1. Preface
With the development of industries such as fiber optic communication, microelectronics, and solar energy, the importance of high-purity quartz sand as an important raw material is becoming increasingly prominent. We know that in order to obtain high-quality quartz sand, it is necessary to purify it.
Impurities in quartz sand can significantly affect the performance of quartz products, among which transition metals such as iron can affect the light transmittance and conductivity of quartz products; Excessive content of alkali metal impurities such as potassium and sodium can reduce the high temperature resistance of quartz products, thereby affecting their thermal stability and optical properties. At present, there are various methods for purifying quartz sand, including magnetic separation, acid washing, flotation, microbial method, and complexation method. Acid washing is an essential step in the purification of quartz ore. Acid washing utilizes the reaction between hydrogen ions and mineral phases. Compared to a single type of acid, mixed acids can produce a synergistic effect and have a higher removal rate.
Acid washing is one of the important processes for quartz beneficiation and purification, which is widely used in practical production. However, how to treat the acid washing waste liquid is also a headache for quartz processing enterprises.
The difficulty in treating quartz pickling waste liquid is the effective removal of fluoride ions. Fluorine is an accumulative toxin that can be absorbed by plant leaves and grass. When cows and sheep consume this contaminated grass, it can cause joint swelling, osteoporosis, and even paralysis. Excessive intake of fluoride can interfere with enzyme activity, disrupt the metabolic balance of calcium and phosphorus, and lead to symptoms such as dental plaque and joint deformities in fluorosis.
2. Treatment technology for quartz sand acid washing waste liquid
2.1 Neutralization treatment of acidic wastewater
Generally, wastewater neutralizers are used to neutralize acidic wastewater. Selection of wastewater neutralizing agent: When choosing a wastewater neutralizing agent, not only should the solubility, reaction rate, cost, secondary pollution, and usage method of the neutralizing agent itself be considered, but also the properties of the neutralizing product should be taken into account. The commonly used wastewater neutralizing agents include sodium hydroxide, lime, composite alkali, calcium carbonate, etc. Sodium hydroxide is easily soluble in water, and after dissolution, it becomes clear and easy to clean, but the cost is high; The composite alkali is partially soluble in water, and there is a small amount of precipitation after dissolution. A small amount of precipitation is easy to clean and has a low cost; Lime is inexpensive and easy to purchase, but using lime for neutralization generates a large amount of waste residue that is difficult to treat. Calcium carbonate is insoluble in water, and the particle size of the calcium carbonate used for neutralization needs to be fine in order to effectively react with acidic wastewater.
2.2 Treatment methods for fluoride ions in wastewater
2.2.1 Lime precipitation method
The lime precipitation method has low operating costs and is currently the most widely used treatment method in the quartz industry for removing fluoride ions from acidic wastewater. By adding lime milk to adjust the pH value of the wastewater, and at the same time, forming CaF2 precipitate with fluoride ions and calcium ions. However, when carrying out the operation, attention should be paid to the following: when lime milk is added alone as a chemical precipitant, CaF2 particles with small particle size are generated, which are difficult to settle, and the concentration is difficult to meet the fluoride ion discharge standard for wastewater. It is necessary to consider adding coagulation precipitant to assist in the precipitation of CaF2.
2.2.2 Adsorption method
Adsorption method is the most widely used method for fluoride removal, which can be directly used for the treatment of low fluoride wastewater, as well as for deep treatment after chemical precipitation and coagulation precipitation methods. The advantage of adsorption method is that it can reduce the fluoride ion content to the level of drinking water, but the main disadvantage is that in practical applications, fluoride ions compete with other coexisting anions in wastewater, and the adsorbent must have priority selectivity for fluoride ions.
Activated alumina filter adsorption filtration is currently the most mature, widely used, and effective method for fluoride removal. However, when carrying out the operation, attention should be paid to the following: when treating fluoride ions in wastewater, if the concentration of fluoride ions in the detection tank is low and meets the requirements, there is no need to filter with an activated alumina filter again.
