment requirements for this indicator.
| Raw Water Fluoride Content | Treated Water Fluoride Content | Removal Rate |
| 10.5mg/L | 0.29mg/L | 97.24% |
| 10.5mg/L | 0.17mg/L | 98.38% |
| 10.5mg/L | 0.15mg/L | 98.57% |
| 10.5mg/L | 0.11mg/L | 98.95% |
Core advantages
The advantages of using adsorption method to treat fluorine-containing wastewater are as follows:
(1) Remove fluoride from wastewater with high removal efficiency, strictly control the concentration of fluoride in the treated wastewater, and keep the fluoride content below 0.5 mg/L;
(2) Conduct experiments on sampling samples of wastewater generated on the enterprise site, based on technology, and design adsorption processes based on experiments. The matching degree between wastewater and processes is 100%;
(3) The equipment occupies less land, has a compact structure, and requires less investment in civil engineering and equipment; The desorption agent is applied multiple times and concentrated step by step, resulting in high drug utilization and low operating costs;
(4) It can be implemented in module component form, flexibly adjusted according to production capacity, and easy to install;
(5) Advanced and mature technology, no secondary pollution, and services provided with strong technology and rich engineering application experience.




 CN
CN






