In recent years, the national requirements for VOCs control have become increasingly high, and various industries across the country have successively issued multiple emission labels on VOCs control, including but not limited to the following standards:
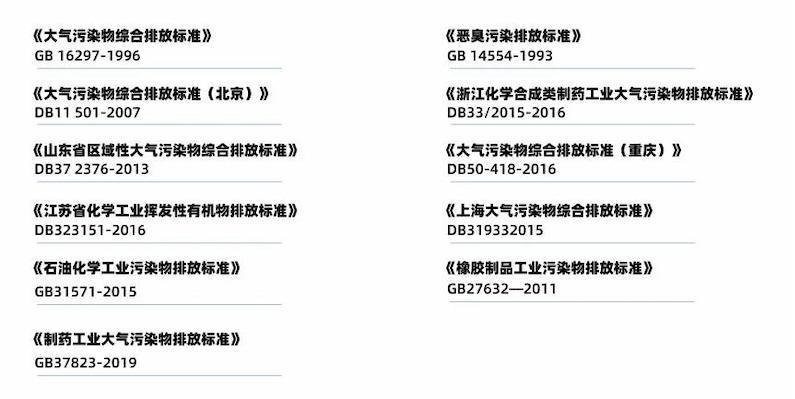
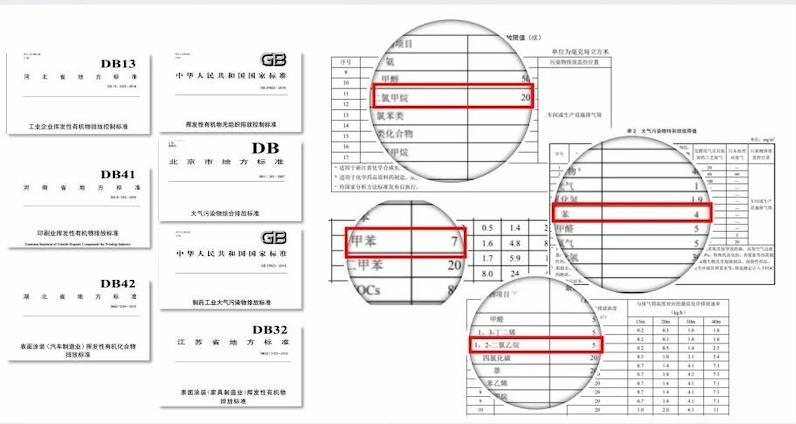
There are 26 national environmental standards and over 50 local standards related to VOCs control.
Some standards have extremely high emission requirements, such as a limit of 20mg/m³ for dichloromethane, 7mg/m³ for toluene, 5mg/m³ for dichloroethane, 4mg/m³ for benzene, etc.
In addition, the economic development situation varies in different regions, so the emission of organic waste gas also varies greatly, making it impossible to achieve unified control.
At the same time, there are various types of VOCs emitted by industries, with large fluctuations in concentration ranges. However, enterprises lack targeted technology in their use, resulting in poor effectiveness of waste gas treatment facilities.
Application scope of Haipu special adsorption process for VOCs treatment
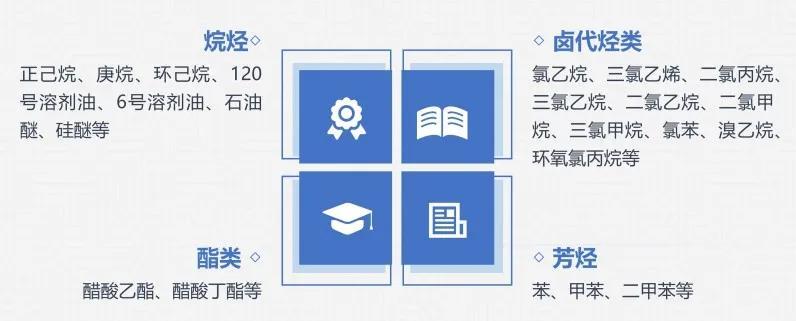
Based on the existing standards for exhaust emissions, the special adsorption materials developed by our company can treat exhaust gases roughly divided into the following five categories:
1. Alkanes: n-hexane, heptane, cyclohexane, 120 solvent oil, 6 solvent oil, petroleum ether, silicon ether, etc
2. Halogenated hydrocarbons: chloroethane, trichloroethylene, dichloropropane, trichloroethane, dichloroethane, dichloromethane, trichloromethane, chlorobenzene, bromoethane, epichlorohydrin, etc
3. Aromatic hydrocarbons: benzene, toluene, xylene, etc
4. Esters: ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, etc
5. Other non water soluble organic solvents with boiling points of 10-145 ℃
The commonly used processes for treating VOCs currently include low-temperature condensation, solvent absorption, activated carbon adsorption, and membrane separation.
