In the development process of the chemical industry, industrial wastewater is also constantly increasing. Among them, dye wastewater is one of the main harmful industrial wastewater, mainly from the production industry of dyes and dye intermediates. It is composed of mother liquor of various products and intermediates crystallization, materials lost in the production process, and sewage that washes the ground. It is necessary to treat dye wastewater.

According to the United States, C I. There are currently tens of thousands of types of dyes available, including Color Index. China is a major producer of dyes, and the textile dye industry has developed rapidly in recent years. Currently, the production of various dyes in China has reached 900000 tons, accounting for about 60% of the world's dye production.
Dyes can be classified according to their different characteristics.
According to the chemical structure of dyes, they can be divided into azo dyes, anthraquinone dyes, indigo spin dyes, sulfur dyes, cyanine dyes, triarylmethane dyes, and heterocyclic dyes.
According to the application characteristics of dyes during dyeing, dyes can be divided into direct dyes, sulfide dyes, reducing dyes, acid dyes, acid complex dyes, reactive dyes, ice dyes, oxidative dyes, dispersed dyes, and alkaline dyes.
In the field of environmental engineering, dyes are often classified into anionic dyes, such as direct dyes and acid dyes, based on the ionic state of dye molecules dissociated in aqueous solutions; Cationic dyes, such as alkaline dyes; Non ionic dyes, such as dispersed dyes.
The chromophores in both ionic and non-ionic dyes are mostly nitrogen-containing or anthraquinone based. The reduction and cleavage of nitrogen bonds in nitrogen-containing groups can easily form toxic amines in wastewater, while anthraquinone based dyes are more difficult to decolorize due to their aromatic structures.
Reactive dyes are typical dyes with nitrogen bonds in the chromophore group. The chromophore group is connected to various reactive groups, such as sulfonyl groups, dichlorotriazine reactive groups, vinyl sulfone groups, etc. In the dyeing and printing process, the reactive groups of the dye form covalent bonds with the fiber molecules, forming a whole. Due to its bright color, good water solubility, and simple application technology, reactive dyes are widely used in the printing and dyeing industry. However, wastewater containing these water-soluble reactive dyes is also one of the most difficult to treat, and traditional water treatment processes are not very effective in treating these dyes. Alkaline dyes have a very bright color, which makes the chromaticity of water very high even when the concentration of alkaline dyes is very low. Most dyes containing heavy metals contain chromium, which is carcinogenic. Disperse dyes do not exist in ionic form in solution. Many dispersed dyes have bioaccumulation, and their chemical structure is stable with poor biodegradability. Therefore, traditional water treatment biological treatment systems have poor removal efficiency for dispersed dyes.
Characteristics and current situation of handling
1. The vast majority of organic matter in wastewater is composed of aromatic groups such as benzene, naphthalene, anthracene, quinone, etc., which carry color developing groups and have a deep color with a chromaticity of 500-500000, indicating strong pollution.
2. Due to the production process and molecular structure requirements, dye substances and intermediate molecules often contain polar groups, which enhance their water solubility and result in a large amount of material loss. Wastewater usually contains many raw materials and by-products, such as halides, nitro compounds, amino compounds, aniline, phenols and other series of organic compounds, as well as some inorganic salts such as sodium chloride, sodium sulfate, sulfides, etc. The concentration is high and the toxicity is high. The COD can generally reach 1000-73000mg/L.
3. Dye wastewater is often acidic or alkaline, and generally has a high salt content.
4. Due to the increasing demand for colorful colors and the growing variety of dyes, which are developing towards resistance to photolysis, oxidation, and biodegradation, these wastewater are becoming increasingly difficult to treat with conventional water treatment systems.
5. In the printing and dyeing industry, different dyes, auxiliaries, and dyeing methods are often used according to the needs of different fiber raw materials and products. In addition, the coloring rate of various dyes and the concentration of dyeing solution are different, resulting in significant changes in the quality of the dyeing wastewater produced. The color of dyeing wastewater is generally darker and has poor biodegradability. In addition, in the printing process, the wastewater contains not only a large amount of dyes and additives, but also a large amount of pulp, so the BOD5 and COD of the wastewater are relatively high.
