In 1817, Alphonsen discovered a new metal while analyzing lithium feldspar near Stockholm, and subsequently named the metal Lithium after his teacher, Swedish chemist Berzelius, with the element symbol Li (lithium).
As the smallest atomic weight metal element, lithium has extremely strong electrochemical activity and highly reactive chemical properties. Therefore, lithium can easily react with other materials to form various alloys, which are widely used in various fields.

The content of lithium in the Earth's crust is about 0.0065% (approximately 600 trillion tons, although it is difficult for humans to extract the entire crust), ranking 27th in the richness ranking. Although it is called a "rare metal", from the perspective of its natural content, it does not belong to the rare category. The reason why lithium is "rare" is not because of its stock, but because of its difficulty in purification.
At present, the level of technology makes a large amount of lithium minerals have no development value, such as lithium in seawater (the lithium reserves in seawater are about 260 billion tons), which is difficult to extract due to its low concentration.
At present, the industry consensus is that lithium can exist in both solid mineral resource states and liquid mineral deposit resource states.
Solid lithium deposits exist in two forms: pegmatite type lithium deposits and sedimentary type lithium deposits. Liquid lithium deposits refer to brine type lithium deposits, mainly occurring in salt lake brine, seawater, oilfield brine, and well brine.

Survey

The lithium reserves in China's salt lakes are about 24.4738 million tons (calculated as lithium chloride), accounting for about 85% of the total lithium resources reserves in China.
Generally speaking, the high or low magnesium lithium ratio in salt lake brine determines the feasibility of using brine resources to produce lithium salts, as well as the production cost and economic benefits of lithium salt products.
The industrial facilities for lithium extraction from brine in China are relatively immature, and the actual production capacity is far lower than the construction capacity.
The main reason is that the grade of brine in China's salt lakes is relatively low, especially in Qinghai salt lakes, which mostly have a high magnesium lithium ratio. Magnesium and lithium are located in adjacent diagonal positions in the periodic table, and their chemical properties are extremely similar. It is difficult to effectively separate them using general physical and chemical methods, which brings difficulties to the exploitation of lithium resources.
Current status of lithium extraction technology from salt lakes
The following compares the advantages and disadvantages of existing brine lithium extraction methods.
Calcination method
The process is simple, but hydrated magnesium chloride is difficult to completely decompose, and the generated hydrogen chloride gas is highly corrosive to equipment, requiring a large amount of water to be evaporated, resulting in high energy consumption in the process.
extraction method
The process is simple, but there are problems such as degradation and loss of extractants, which significantly increase the cost. At the same time, the environmental problems caused by the loss of extractants are prominent, and the cost of environmental protection treatment is high.
Membrane separation
The cost of extracting lithium from high magnesium lithium is higher than that from brine. On the one hand, it needs pure water to dilute, on the other hand, the recovery rate of facial mask is low, and industrial amplification is not economical.
Adsorption method
It has the advantages of simple process, high recovery rate, and environmental friendliness, but most of the existing adsorbents on the market have poor strength, severe dissolution, short service life, and low adsorption capacity.
Compared to other methods, adsorption is a simple and efficient approach, and the key to lithium extraction in this method is high-performance adsorbents.
At present, most of the research reports at home and abroad are on inorganic adsorbents, which utilize the special internal structure of adsorbents to block larger alkali metal and alkaline earth metal ions during lithium adsorption, thereby achieving efficient screening of magnesium and lithium.
But these inorganic adsorbents are mostly in powder form, with small particle size, poor mechanical strength, flowability, and permeability, and high adsorbent loss rate.
To solve the above shortcomings, it is usually necessary to bond and granulate the powder adsorbent. For example, a lithium extraction enterprise in a salt lake in China introduced foreign adsorbent technology and manufactured it through this granulation method.
In actual industrial use, there is a large amount of dissolution and loss of adsorbents, which means that the loss of adsorbents is relatively large.
Therefore, high-performance adsorbents with large adsorption capacity, fast adsorption rate, and long service life are the key issues that urgently need to be solved for lithium extraction by domestic adsorption methods.
Special adsorbent for lithium extraction
To solve the problems of low capacity, poor mechanical strength, and high dissolution rate of existing adsorbents in the market, we have developed a new lithium extraction adsorbent material DL760.
By synthesizing nano active lithium extraction particles and using special granulation technology, it is ensured that the active nanoparticles do not aggregate or become inactive, and still have nanometer size; At the same time, the lithium extraction adsorbent has excellent mechanical strength, thereby ensuring the lithium extraction activity, capacity, and stability of the lithium extraction adsorbent.
As shown in the figure, the left image is an electron microscope image of the appearance of DL760, and the right image is a further magnified lens image of the nanoparticle.
It can be seen that the active lithium extraction nano material has good nano size and dispersibility, which can maintain nano activity and stability. The adsorbent has excellent mechanical strength, low dissolution rate, and is suitable for various magnesium lithium ratio brines. It also has high lithium extraction yield, green environmental protection, no secondary pollution, and low operating costs.
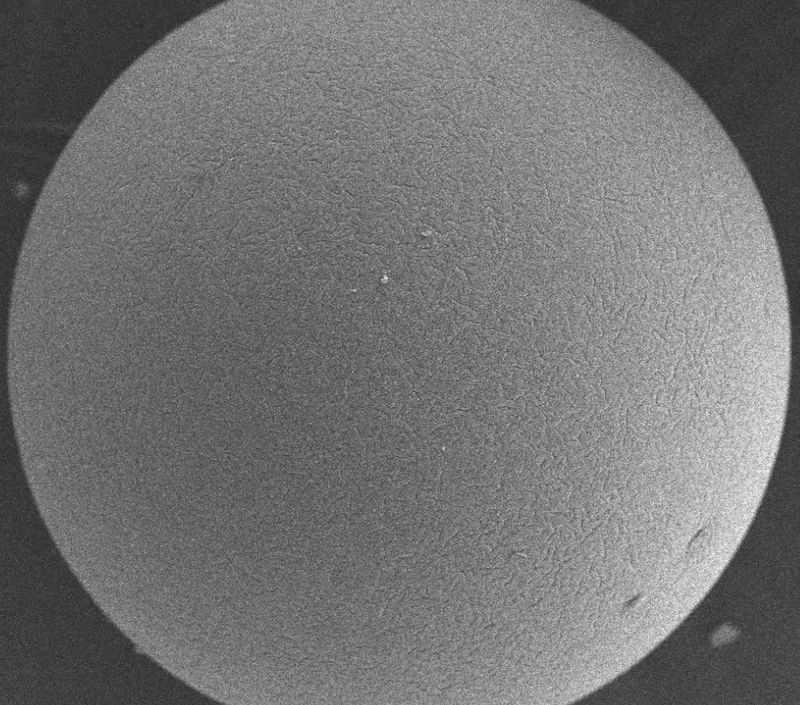

