For many years, China's No. 1 central document of the Central Committee has been prepared to address the development of agriculture and rural areas. Pesticides play an important role in modern agricultural production processes. Not only can it effectively prevent and control pests, but it can also greatly increase crop yields. Although China's overall pesticide production is among the top in the world, the industry concentration is low, and many enterprises have outdated technical equipment and insufficient investment in environmental protection, which seriously restricts the green development of agriculture.
The production process of pesticides generates a lot of exhaust gas, causing serious environmental pollution and easily leading to occupational diseases. The types of exhaust gases generated vary depending on the type of pesticide and the raw materials used. The main components of the waste gas emitted by pesticide factories are generally organic waste gases, such as methanol, toluene, chloroform, dichloroethane, etc. These organic waste gases are emitted into the atmosphere to form photochemical smog, which not only directly damages the atmospheric environment, but also endangers the healthy growth of surrounding organisms. The emission of chlorofluorocarbons can even cause damage to the ozone layer. Therefore, the treatment of pesticide industry waste gases is becoming increasingly important and has become one of the key focuses of air pollution control. Common pesticide waste gas treatment processes include low-temperature condensation, pyrolysis, membrane separation, and activated carbon adsorption.
Low temperature condensation method is a process that utilizes the characteristic of the saturation vapor pressure of organic pollutants decreasing with temperature, lowering the temperature below the boiling point of the pollutants, and transforming them from a gaseous state to a liquid state. This process has a good recovery effect on high concentration organic waste gas, but if the condensation is not thorough, there will still be high concentration waste gas discharged, which is generally used as a pre-treatment process for waste gas treatment.
Thermal destruction method can be divided into direct combustion method and catalytic combustion method. The direct combustion method burns the combustible components in the exhaust gas directly as fuel, but the calorific value of the exhaust gas concentration is generally not sufficient to maintain its own combustion, and auxiliary fuel needs to be added for combustion. The initial investment and operating costs are both relatively high, often used as the final measure for the treatment of agricultural waste gas. Catalytic combustion method utilizes the catalytic effect of a catalyst to convert large organic molecules in exhaust gas into harmless substances or substances that are easier to separate and remove from the airflow. The catalyst price of this process is relatively high, and the process conditions are strict. It is not allowed for the exhaust gas to contain dust particles and droplets (which affect the catalyst life), nor is it allowed for substances that can poison the catalyst. Therefore, the catalytic combustion treatment effect is relatively unstable.
The basic principle of membrane separation method is to use a polymer membrane with selective permeability for organic waste gas, which allows organic matter to permeate through the polymer membrane under a certain pressure and be enriched. The gas with removed organic components is left in the permeate side discharge system. This process is simple and has low energy consumption. But at the same time, the investment cost is high and limited to the field of high concentration, low air volume waste gas treatment.
Activated carbon adsorption method is a process that utilizes the adsorption properties of activated carbon to adsorb organic components in exhaust gas, and then recovers the organic components through thermal desorption and condensation. The adsorption effect of activated carbon in this process is greatly affected by moisture, and the adsorption performance decreases significantly after multiple regenerations; Frequent replacement of activated carbon is required, and the replaced activated carbon is hazardous waste with high processing costs.