Present situation:
Dyes not only have specific colors, but also complex structures, mainly composed of polymer complexes, which are difficult to break and have low biodegradability. Most of them have potential toxicity and their fate in the environment depends on many unknown factors. In addition, dye production has the characteristics of multiple varieties, small batches, and fast updates, which makes it difficult to find effective treatment methods for dye wastewater.
Membrane separation method:
The general term for the selective permeation of certain components in a liquid using special membranes includes dialysis, electrodialysis, ultrafiltration, and reverse osmosis. The concentrated solution can be used for dye recovery, and the permeate can also be reused. It can achieve effective treatment of wastewater and prevent dye loss with drainage, without causing water pollution. However, due to concentration polarization, membrane fouling, and high membrane prices, the replacement frequency is fast, resulting in higher processing costs.
Extraction method:
By using extraction agents that are insoluble in water but can effectively dissolve pollutants, and thoroughly mixing them with wastewater, pollutants can be separated and extracted using different distribution ratios in water and solvents to purify wastewater. There are methods such as solution extraction, electrophoresis extraction, liquid membrane method, etc. Research has shown that anionic methyl orange can be effectively separated from water in the presence of cationic hexadecyltrimethylamine surfactant; In the presence of anionic dodecylbenzenesulfonate surfactant, pentylethanol was used as the extraction solvent, and cationic methylene blue was effectively separated. However, in practical applications, there are disadvantages such as high consumption of extractants, difficult separation of extracts, high cost per ton of water treatment, and inability to continuously process large amounts of water
Radiation method:
Common methods for treating dye wastewater. Microwave radiation for eliminating organic pollutants is a new technology that emerged in the 1980s. Microwave is located between infrared radiation and radio waves in the electromagnetic spectrum, and only acts on polar molecules in liquids. It can cause high-speed rotation and collision of polar molecules to produce thermal effects, change the thermodynamic function of the system, reduce the activation energy of reactions and the chemical activity of molecules. The main challenges of this technology are that the equipment used to generate high-energy particles is expensive, the technical requirements are high, and the energy consumption and energy utilization efficiency of this method are high. In order to avoid the harm of radiation to the human body, special protective measures are also required. Therefore, in order for this law to be put into operation, a lot of research and exploration work is still needed.
In addition, there is also the oxidation method, which uses light and specific catalysts to generate strong oxidation and decompose organic matter in wastewater. The coagulation methods mainly include coagulation precipitation method and coagulation air flotation method.
In recent years, the development, research, and application of inorganic or organic polymer coagulants have been increasing both domestically and internationally to address the shortcomings of traditional coagulants, such as unsatisfactory treatment effects. Li Chunhua and others provided a detailed introduction to the application of coagulants in printing and dyeing wastewater. Inorganic coagulants such as aluminum salts and iron salts have good coagulation effects on dispersed dyes, sulfide dyes, and other dyes that exist in colloidal or suspended form in wastewater, but have poor coagulation effects on water-soluble dyes such as acid dyes, reactive dyes, and cationic dyes; The coagulation effect of high molecular weight basic aluminum chloride and polyacrylamide is better than that of inorganic salt coagulants; Low dosage of organic flocculant and fast flocculation speed; Microbial flocculants are non-toxic, harmless, and easy to separate solids and liquids. Qiu Hexiang et al. used hydrolysis acidification A/O-chemical coagulation precipitation method to treat this type of wastewater, with high removal rates of various pollutants, strong resistance to impact loads, stable treatment effects, and low treatment costs. The coagulation method has a simple process flow, convenient operation and management, low equipment investment, small footprint, and high decolorization effect on hydrophobic dyes. However, the operating cost of this method is relatively high, with a large amount of sludge and difficulty in dehydration. The removal rate of hydrophilic dyes and other soluble N and P compounds in the water is poor, and new efficient coagulants need to be developed.
Biological Law:
The use of pollutants as a nutrient source for microorganisms is an ideal means to achieve the reduction and harmlessness of pollutants. Common biological methods include activated sludge process, biofilm process, and immobilized microbial (enzyme) technology. Since the late 1980s and early 1990s, immobilized cell technology has been used to study the decolorization of printing and dyeing wastewater both domestically and internationally. By immobilizing dominant bacterial strains isolated and screened from activated sludge, a fast, efficient, and continuous wastewater treatment system is formed, with a decolorization rate of over 80% and good CODcr removal efficiency. This indicates that immobilized cell technology has broad application prospects in the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater. The application of biological methods in dye wastewater is the most extensive, with advantages such as good treatment efficiency and low operating costs. However, due to technical reasons, the operation of this law is unstable, its applicability is not wide, and it is greatly affected by external factors, which has limited its practical application to a certain extent.