DL760 Appearance (left), High Power Transmission Electron Microscope (right)
The production process of lithium carbonate with special lithium adsorbent DL760 adsorption as the core includes four steps: lithium extraction, deep magnesium removal, concentration, and precipitation.
The first step of lithium extraction through adsorption is the core and key technology of salt lake lithium extraction, which separates and extracts lithium from brine with high magnesium lithium ratio.
Subsequent deep magnesium removal can be achieved by using magnesium removal adsorbents to remove a small amount of magnesium deeply; Concentration can be achieved through reverse osmosis, followed by further concentration through multi effect evaporation; Finally, lithium carbonate product was obtained by precipitation with sodium carbonate, as shown in the figure.
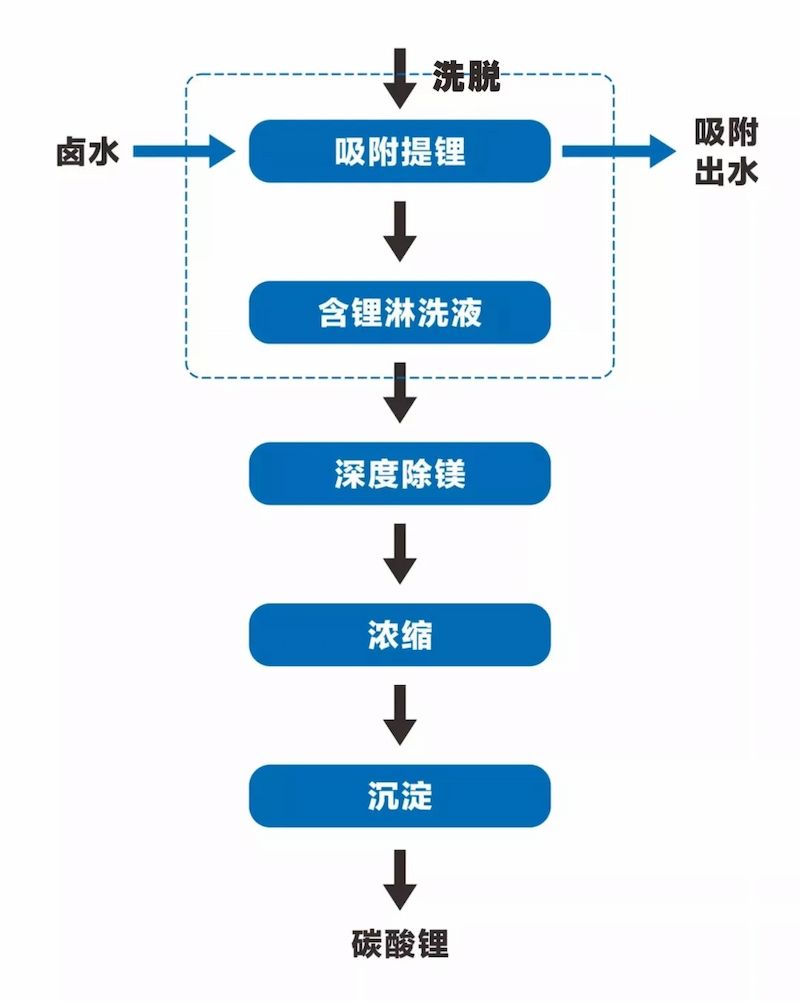
Process flowchart for producing lithium carbonate by adsorption method
The relevant technical indicators and parameters of the new lithium extraction adsorbent are shown in the table
| Serial number | Project | Index |
| 1 | Temperature range for use | 10-100℃ |
| 2 | Density | 900-1000g/L |
| 3 | Adsorption capacity | ≥8.0g Li/L |
| 4 | Lithium extraction rate | ≥90% |
| 5 | 100 batch melting loss rate | ≤0.5% |
| 6 | Minimum bed height | ≥60cm |
| 7 | Operating flow rate | 0.5-20 BV/H |
Technical indicators of new lithium extraction adsorbent
Current situation of industrialization
