With the rapid development of the global economy, environmental issues have become increasingly prominent, and the relationship between environment and development has gradually been valued, mainly due to the emission of a large amount of greenhouse gas carbon dioxide.
By comparison, although the energy consumption of the sewage treatment industry is not as high as that of industries such as power generation, steel, and chemical engineering, its total energy consumption proportion is not small and it is also a major energy consumer. According to statistics, the electricity consumption of sewage treatment plants in China accounts for 0.26% of the total national electricity consumption. Including industrial wastewater treatment and sludge treatment, the proportion will exceed 2%.
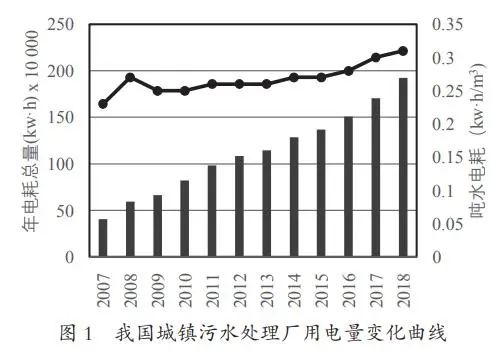
Figure 1: Curve of Electricity Consumption Changes in Urban Sewage Treatment Plants in China
At the same time, during the sewage treatment process, COD in the sewage is consumed by microorganisms, but greenhouse gas carbon dioxide is produced and discharged into the air. At the same time, the power consumption during aeration and other processes also produces many greenhouse gases.
Water pollution has been solved, but it has been transferred to the air. Roughly estimated, by 2030, the greenhouse gas emissions of China's entire sewage treatment industry will reach 2.95% of the national greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore, it is necessary for the sewage treatment industry to change its direction, especially for industrial sewage treatment, which accounts for a large proportion.
Water treatment and carbon reduction
Carbon neutrality not only means cleaner energy, but also higher energy efficiency. Currently, the market is more focused on the clean energy industry, and the value of energy-saving and consumption reducing technologies in the industrial sector has not yet been realized.
Wastewater contains a large amount of organic matter, pollutants, and nutrients, with dual attributes of pollution and resources. Resource recycling is an important method to reduce production carbon emissions and is in line with the development direction of ecological and environmental protection policies. Under the dual drive of "dual carbon policy" and environmental protection, there is ample space for resource utilization and growth.
Therefore, achieving carbon peak and carbon neutrality planning is imperative for industrial production to save energy and reduce consumption, while resource utilization can promote carbon reduction from three aspects: 1) reducing resource demand in the front-end and reducing carbon emissions during resource extraction; 2) In the mid-range production process, resource utilization reduces carbon emissions significantly compared to traditional processes; 3) The tail end alleviates the carbon emissions generated during the environmental treatment process.
So in water treatment, it reflects the important significance of carbon reduction in the deep treatment and resource recycling process of sewage for the carbon neutrality of the sewage treatment industry. Correspondingly, the feasible green path for low-carbon development of industrial wastewater treatment is to achieve near zero emissions and water resource utilization.

Based on the major strategic needs of national water pollution prevention and control, accelerate the process of sewage resource utilization, and help achieve the goal of "2060 carbon neutrality". The Haipu team continues to follow up on the near zero discharge and resource utilization of industrial wastewater, and develops wastewater reuse, near zero discharge, and resource utilization covering industries such as surface treatment, coal chemical, printing and dyeing, and agrochemical.