Adsorption method:
The ability to selectively enrich certain compounds holds a special position in the field of wastewater treatment. Adsorption refers to the residual surface energy of molecules or atoms on a solid surface due to unbalanced forces. When certain substances collide with the solid surface, they are attracted by these unbalanced forces and remain on the solid surface. There are two mechanisms for adsorption decolorization of dye wastewater: adsorption and ion exchange. The adsorption efficiency is influenced by many physical and chemical factors, such as the interaction between dye and adsorbent, the specific surface area of adsorbent, the particle size, temperature, pH value, and adsorption time of adsorbent.
(1) Activated carbon adsorption method
Activated carbon, as an excellent adsorbent, has been widely used for decolorization of dye wastewater. Activated carbon can remove various colors of dyes, and the treatment effect depends on the type of activated carbon and the characteristics of dye wastewater. Increasing the amount of activated carbon can improve the adsorption rate. The high price of activated carbon limits its application. After use, activated carbon needs to be regenerated using two methods: high temperature and desorption treatment. Regeneration can result in a loss of 10-15% of activated carbon.
(2) Mineral and waste adsorption method
Many substances in nature have porous structures and good adsorption properties, which can be used to treat dye wastewater. Natural minerals mainly include various clays, ores, coal, etc., which are generally abundant in reserves. In China, there are also a large amount of waste such as slag, slag, coal slag, fly ash, etc., which are more cost-effective. Therefore, the application prospects of these inorganic adsorbents are relatively broad. Zeng Xiuqiong used modified natural bentonite to adsorb Reactive Brilliant Red X-3B and compared it with activated carbon.
The results indicate that both have a decolorization rate of over 90% for wastewater. Konduru R. Ramakrishna et al. compared the adsorption performance of inorganic adsorbents such as peat, steel slag, bentonite, and fly ash on dyes with activated carbon. The experimental results showed that the adsorption effects of steel slag and fly ash on acidic dyes and peat and bentonite on alkaline dyes were comparable to activated carbon, while the adsorption effects of these four adsorbents on dispersed dyes were better than activated carbon. This result provides a scientific basis for the industrial application of low-cost adsorbents. Many scientists have further processed some natural raw materials and agricultural refined carbon, and studied the adsorption behavior of these substances. Among them, natural carbon fibers such as eucalyptus bark, rice husk, bamboo, wheat straw, coconut shell, wild grass, cassava peel, peanut shell, plum kernel, palm fruit, etc. have good adsorption effects on dyes after treatment. However, how to dispose of these adsorbents after saturation is a difficult problem that needs to be solved. Finding an effective adsorbent can better treat dye wastewater.
(3) Adsorbent adsorption method
In the late 20th century, with the successful development of structurally improved ion exchange resins, adsorption resins, and composite functional resins, resin adsorption methods were widely used in the treatment and resource utilization of chemical wastewater. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has synthesized adsorbents with different physical and chemical properties to treat dye wastewater, and has achieved good treatment results. The adsorbents synthesized by the company can not only effectively remove COD from dye wastewater, but also remove indicators such as ammonia nitrogen in the wastewater. The wastewater can be discharged continuously and stably in compliance with standards.
Industry customer demand
The characteristics of dye wastewater determine that it cannot meet discharge standards through traditional treatment methods. Therefore, the adsorption method developed by Haipu functional materials can be used to treat this type of wastewater, in order to achieve the optimal treatment effect and economic cost, which is a development direction in dye wastewater treatment.
The needs of dye wastewater treatment for enterprise customers include the following three points:
(1) Efficiently and stably remove COD, chromaticity, and other pollutants from wastewater to below discharge limits;
(2) Low investment cost, low operating cost, and convenient equipment operation and maintenance;
(3) Advanced and reliable technology, with no secondary pollution.
The principle of adsorption technology is to use developed special adsorption materials to selectively adsorb the components or substances to be removed. When the adsorption is saturated, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to regenerate. This process is continuously repeated. The conventional process diagram for treating wastewater by adsorption method is shown in Figure 4-1.
