In the Earth's crust, fluorine content is 544ppm, ranking 13th in abundance. Fluorine mainly exists in the form of compounds such as fluorite (CaF2), calcium fluorophosphate (Ca10F2(PO4)6), and cryolite (Na3AlF6) in nature. Fluorine in rocks, minerals, and soil is the main source of fluoride in surface water and groundwater. During the industrial production process, a large amount of fluorine-containing waste gas, waste liquid, and waste residue are also emitted. The fluoride that causes industrial fluoride pollution mainly comes from the smelting of aluminum and steel in the metallurgical industry, the production of phosphate fertilizers and fluoroplastics in the chemical industry, the production of bricks, ceramics, glass, and refractory materials in the silicate industry, and coal-fired power generation in the power industry.
Waste gas and liquid can directly pollute the environment, while fluorine-containing waste residue can also become an indirect source of fluoride pollution. The characteristics of these fluorine-containing waste gases, liquids, and residues are concentrated emissions, which can cause poisoning of people and animals in the surrounding area and trigger endemic fluorosis.
Scientific research has found that fluoride has a strong affinity for calcium and phosphorus in the human body. It can disrupt the normal metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body and inhibit the activity of certain enzymes, leading to a series of diseases including dental fluorosis, skeletal fluorosis, kidney, liver, brain damage, immune dysfunction, pulmonary edema, pulmonary hemorrhage, and intellectual decline in children.
There are various methods for treating fluorine-containing wastewater, and the commonly used methods at home and abroad can be roughly divided into two categories - precipitation method and adsorption method. In addition to these two methods, there are also ion exchange resin defluorination method, ultrafiltration membrane method, electrocoagulation method, and electrodialysis method. Due to high cost and low defluorination rate, these methods are rarely promoted and applied in commonly used defluorination processes.
1. Chemical precipitation method
For high concentration fluorine-containing water (fluoride ion concentration greater than 20mg/L), lime or carbide slag precipitation method is generally used to remove fluoride ions by using calcium ions in lime to form calcium fluoride precipitation with fluoride ions. The chemical precipitation method has the characteristics of simple principle, convenient treatment, low cost, and good effect, and is currently widely used in the treatment of high concentration fluorine-containing water. However, to some extent, there are disadvantages such as large equipment, difficulty in meeting standards for treated effluent, slow sedimentation of sediment, and difficulty in dehydration. Therefore, it is often necessary to add calcium chloride or other coagulants to accelerate sedimentation.
2. Coagulation sedimentation method
This method is to produce high-quality copper sulfate by first neutralization, centrifugal filtration, re neutralization crystallization, screening and dehydration of acid and alkali copper containing waste liquids. This method yields the product copper sulfate, which has a higher added value than copper paste. But after the copper in the waste liquid is recovered in the form of copper sulfate, the wastewater also needs to be discharged, polluting the environment.
3. Coagulation sedimentation method
For low concentration fluorine-containing water (fluoride ion concentration less than 20mg/L), coagulation sedimentation method is generally used, which uses coagulants to form positively charged colloidal particles in the water to adsorb F - in the water, causing the colloidal particles to coalesce into larger flocculent precipitates to achieve the purpose of fluoride removal. The coagulation sedimentation method has the advantages of low dosage of chemicals and large water treatment capacity, but it is generally only suitable for water treatment with low fluoride content. If better results are to be achieved, it needs to be combined with other methods. However, the defluorination effect is greatly affected by operational factors such as stirring conditions, settling time, and the concentration of anions such as CO32-, SO42-, Cl - in water. In recent years, with the continuous development of the chemical and water treatment industries, many efficient coagulation and defluorination agents have emerged, revitalizing reinforced coagulation technology. With the application of sensing technology and automatic control technology, real-time control of coagulant dosage has become possible.
4. Haipu customized processing technology
The defluorination treatment process developed by Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. selectively adsorbs and enriches fluoride ions in wastewater or waste acid into adsorption materials, thereby achieving the goal of separating fluoride ions. The fluoride content in the adsorbed water is greatly reduced, meeting the relevant requirements of subsequent steps.
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is committed to the research and industrialization of high-performance adsorbents and catalysts. In 2018, it was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalytic Functional Nanomaterials Engineering Technology Research Center. Through years of independent research and development, it has achieved international leading levels in ion exchange technology and adsorption technology, nano inorganic material hybridization technology, etc., realizing the serialization of adsorption and catalytic products and successfully applying them in the fields of environmental protection and resource recycling. With a series of independently developed high-performance adsorbents and catalysts as the core, combined with self-developed process technology, Haipu has become a professional supplier of green and environmental protection solutions.
After adjusting the pH of the liquid, it is first filtered to retain suspended solids and fine particles, preventing impurities from entering the adsorbent material and affecting its adsorption performance. The filtered material liquid is then sent to an adsorption tower containing special adsorption materials for adsorption. After adsorption saturation, the adsorption materials are subjected to desorption and regeneration treatment. After regeneration, the adsorption materials can be reused. The adsorbed water material liquid is subsequently recovered and processed by the customer, while the high concentration desorption liquid is subjected to defluorination treatment by the customer themselves.
