Keywords: Coal chemical wastewater treatment
The wastewater generated by coal chemical enterprises can be divided into three categories: domestic wastewater, production wastewater, and coking wastewater. Domestic sewage comes from wastewater generated by living facilities and laboratories, with low pollutant concentration and good biodegradability; The main source of production wastewater is the cooling water of process equipment, which is discharged to prevent equipment scaling. Due to long-term recycling, the wastewater is concentrated. Although the pollutant concentration is low, the suspended solids concentration is high and the biodegradability is poor. Generally, the drainage water quality can reach the second level standard in the "Comprehensive Wastewater Discharge Standard" GB8987-1996. Most enterprises do not collect and treat the wastewater, but directly discharge it. Coking wastewater mainly comes from coking and gas purification processes. It is a difficult to degrade industrial wastewater containing toxic and harmful substances such as phenols, cyanides, polycyclic aromatic compounds, etc. Most enterprises mix it with domestic sewage and generally use biochemical treatment. After treatment, the drainage water quality meets the second level standard in the "Comprehensive Wastewater Discharge Standard" (GB8987-1996) and is used in the wet quenching coke production process of enterprises. In recent years, with the rapid development of China's coal chemical industry, especially the adjustment of national environmental protection industry policies, the dry quenching production process, and the mandatory implementation of the "Pollutant Discharge Standards for Coking Chemical Industry" (GB16171-2012), on the one hand, enterprises have intensified their demand for industrial new water consumption, and on the other hand, they have generated a large amount of production wastewater and coking wastewater, posing severe challenges to the sustainable development of China's water environment. The limitation of 0.4m³/t coke discharge has become a serious bottleneck restricting the sustainable development of enterprises. Therefore, seeking efficient and stable wastewater treatment processes and reclaimed water reuse technologies to achieve wastewater resource utilization and "zero discharge" has become an important measure for enterprises to reduce production and operation costs, as well as their own development needs and external objective requirements.
After biochemical treatment, the concentration of CODcr, ammonia nitrogen, and other pollutants in the effluent of coal chemical wastewater has greatly decreased. However, due to the presence of recalcitrant organic matter, the COD, chromaticity, and other indicators of the effluent have not yet reached the discharge standards. Therefore, the effluent after biochemical treatment still needs further treatment. The main methods for deep processing include coagulation precipitation, immobilized biotechnology, adsorption catalytic oxidation, and reverse osmosis membrane treatment technologies.
1) Coagulation sedimentation
The precipitation method is a process that utilizes the settling property of suspended solids in water to sink under the action of gravity, in order to achieve solid-liquid separation. The purpose is to remove suspended organic matter in order to reduce the organic load of subsequent biological treatments.
In production, coagulants such as aluminum salts, iron salts, polyaluminum, polyiron, and polyacrylamide are usually added to enhance the precipitation effect. The influencing factors of this method include the pH of the wastewater, the type and dosage of coagulants, etc.
2) Fixed Biotechnology
Fixed biotechnology is a new technology developed in recent years, which can selectively immobilize dominant bacterial strains and treat wastewater containing recalcitrant organic toxins in a targeted manner.
The domesticated dominant bacterial strains have a degradation ability 2-5 times higher than that of ordinary sludge for quinoline, isoquinoline, and pyridine, and the degradation efficiency of the dominant bacterial strains is higher. After 8 hours of treatment, quinoline, isoquinoline, and pyridine can be degraded by more than 90%.
3) Advanced oxidation technology
Due to the complexity and diversity of organic compounds in coal chemical wastewater, the majority of which are difficult to degrade, such as phenols, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The presence of these difficult to degrade organic compounds seriously affects the effectiveness of subsequent biochemical treatments.
Advanced oxidation technology generates a large amount of free radicals in wastewater, which can non selectively degrade organic pollutants into carbon dioxide and water. Advanced oxidation technologies can be divided into homogeneous catalytic oxidation, photocatalytic oxidation, multiphase wet catalytic oxidation, and other catalytic oxidation methods.
Catalytic oxidation method can be applied in the early stage of coal chemical wastewater treatment process to remove some COD and enhance the biodegradability of wastewater, but it has the problems of high consumption and uneconomical operation. Therefore, the application of this technology in subsequent deep treatment units can achieve better economic and degradation effects.
Introduction to Haipu Technology
The coal chemical wastewater deep adsorption process+zero discharge recycling process developed by Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. When using Haipu's zero discharge process, the wastewater is pre filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, and then enters the adsorption tower for adsorption. The special adsorption material filled in the adsorption tower can adsorb COD in the wastewater on the surface of the material, significantly reducing the COD concentration in the effluent, and then membrane reuse is carried out. After adsorption saturation, specific desorption agents are used to desorb the adsorbent material, allowing it to regenerate, and this process is continuously repeated. The process flow of deep adsorption treatment for wastewater is shown in the following figure.
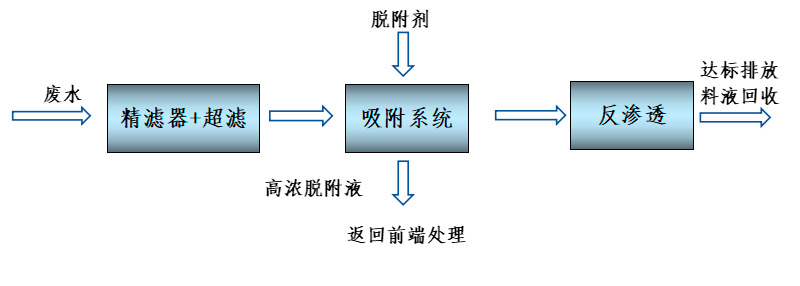
Figure 1 Zero discharge process diagram of coal chemical wastewater
Introduction to Coal Chemical Wastewater Treatment Cases
This newly built coal chemical wastewater deep adsorption treatment facility has a total designed wastewater treatment capacity of 130m3/h. Haipu has customized the process design for the wastewater, and the wastewater design indicators are shown in the table below.
Table 1 Wastewater Design Parameters Table
| Indicator | Water volume(m³/d) | COD(mg/L) |
| Device water inlet | 130 | <150 |
| Device effluent | 130 | <60 |
Advantages of adsorption method
1. Deeply removing COD from wastewater can ensure that the effluent meets the discharge standards or meets the operational requirements of subsequent processes;
2. Using specially modified adsorption materials, with large adsorption capacity, low equipment investment, and low operating costs;
3. The process flow is simple and can achieve full automation operation, making operation and maintenance convenient;
4. It can be arranged in multiple layers, with a small footprint and a short installation cycle.




 CN
CN