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise dedicated to the research and development of high-performance adsorbents, catalysts, and their process applications. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise dedicated to the research and development of high-performance adsorbents, catalysts, and their process applications. Based on the characteristics of fluorine-containing wastewater and the physicochemical properties of fluoride ions, Haipu has developed a series of high-performance fluoride removal adsorbents. In addition to being used for standard treatment of conventional fluorine-containing wastewater, they can also be used for high fluoride and high salt feed solutions to meet customer production needs.
Figure 1 Adsorption treatment process flow of fluorine-containing wastewater
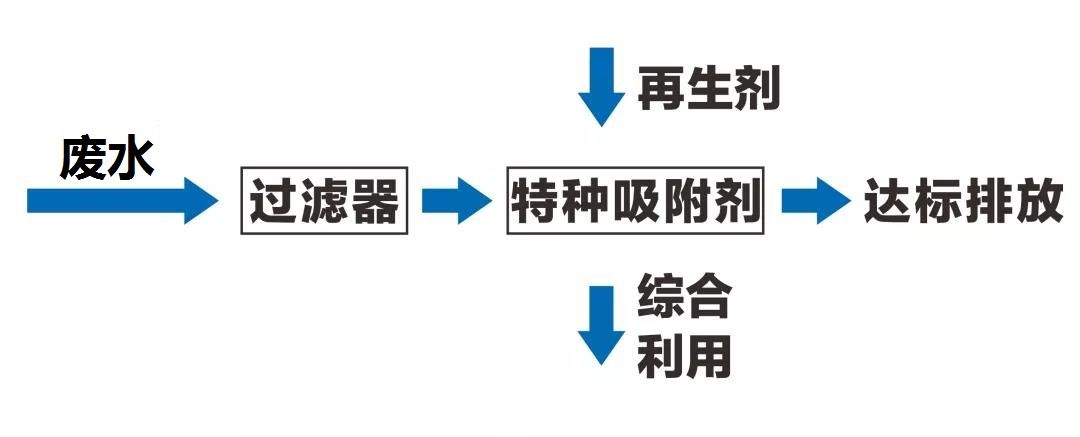
A mining enterprise produces groundwater with a fluoride content of about 1.4 mg/L during the process of mining ore. The enterprise requires that the fluoride content in the treated wastewater be less than 0.5 mg/L. Experimental treatment results show that using Haipu nano hybrid fluoride removal adsorbent products for treatment can stabilize the fluoride ion removal rate in the wastewater at over 92%, and the fluoride content in the effluent can be controlled below 0.5 mg/L. Keeping a certain safety margin while ensuring compliance with customer requirements can effectively prevent water quality fluctuations in the incoming wastewater from causing substandard effluent
Comparison of raw water and adsorbed effluent data
| Fluorine content in raw water | Fluorine content in effluent | Removal rate |
| 1.4mg/L | 0.04mg/L | 97.14% |
| 1.4mg/L | 0.10mg/L | 92.86% |
| 1.4mg/L | 0.08mg/L | 94.28% |
2.3 Treatment methods for iron and heavy metal ions in wastewater
Neutralization precipitation method is currently the most widely used heavy metal wastewater treatment method, which has the characteristics of simplicity and ease of operation. Adding alkali to wastewater containing heavy metals for neutralization reaction to separate the insoluble hydroxide precipitation form of heavy metals. The neutralization precipitation method is simple to operate and is commonly used to treat heavy metals in wastewater. However, when carrying out the operation, the following points should be noted: after neutralization and sedimentation, if the pH value in the wastewater increases, it needs to be diluted with flushing water before discharge can be carried out; There are often multiple heavy metals coexisting in wastewater. When the wastewater contains amphoteric metals, the pH value may be high and there may be a tendency for re dissolution. Therefore, it is necessary to strictly control the pH value and implement segmented precipitation; In general, iron and heavy metal ions can be precipitated during acidic neutralization without the need for additional neutralization processes.