However, the low-temperature condensation method still has the problem of incomplete condensation and the discharge of high concentration exhaust gas.
The adsorption effect of activated carbon is greatly affected by moisture, and the adsorption performance decreases significantly after multiple blow off regenerations; And volatile solvents are easily catalyzed and decomposed by impurities in activated carbon, producing hydrogen chloride gas. When it comes into contact with water, it turns into hydrochloric acid and corrodes equipment severely, shortening the service life of pipeline equipment.
In addition, membrane separation method has a short membrane life, high investment cost, and is limited to the field of high concentration and low air volume waste gas treatment. The concentration of waste gas after removing volatile solvents is still high, and it is generally used as a pretreatment process for low air volume and high concentration waste gas.
Introduction to Special Adsorption Materials
Haipu Functional Materials focuses on the research and industrial application of special adsorption functional materials. Based on the physical and chemical characteristics of different VOCs, adsorbents with different pore structures and surface properties are used to achieve efficient adsorption recovery and standard treatment of VOCs, ensuring the reliability and stability of the engineering application of adsorption materials.
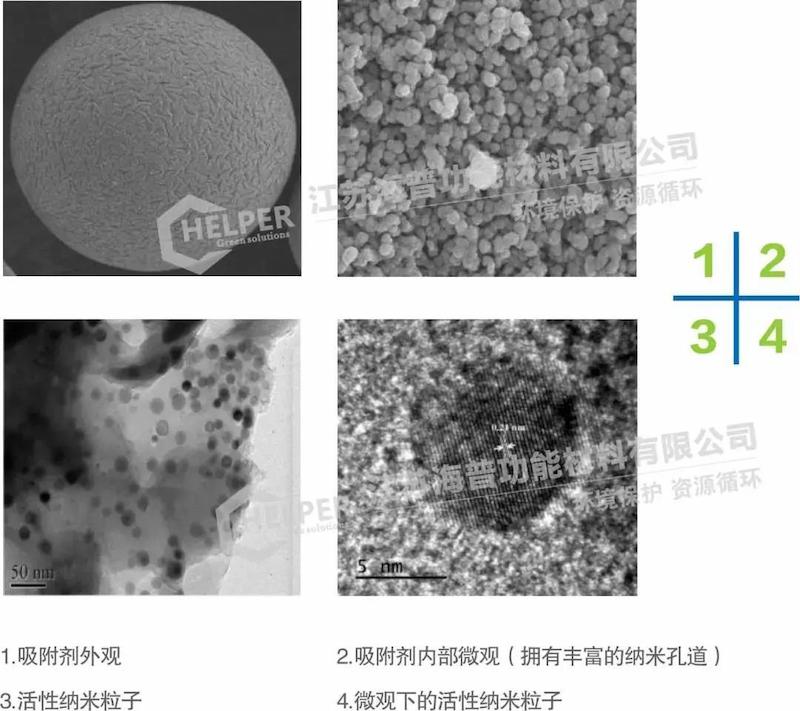
In terms of materials, Haipu special adsorption materials have the following characteristics:
1. Structural features:
Formed by polymerization and activation of different organic monomers, it has a large specific surface area, uniform and controllable pore size, and strong selectivity.
2. Adsorption effect
Multiple on-site verifications have shown that after effective duration of exhaust gas adsorption treatment, it can stably meet emission standards.
3. Reproducibility
Stable regeneration performance, capable of repeated use, and stable adsorption treatment performance.
4. Service life
No need for overall replacement, annual replenishment ≤ 5%, surface hydrophobic, stable adsorption performance; Good mechanical strength, no hole collapse, no powdering, high temperature resistance, long service life.
Introduction to related processes, equipment, and self-control
The project adopts PLC program automatic control to monitor the temperature, pressure, liquid level and other parameters of the adsorption device in real time, achieving full automation operation. The PLC communicates with the upper computer, making it easy to grasp the operation of the device during production.
(1) Equipped with an independent operation control cabinet for easy management and daily maintenance;
(2) Control of the pump: The pump is linked to the corresponding tank level gauge and operates according to the height of the tank level; And each motor is equipped with an on-site operation column, which can switch between manual/automatic operation modes as needed.