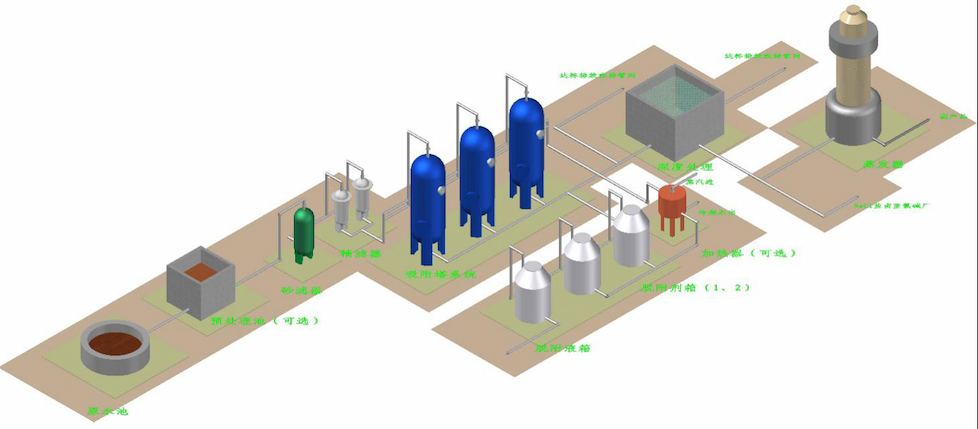
Figure 4-1 Conventional Process Diagram for Adsorption Treatment of Wastewater
When using adsorption technology to treat dye wastewater, the wastewater is pre filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, and then enters the adsorption tower for adsorption. The special adsorption material filled in the adsorption tower can adsorb organic matter in the wastewater on the surface of the material, ensuring that the effluent COD and other indicators continue to meet the discharge standards. After adsorption saturation, first use a dilute acid solution to desorb the organic matter on the adsorbent material, and transfer the organic matter into the desorption solution. Then use a small amount of soft water to wash away the acid solution remaining on the surface of the adsorbent material, and evaporate or treat the desorption solution. The washing solution contains trace amounts of adsorbed substances and can be used as dilution water for dilute acid. The adsorbed effluent is wastewater with COD lower than the discharge limit, which can be directly discharged or reused in the front-end production line. The process flow of dye wastewater adsorption treatment is shown in Figure 4-2.
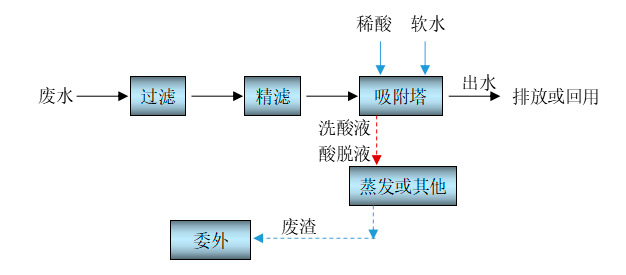
Figure 4-2 Adsorption treatment process flow of dye wastewater
5. Process treatment effect
The use of adsorption technology to treat dye wastewater can effectively remove COD from the wastewater. The specific treatment data are shown in Tables 5-1 to 5-2.
Table 5-1 Data on Adsorption and Removal of Pyridine from Wastewater
| Raw water COD content | COD content in effluent | Compliance rate |
| 15600 mg/L | 400mg/L | 100% |
| 15300mg/L | 350 mg/L | 100% |
| 16000mg/L | 420 mg/L | 100% |
A certain enterprise in Shandong requires that the COD content in the treated wastewater be less than 500mg/L. Experimental treatment results show that using adsorption treatment can stabilize the COD in the wastewater to be less than 500mg/L. While ensuring compliance with customer requirements, a certain safety margin is left, which can effectively prevent water quality fluctuations in the incoming wastewater from causing the effluent to not meet standards. The treatment effect is shown in the following figure.
The production process of this enterprise generates 100 tons of dye wastewater per day. After adsorption treatment, the COD in the wastewater can meet the discharge requirements. The enterprise has adopted adsorbents and process packages, and the adsorption system is currently running smoothly.