The Haipu team targets the characteristics of specific heavy metal ions and utilizes the special functional groups of chelating resins to form complexes with heavy metal ions, achieving the recovery and utilization of heavy metal ions. This type of resin has high selectivity for heavy metal ions, and the treated wastewater can meet the discharge standards.
Figure 3 Adsorption treatment process flow of wastewater containing metal ions
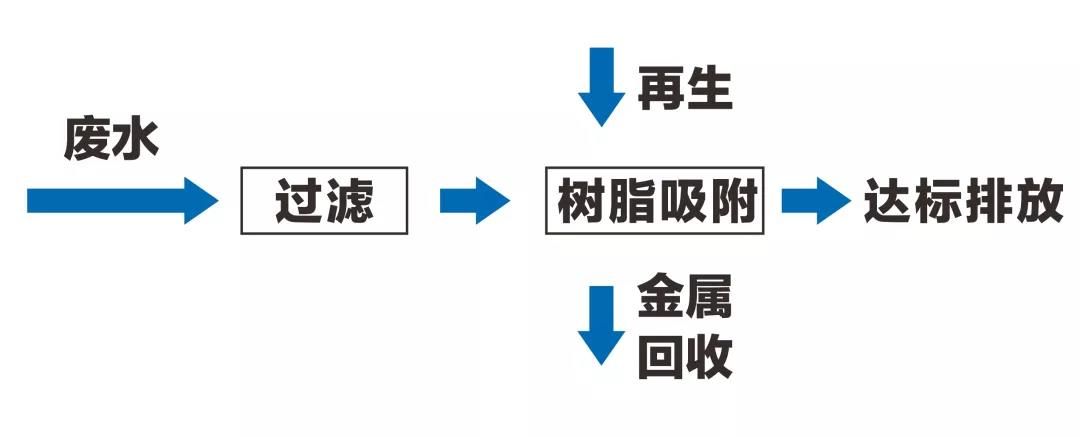
The adsorption method for removing metal ions from acid pickling wastewater has the advantages of large material adsorption capacity, low operating cost, easy regeneration, and long service life; The equipment has the characteristics of low operating cost, low maintenance cost, and simple operation. Can meet environmental protection requirements and meet emission standards (nickel content ≤ 0.1ppm, copper content ≤ 0.5ppm).
2.4 Treatment methods for particulate matter in wastewater
The treatment of particulate matter in wastewater generally adopts sedimentation coagulation/flocculation method: coagulants can accelerate the aggregation and sedimentation of solid particulate matter in wastewater, and also remove some dissolved organic matter. This method has the advantages of low investment, simple operation, and flexibility, and is particularly suitable for treating wastewater with small water volume and high suspended impurity content. Common coagulants include polyacrylamide (PAM), polyaluminum chloride (PAC), etc.
Polyacrylamide (PAM) has good flocculation properties, which can accelerate the settling of suspended solids and promote filtration and other effects. Simultaneously reducing the frictional resistance between liquids, with a small dosage but high unit price and high processing cost.
Polyaluminum chloride (PAC) has good flocculation properties for raw water with severe pollution or low turbidity, high turbidity, and high chromaticity; When the water temperature is low, stable coagulation effect can still be maintained, and the formation of flocs is fast and the settling speed is fast, which has a greater processing capacity than products such as aluminum sulfate. The corrosion effect on the equipment is small, and excessive addition will not cause water turbidity or adverse effects, and the pH and alkalinity decrease slightly after treatment. Although the cost is low, the usage is large, and the formed sludge is loose and the settling speed is slow, making it difficult to meet the requirements for wastewater treatment and reuse.
When selecting coagulants, if the wastewater treated by flocculation still needs to be recovered or reused, it is recommended to choose PAM to avoid the ions in the flocculant affecting the quality of the recovered/reused water. In addition, the performance (such as molecular weight, applicable environment, etc.) and concentration requirements of the flocculant need to be considered.
In summary, direct discharge of acid pickling waste liquid not only poses serious environmental hazards, but also wastes the recyclable resources in the acid pickling waste liquid, which does not meet the strategic requirements of sustainable green development in China and needs to be properly and carefully treated.

 CN
CN