*On site project for advanced treatment and reuse of wastewater from printing and dyeing enterprises
Haipu DEEP process: energy conservation, consumption reduction, and water reuse
For a long time, the efficiency and cost of wastewater treatment in the printing and dyeing and coal chemical industries have been low. At present, relevant industries require deep treatment and reuse of wastewater, and even near zero discharge. At present, most of these major water consuming industries mainly use biochemical wastewater for deep treatment and reuse through the "double membrane method" (i.e. "ultrafiltration+reverse osmosis").
However, due to the low COD removal rate of ultrafiltration, the COD of the wastewater entering reverse osmosis is still relatively high (about 100-400 mg/L), with a large color and often problems such as membrane fouling and short lifespan. It is necessary to regularly clean and replace the membrane, which undoubtedly increases operating costs.
At the same time, many reverse osmosis systems have a decent initial water quality, but soon the quality of the produced water gradually deteriorates and cannot meet the standards for production reuse; In addition, the organic content (COD generally around 1000 mg/L) and chromaticity of reverse osmosis concentrated water are still relatively high, requiring additional treatment and making it difficult.
In short, although the double membrane method is widely promoted, it has not effectively solved the pain points in related industries.
How to save energy, reduce emissions, and lower consumption to truly solve the wastewater problem in related industries has put forward higher requirements for environmental protection enterprises in the industry.
The key to solving environmental problems in related industries is breakthroughs in new technologies and materials, including: 1. Efficient separation technology; 2. High performance pollution separation materials; 3. Try to avoid adding chemical agents as much as possible to prevent the generation of new pollutants that may affect reuse; 4. Economically reasonable.
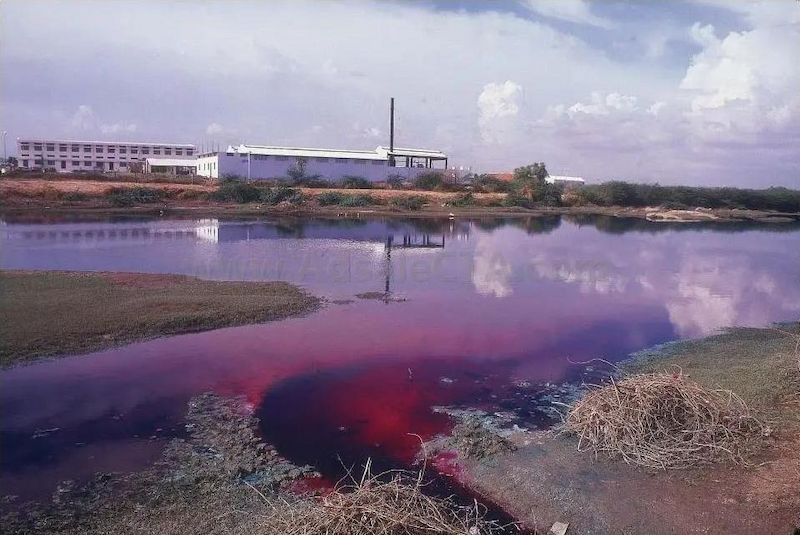

*Discharge of printing and dyeing wastewater
Haipu has developed a DEEP process based on "ultrafiltration+deep adsorption+reverse osmosis" to efficiently achieve water resource reuse, in response to the deep treatment and reuse needs of coal chemical and printing and dyeing wastewater, based on the characteristics and difficulties of wastewater in related industries.

*DEEP process applied in coal chemical engineering project site
Introducing deep adsorption between dual membranes, due to the high adsorption capacity, stability, and easy regeneration ability of nano adsorbents, they can adsorb organic matter in biochemical wastewater, reducing COD to below 50mg/L and chromaticity to below 50, avoiding fouling of reverse osmosis membranes, reducing cleaning times, improving service life, and reducing operating costs.
At the same time, it can enhance its water production rate (the single-stage RO water production rate can be increased from 45-50% to 65-70%), ensuring high-quality water that can be reused. In addition, it can also make reverse osmosis concentrated water colorless, with low COD, and can be directly discharged or further evaporated to obtain by-product salt, achieving near zero discharge of wastewater.

*Near zero emission project site in the coal chemical industry
Practice has proven that the DEEP process can achieve near zero discharge of wastewater and water resources in the printing and dyeing industry, as well as coal chemical wastewater. Carbon emissions are also reduced due to resource reuse and other cost reductions, achieving the goal of energy conservation and consumption reduction, and achieving ecological carbon sequestration.
Resource recycling and carbon reduction
Realizing the goals of peak carbon emissions and carbon neutrality is a tough battle. Haipu will further strengthen its research and development capabilities, continuously optimize water treatment efficiency, and provide resource recycling and carbon reduction services to customers in related industries using innovative processes to address environmental issues, helping customers contribute to energy conservation, consumption reduction, and carbon emission reduction.




 CN
CN