6. Core advantages of the process
(1) Stable and compliant emissions can effectively alleviate the environmental pressure on enterprises;
(2) Conduct experiments on sampling samples of wastewater generated on the enterprise site, based on technology, and design adsorption processes based on experiments. The matching degree between wastewater and processes is 100%;
(3) The equipment occupies less land, has a compact structure, and requires less investment in civil engineering and equipment; The desorption agent is applied multiple times and concentrated step by step, resulting in high drug utilization and low operating costs;
(4) It can be implemented in module component form, flexibly adjusted according to production capacity, and easy to install;
(5) Advanced and mature technology, no secondary pollution, strong technical support, and rich engineering application experience.
7. Case Introduction
100t/d dye wastewater treatment project of a dye enterprise in Shandong
The company uses adsorption technology to treat the dye wastewater generated during its production process. Experiments have shown that the COD content in the wastewater has decreased from 15000mg/L to below 500mg/L. The treated wastewater has a particularly low COD content and can be directly discharged or reused, solving the problem of production constraints for enterprises and reducing their environmental pressure.
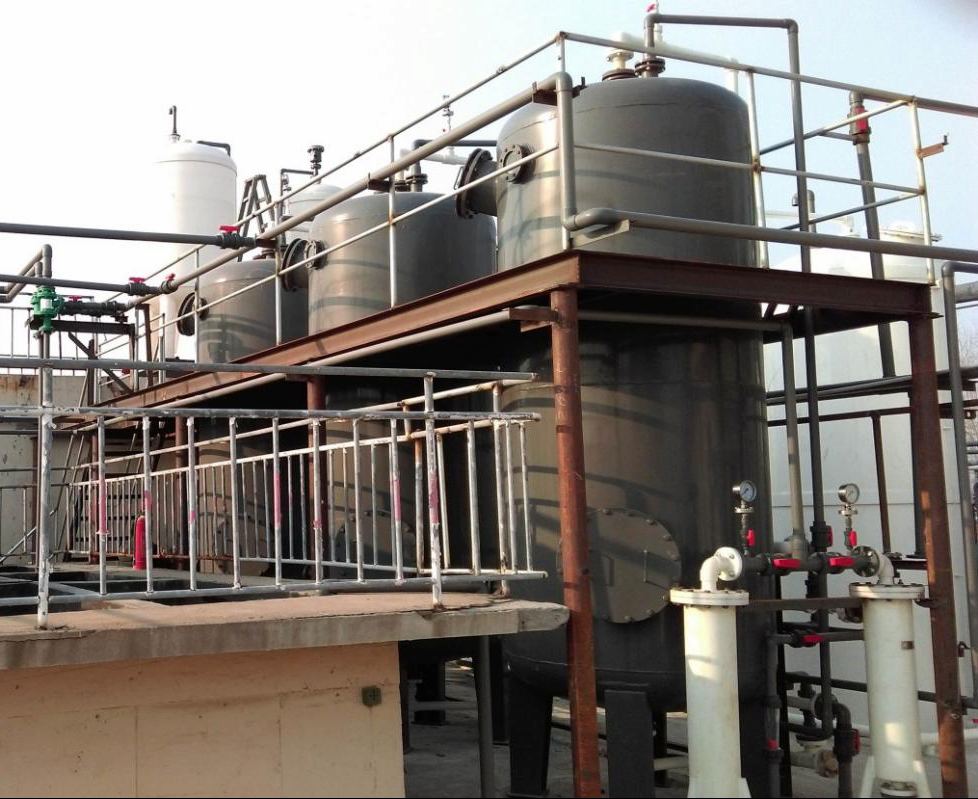

Figure 7-1 On site application of adsorption tower
The above content is a national high-tech enterprise developed and produced by Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. with special adsorbents and catalysts as the core technology, supporting application process development, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to solve related environmental problems for customers. Haipu's technical team won the Suzhou Industrial Park Leading Talent Award in 2013 and 2015, and the Gusu Leading Talent Award in 2015. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. was rated as a national high-tech enterprise twice in 2015 and 2018, and was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalytic Functional Nanomaterial Engineering Technology Research Center in 2018. It has a high level of technology in the treatment of adsorption materials, and the supporting adsorption treatment process is efficient and stable, which has solved multiple environmental problems for many leading enterprises in the domestic industry.




 CN
CN