(3) Automatic control of adsorption system: The fan and automatic control valve switch automatically according to temperature, pressure, and operating time processes;
(4) Manual control of adsorption system: In order to cope with occasional situations that require individual device actions, the central console also has a manual system, which means that the control of each device is independent and may not be associated with other devices.
(5) The logic control diagram includes adsorption and desorption modules. The adsorption module has functions such as manual, automatic, stop, and start, while the desorption module has functions such as end, pause, resume, stop, and desorption start.
(6) All pumps and valves have two operation modes, manual control and automatic control, in the upper computer, which can achieve control of a single pump or valve.
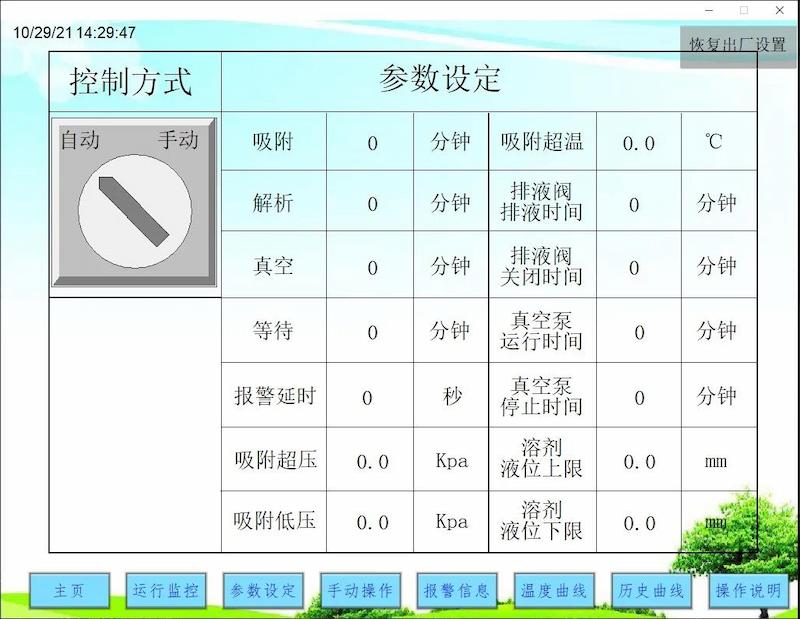
*Automatic control interface
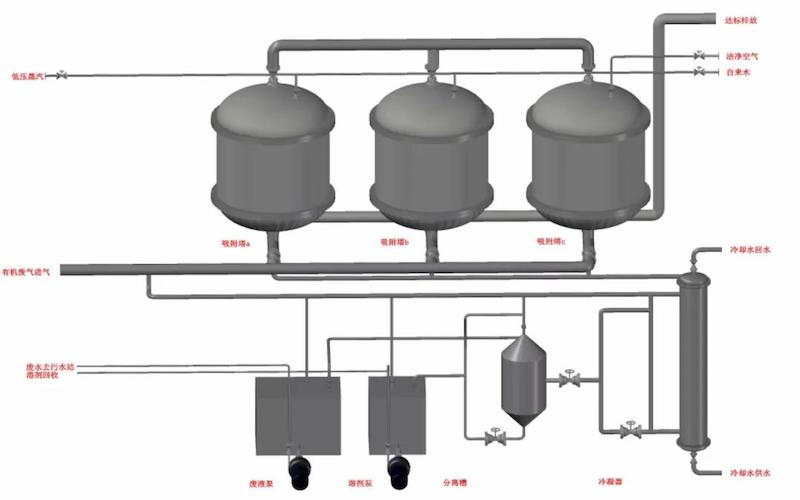
*Model diagram of adsorption process equipment
Related case data
A certain dichloroethane waste gas treatment project
| Serial number | Entry name | Technical parameter |
| 1 | Waste gas components | Mainly dichloroethane |
| 2 | Waste gas content | -3049 mg/m³ |
| 3 | Exhaust condition | Normal temperature and pressure |
| 4 | VOCs emissions | 4.7 mg/m³ |
A certain dichloromethane waste gas treatment project
| Serial number | Entry name | Technical parameter |
| 1 | Waste gas components | Mainly dichloromethane |
| 2 | Waste gas content | 24398 mg/m³ |
