This year, the National Development and Reform Commission and 10 other departments jointly issued the "Guiding Opinions on Promoting the Utilization of Wastewater Resources" (hereinafter referred to as the "Guiding Opinions"), and the "zero discharge" of wastewater was once again emphasized as an important path to achieve the utilization of wastewater resources.
The Guiding Opinions propose to implement key projects such as the construction of sewage collection and resource utilization facilities, regional recycled water utilization, industrial wastewater recycling, agricultural and rural sewage utilization for treatment, near zero discharge technology innovation pilot for sewage, and pilot demonstration of sewage resource utilization.
By 2025, several national high-tech zone industrial wastewater near zero discharge technology innovation pilot projects will be established.
With the increasingly strict environmental policies, the heat of near zero discharge of wastewater is rising steadily, and near zero discharge projects continue to be launched.
Although nearly zero discharge water treatment technology has only undergone more than 40 years of development, its technological level continues to improve and its application fields continue to expand. Currently, it has been widely used in industries such as energy, chemical, and papermaking, and is quietly leading the development direction of industrial wastewater treatment technology.
The dilemma of near zero discharge of coal chemical wastewater
In order to meet future economic development and reduce dependence on numerous resources such as oil and natural gas, the production and synthesis of alternative products have become the main projects in the coal chemical industry.
At present, there is a phenomenon of high investment, cost, and energy consumption in the discharge process of coal chemical wastewater in China, which is one of the important factors restricting the popularization of the entire zero discharge scheme for wastewater.
Based on the current situation, it can be known that in order to achieve efficient and low-energy production, it is necessary to adjust the relevant parameters used in the past, mainly because the engineering demonstration stage is still the core content of coal chemical projects.
Not only does it affect the final treatment and reuse of wastewater, but it is also directly influenced by various factors such as material balance, reaction temperature, and pressure. As for the current environment, wastewater can only be directly output to the outside world. The main reason for this phenomenon is that the current wastewater system cannot meet the standards for reuse, and the front-end production system is not stable enough.

To truly achieve the requirement of nearly zero discharge of wastewater, it is necessary to carry out more diversified treatment of wastewater. Many coal chemical enterprises currently consider comprehensive utilization of wastewater as a solution.

The realization path of near zero discharge of coal chemical wastewater
Cautiously carry out pilot projects
To some extent, the near zero discharge of coal chemical wastewater carries significant risks and costs, making it unsuitable for large-scale open management.
Therefore, it is necessary to take the national strategy as the framework and carry out various targeted zero discharge projects for wastewater, with a focus on regulating the specific planning of the development of the coal industry.
Classified supervision of wastewater near zero discharge projects
At present, coal chemical projects in China are generally in the initial stage of industrial demonstration, and different methods should be adopted to analyze various types of coal chemical projects.
It is suggested to classify the current zero discharge wastewater projects according to specific production processes and immediately carry out supervision.
Due to the need for validation of industrial operation indicators and the lack of direct data as a basis, China will address the issues present in coal gasification demonstration projects.
Accelerate research on key technologies for wastewater treatment
At present, China should gradually attach importance to the development of coal chemical wastewater treatment technology. In terms of coal chemical wastewater treatment, near zero discharge is the main problem that needs to be solved at the management level, and the most important one is the rational mobilization of water.
Therefore, coal chemical enterprises need to first have a comprehensive understanding of the water requirements for various equipment, enhance the recycling of water resources, and use various technologies reasonably, thereby increasing the subsequent utilization of water resources.
Near zero discharge technology solution for coal chemical wastewater
If we want to truly implement near zero discharge of coal chemical wastewater, technology selection is the most crucial, and cost-effective technical solutions will become the core competitiveness.
At present, the industry mainly uses the "dual membrane method" (i.e. "ultrafiltration+reverse osmosis") for deep treatment and reuse.
However, due to the low COD removal rate of ultrafiltration, the COD of the wastewater entering reverse osmosis is still relatively high (about 100-400 mg/L), with a large color and often problems such as membrane fouling and short lifespan. It is necessary to regularly clean and replace the membrane, which undoubtedly increases operating costs.

*Membrane component fouling, blockage, and scrapping
At the same time, many reverse osmosis systems have a decent initial water quality, but soon the quality of the produced water gradually deteriorates and cannot meet the standards for production reuse; In addition, the organic content (COD generally around 1000 mg/L) and chromaticity of reverse osmosis concentrated water are still relatively high, requiring additional treatment and making it difficult.
Haipu has developed a DEEP process based on "ultrafiltration+deep adsorption+reverse osmosis" to efficiently achieve near zero discharge of coal chemical wastewater, taking into account the characteristics and difficulties of coal chemical wastewater.
When using Haipu's adsorption process to treat wastewater, the wastewater is pre filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, and then enters the adsorption tower for adsorption, so that the effluent can continue to meet the discharge standards.
After adsorption saturation, specific desorption agents are used to desorb the adsorbent material, allowing it to regenerate, and this process is continuously repeated.
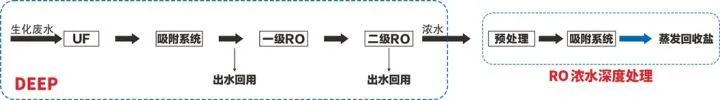
Introducing deep adsorption between dual membranes, due to the high adsorption capacity, stability, and easy regeneration ability of nano adsorbents, they can adsorb organic matter in biochemical wastewater, reducing COD to below 50mg/L and chromaticity to below 50, avoiding fouling of reverse osmosis membranes, reducing cleaning times, improving service life, and reducing operating costs.
At the same time, it can enhance its water production rate (the single-stage RO water production rate can be increased from 45-50% to 65-70%), ensuring high-quality water that can be reused. In addition, it can also make reverse osmosis concentrated water colorless, with low COD, and can be directly discharged or further evaporated to obtain by-product salt, achieving near zero discharge of wastewater.
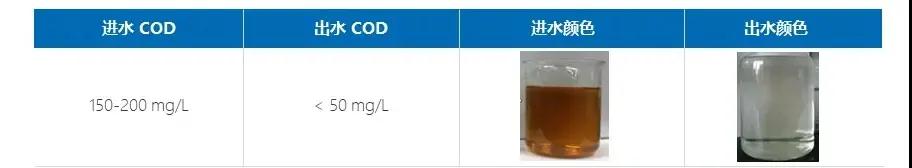
*Comparison of Process Inlet and Outlet Water
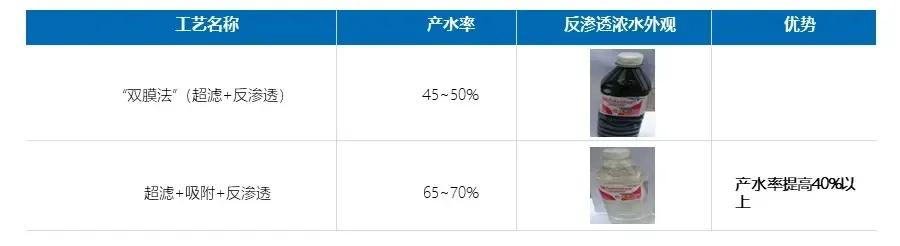
*Introducing adsorption between double membranes increases water production rate

*Near zero emission project site in the coal chemical industry





 CN
CN