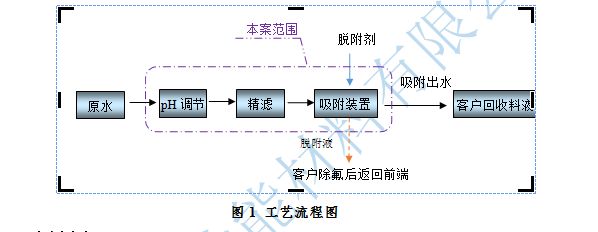
Figure 1 Process Flow Diagram
5. Case Introduction
The business scope of Anhui New Materials Technology Co., Ltd. includes the research and development, production, processing, and sales of precursors, positive electrode materials, and new energy materials. The lithium sulfate liquid generated during the production process of the enterprise needs to undergo defluorination treatment. Based on the characteristics, difficulties, and treatment requirements of the liquid, our company's relevant specialized adsorption materials are selected for adsorption treatment of the liquid. The effluent can meet customer requirements, and the wastewater design indicators are shown in the table below.
Table 1 Wastewater Design Parameters Table
| Index | Water volume (t/d) | Fluorine (mg/l) | pH | remarks |
| Absorb incoming water | 200 | ~250 | ~9 | Product liquid |
| Adsorbed water | 200 | <1 | ~4 |
|
| High concentration desorption solution | ~6.67 | / | Alkalinity | Return to the front end after precipitating fluorine |
The laboratory trial results are as follows:
Table 2 Adsorption Treatment Data
| Index | Water volume (t/d) | Fluorine (mg/l) | Li:Na |
| Absorb incoming water | 200 | ~250 | 60.3:1 |
| Adsorbed water 1 | 200 | 0.5 | 82.9:1 |
| Adsorbed water 2 | 200 | 0.04 | 72.4:1 |
Appearance of processing effect:

Figure 2 shows the raw water on the left and the adsorbed effluent on the right
After pre-treatment to adjust the pH to around 4, the wastewater was treated with a special adsorbent to achieve a fluoride content of less than 1ppm, meeting customer requirements The adsorbent has undergone multiple batches of adsorption and desorption tests, and the results show that its adsorption performance is stable and reliable.
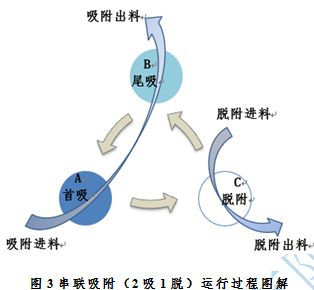
To ensure the continuous and stable operation of the device, and to ensure the effectiveness of the device's water output, the adsorption device adopts a 3 tower 2 series 1 desorption operation mode. Among them, 2 towers are connected in series at the beginning and end to adsorb the water output, and 1 tower is rotated for desorption. During desorption switching, the original first tower is desorbed, and the original tail tower is transformed into the first tower and then reconnected with the desorbed tower (used as the tail tower) to adsorb the water output. The illustrated process is shown in Figure 3, where each adsorption tower rotates its roles in the order of arrows during different operating periods.
This project adopts PLC program automatic control to monitor the temperature, pressure, liquid level and other parameters of the adsorption device in real time, achieving full automation operation. The PLC communicates with the upper computer, making it easy to grasp the operation of the device during production.
(1) Equipped with an independent operation control cabinet for easy management and daily maintenance;
(2) Control of the pump: The pump is linked to the corresponding tank level gauge and operates according to the height of the tank level; And each motor is equipped with an on-site operation column, which can switch between manual/automatic operation modes as needed.
(3) Automatic control of adsorption system: The water pump and automatic control valve switch automatically according to temperature, pressure, and operating time processes;
(4) Manual control of adsorption system: In order to cope with occasional situations that require individual device actions, the central console also has a manual system, which means that the control of each device is independent and may not be associated with other devices.
(5) The logic control diagram includes adsorption and desorption modules. The adsorption module has functions such as manual, automatic, stop, and start, while the desorption module has functions such as end, pause, resume, stop, and desorption start.
(6) All pumps and valves have two operation modes, manual control and automatic control, in the upper computer, which can achieve control of a single pump or valve.
6. Advantages of adsorption method
(1)Effectively reducing the concentration of fluoride ions in the effluent can ensure that the effluent meets the discharge standards or the operational requirements of subsequent processes;
(2) Using specially modified adsorption materials, with large adsorption capacity, low equipment investment, and low operating costs;
(3) The process flow is simple and can achieve full automation operation, making operation and maintenance convenient;
(4) It can be arranged in multiple layers, occupying a small area and having a short installation cycle.




 CN
CN