| 3 | Exhaust condition | Normal temperature and pressure |
| 4 | VOCs emissions | 16 mg/m³ |
A cyclohexane waste gas treatment project
| Serial number | Entry name | Technical parameter |
| 1 | Waste gas components | Mainly cyclohexane |
| 2 | Waste gas content | 3075 mg/m³ |
| 3 | Exhaust condition | Normal temperature and pressure |
| 4 | VOCs emissions | 2.7 mg/m³ |
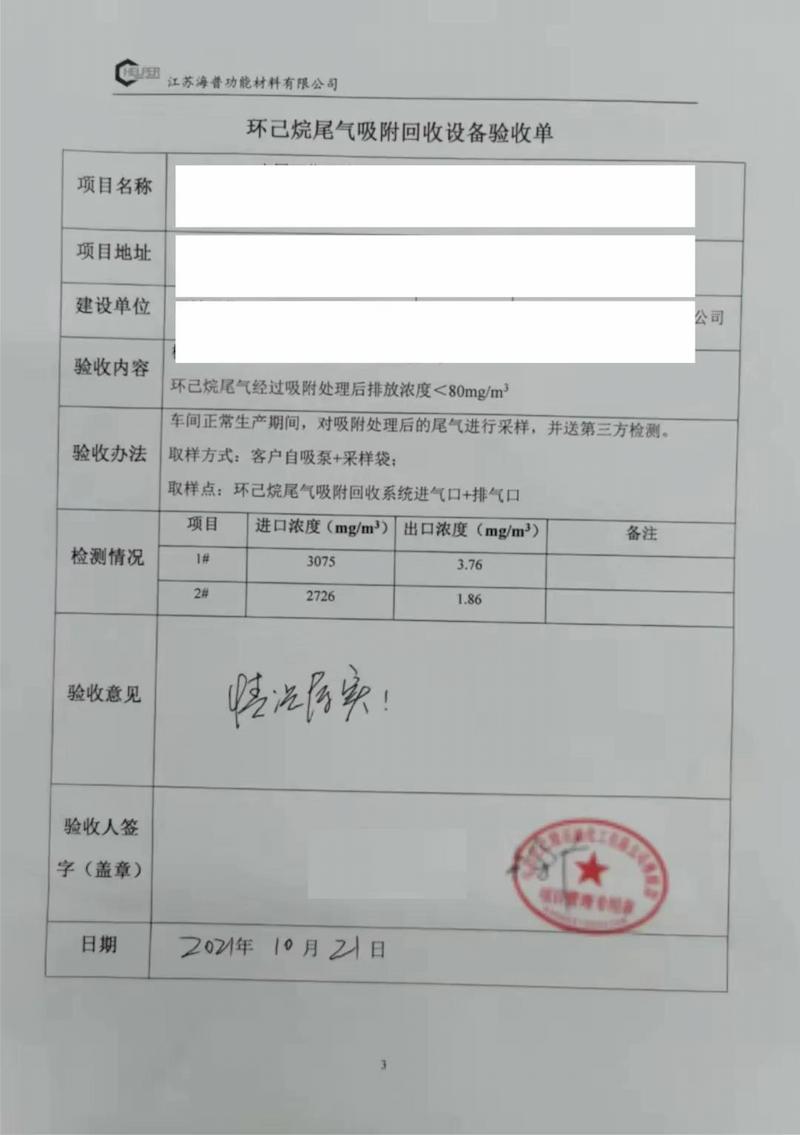
*Customer acceptance form, cyclohexane outlet concentration is only 1.86mg/m³
A certain benzene waste gas treatment project
| Serial number | Entry name | Technical parameter |
| 1 | Waste gas components | Mainly benzene and toluene |
| 2 | Waste gas content | 2954 mg/m³ |
| 3 | Exhaust condition | Normal temperature and pressure |
| 4 | VOCs emissions | 3 mg/m³ |