In response to the current problems in the treatment of agricultural waste gas, Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has developed an HDV type polymer nano adsorbent that can adsorb and remove organic components from waste gas. After adsorption saturation, the nano adsorbent is desorbed and regenerated using thermal desorption, and organic vapor can be condensed and recovered. The specific process is as follows:
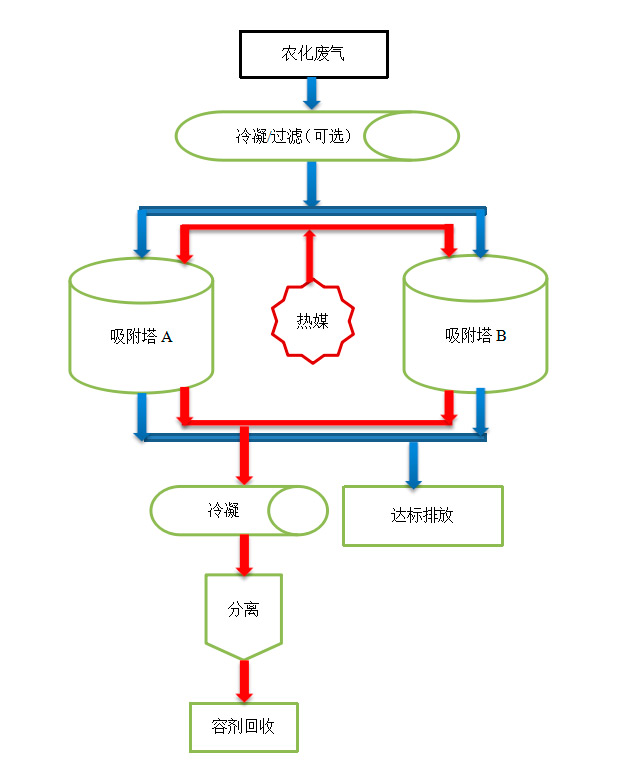
The specific process description is: the agricultural waste gas is first extracted by a vacuum pump/fan/compressor, and then pre condensed/filtered (optional). The condensed and liquefied solvent is received in a storage tank, and the uncondensed organic components are transferred to an adsorption tower containing nano adsorbents for adsorption and enrichment. The exhaust gas can be discharged in compliance with standards after adsorption. After the adsorbent is saturated, low-pressure steam (or hot nitrogen) is introduced into the adsorption tower for stripping. The blown organic vapor is then condensed and liquefied, and allowed to settle and separate into layers, allowing for the separation and recovery of organic solvents. The temperature of the nano adsorbent after thermal desorption is relatively high. After cooling to room temperature with clean air, it can be reused for adsorption. The adsorption tower is usually equipped with two units, one for adsorption and one for desorption as a backup. For high concentration exhaust gases, two or more units can also be configured.
This process can achieve a removal rate of over 99% for organic components in agricultural waste gas and has been validated on multiple project sites.
Advantages of HDV type nano adsorbent:
1. Controllable pore structure and high pore volume;
2. It has good physical and chemical stability, is resistant to acid, alkali, and organic solvents, has high thermal stability and mechanical strength, and is wear-resistant;
3. The surface exhibits high hydrophobicity, and humidity has no effect on adsorption performance;
4. Easy to regenerate and stable adsorption performance;
5. No hazardous waste is generated without the need for replacement.
In summary, the comparison of various processing methods is shown in the following table:
| Serial number | Process method | Scope of application | Advantage | Shortcoming |
| 1 | Low temperature condensation method | Organic waste gas with high concentration and single component | Recyclable organic solvents | Low purification rate, generally used as a pre-treatment |
| 2 | Direct combustion | Low to medium concentration combustible exhaust gas | High purification efficiency, thoroughly oxidizing and decomposing odorous substances | Consuming fuel, high investment and operating costs, and easily causing secondary pollution |
| 3 | Catalytic combustion | Low concentration and low gas volume macromolecular waste gas | Low temperature catalytic decomposition without the need for auxiliary fuel | Catalysts are prone to poisoning, and some harmful substances do not decompose sufficiently, resulting in unstable effects |
| 4 | Membrane separation method | Organic waste gas with high concentration, low gas content, and a single component | Simple process and low energy consumption | The initial investment cost is high, and the exhaust gas still needs to be treated, resulting in a limited range of applicable exhaust gas types |
| 5 | Activated carbon adsorption method | Organic waste gas with low to medium concentration and high purification requirements | High purification efficiency, capable of processing multi-component gases | The regeneration and utilization effect of adsorbents is poor, and hazardous waste is easily generated |
| 6 | Nano material adsorption method | Organic waste gas with medium to high concentration and high purification requirements | High purification efficiency, capable of processing multi-component gases, good regeneration and utilization effect, no hazardous waste generated, relatively simple process | The initial investment cost is relatively high |




 CN
CN