Based on the preliminary small-scale, pilot scale, and hundred kilogram scale trial production, as well as the development of related application processes, the production and industrial application of a ten ton new lithium extraction adsorbent have been completed. A lithium extraction trial production device with a daily processing capacity of 100 tons of brine has been established at a salt lake site in Qinghai, as shown in the figure.
Further carry out industrial application research, simulate industrial application scenarios, optimize operating process conditions, investigate the performance and stability of new lithium extraction adsorbents, and prepare for subsequent industrial scaling up.
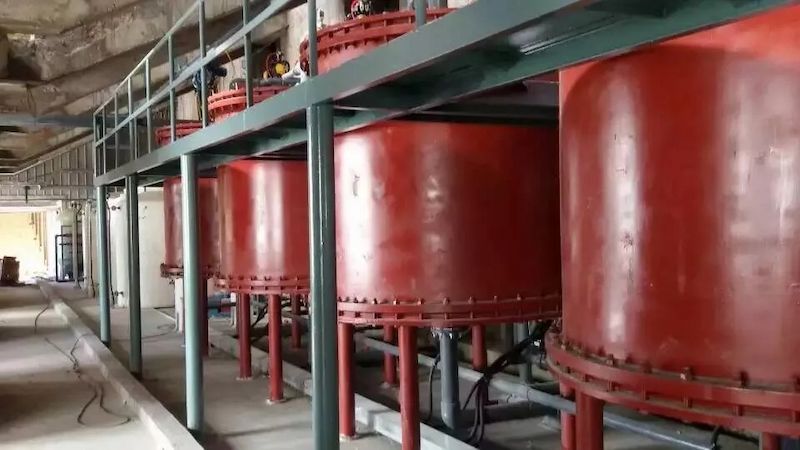
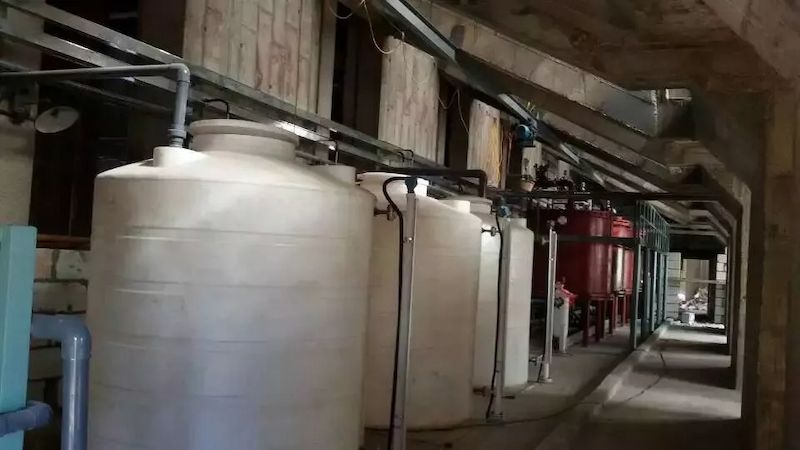


Salt Lake Lithium Extraction Site
The following table shows that after 6 months of continuous operation, all technical indicators have met the requirements and are suitable for lithium extraction from various brines with lithium content of 50-2500mg/L and the highest magnesium content in a saturated state, achieving efficient lithium magnesium separation.
| Serial number | Index | Removal rate |
| 1 | Adsorption temperature ≤40 ℃ | 25-40℃ |
| 2 | Desorption temperature ≤50 ℃ | 25-45℃ |
| 3 | Lithium content in lithium leaching solution ≥1g/L | 1.0-1.2g/L |
| 4 | Lithium leaching solution with magnesium content ≤3g | 1.5-3.0g/L |
| 5 | Lithium adsorption rate ≥90% | 90-95% |




 CN
CN