A petroleum ether waste gas treatment project
| Serial number | Entry name | Technical parameter |
| 1 | Waste gas components | Mainly acetate esters and petroleum ethers |
| 2 | Waste gas content | 5093 mg/m³ |
| 3 | Exhaust condition | Normal temperature and pressure |
| 4 | VOCs emissions | 33 mg/m³ |
Partial VOCs waste gas treatment on-site project display
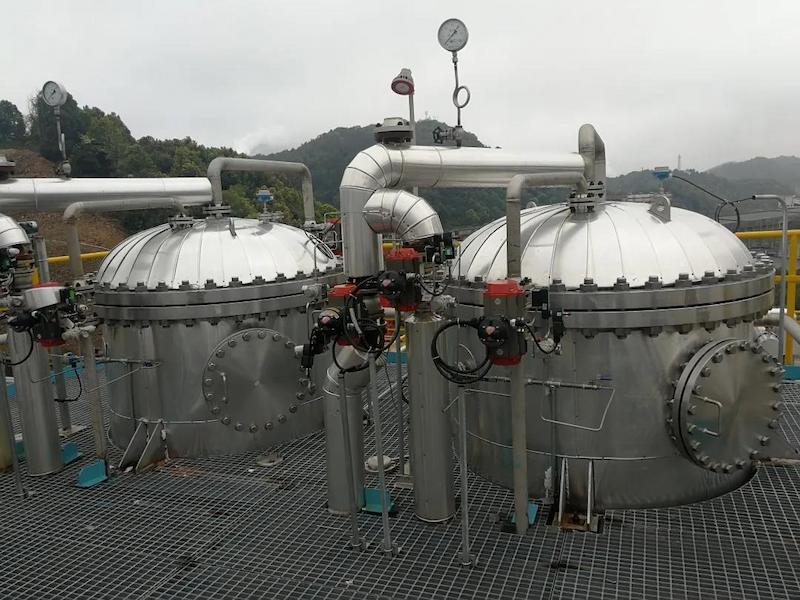
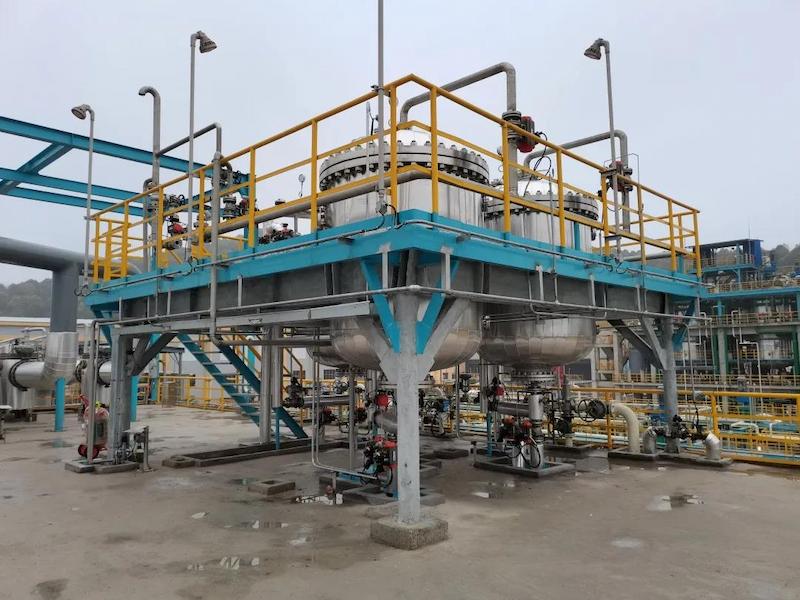


*On site cyclohexane waste gas treatment project
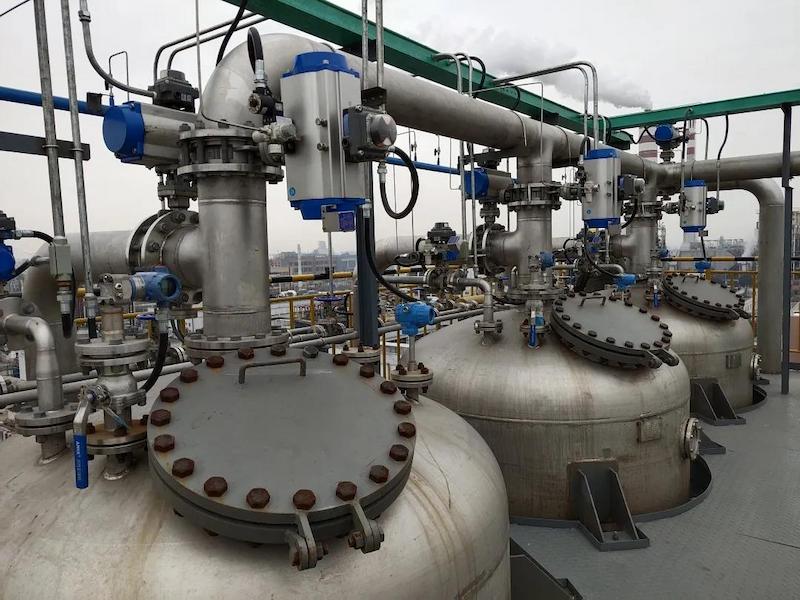
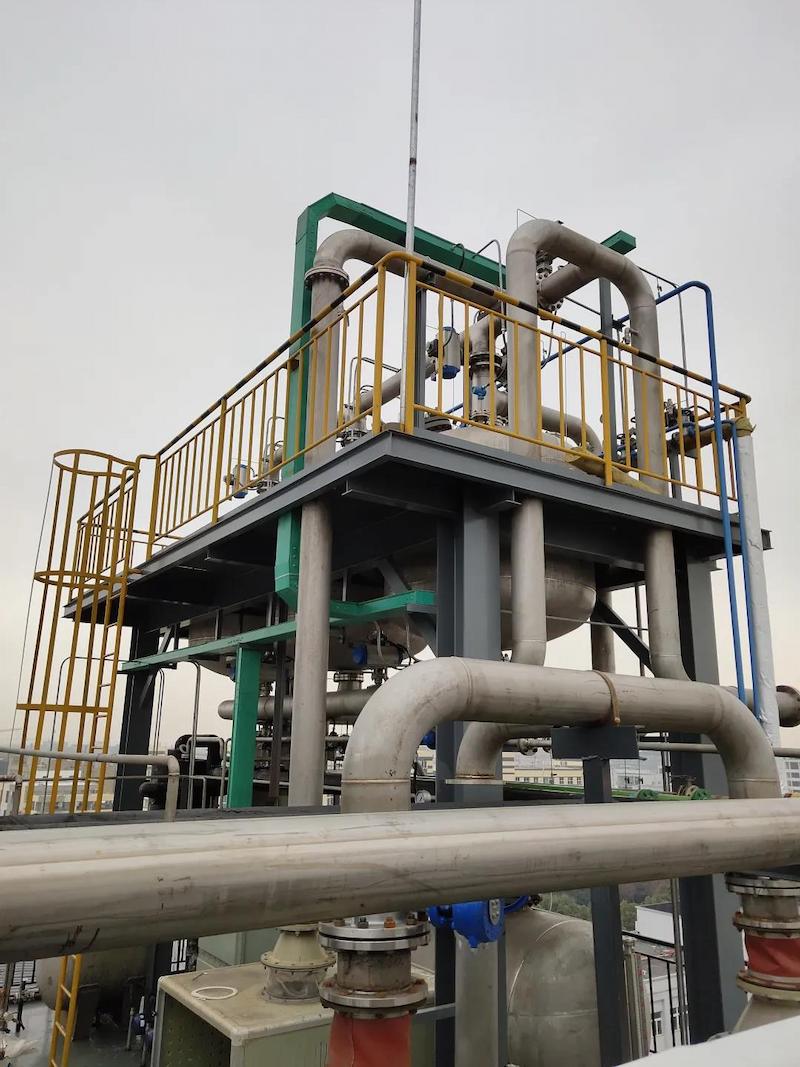


*On site dichloroethane waste gas treatment project
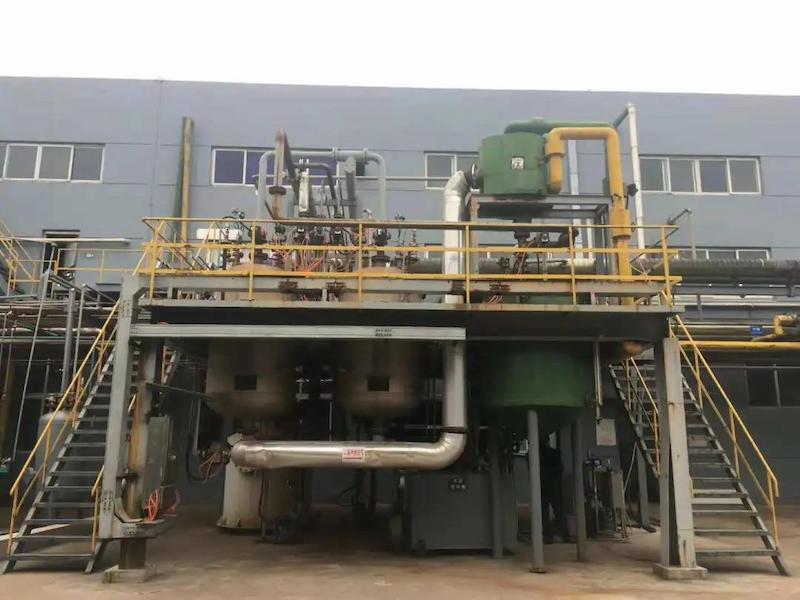


*On site treatment project for benzene and ester waste gas




 CN
CN















