1 Introduction
Waste acid can be divided into organic waste acid and inorganic waste acid according to the different media in the acid, with inorganic waste acid accounting for about 65% and organic waste acid accounting for about 35%; In addition to containing various residual acids, organic waste acids also have high COD and chromaticity, while inorganic waste acids contain heavy metal salts and total phosphorus. Waste acid is generated in various industries. According to comprehensive industry research and statistics, the chemical industry produces nearly 80 million tons of waste acid of various concentrations every year, making it a major producer of waste acid; Steel enterprises, metal processing, and pickling industries generate approximately 65 million tons of various waste acids annually; In addition, in the fields of light industry, petroleum smelting, fiber industry, mineral processing industry, battery industry, military industry, and nuclear materials industry, the annual production of waste acid also exceeds 50 million tons; Based on this calculation, China produces over 200 million tons of waste acid annually. Discharging these acidic waste liquids without treatment not only pollutes the environment but also wastes valuable resources.
2 Waste acid treatment and purification methods
The existing purification methods for waste acid mainly include calcination, extraction, ion exchange resin, membrane separation, adsorption, concentration and impurity removal, stripping, freeze crystallization, hydrolysis, oxidation, thermal decomposition, etc.
2.1 Roasting method
Purified acid is usually obtained by spray roasting through pre concentration, spray roasting gasification, cyclone separation, washing water absorption and other steps. This method is suitable for recovering volatile acids such as hydrochloric acid.
2.2 Extraction method
The extraction method for treating waste acid utilizes the principle of similar solubility to transfer organic matter from the waste acid to the extractant, thereby separating sulfuric acid. The main steps are: 1) adding the extractant to the waste liquid and allowing them to fully contact, transferring harmful substances from the waste liquid as extractants to the extractant. (2) Separate the extract from the waste liquid, and the waste liquid is treated. (3) Separate the extract from the extractant and reuse the extractant in the extraction process.
2.3 Ion exchange resin method
Ion exchange method is a method of separating acid salts by using certain ion exchange resins to absorb acid from waste acid solution and discharge metal salts, with a recovery rate of over 70%. This method has low energy consumption, short process flow, and easy operation; If treated at room temperature, it can improve the service life of equipment and pipelines and reduce the overflow of chloride. However, the concentration of hydrochloric acid recovered at room temperature is low, and concentrated hydrochloric acid needs to be added before use.
2.4 Membrane Separation Method
Membrane treatment refers to the use of selective permeability such as dialysis membranes and ceramic membranes to achieve the separation of acid salts; It is a general term for treatment methods such as diffusion dialysis, electrodialysis, membrane distillation, ceramic membranes, etc.
2.5 Adsorption method
Adsorption method mainly refers to the method of using the physical and chemical adsorption properties of solid adsorbents (activated carbon, bentonite, resin, polymer adsorbent materials) to remove pollutants from waste acid.
3 Haipu Customized Purification Waste Acid Process Flow
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in Suzhou Industrial Park. It is a national high-tech enterprise that uses special adsorbents and catalysts as its core technology, supporting the development of application processes, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to solve related environmental problems for customers. There are already many mature application cases in the purification of waste acid. The following figure shows the commonly used process flow for purifying waste acid:
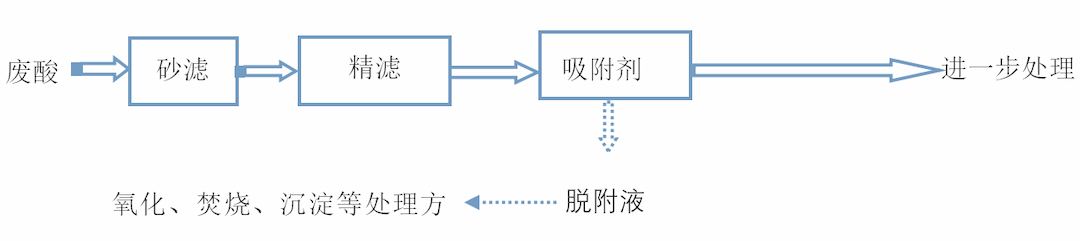
Figure 1. Waste acid purification process flow
4 Waste Acid Purification Cases
4.1 Removal of Heavy Metals from Waste Acid
4.1.1 Copper Removal
The copper containing waste acid generated in the production process of a certain enterprise producing saccharin sodium can meet the requirements of the recycling production line after treatment.
Table 1
| Index | Cu/ppm | Hydrochloric acid content |
| Original acid | 5000 | 8% |
| Purification acid | <500 | 8% |
4.1.2 Zinc Removal
The zinc containing waste hydrochloric acid generated by a certain metal surface treatment enterprise can be purified and used to produce the water purification agent ferrous chloride.
Table 2
| Index | Zn/ppm | Hydrochloric acid content |
| Original acid | 8000 | 8% |
| Purification acid | <1500 | 8% |
4.1.3 Lead removal
The lead containing waste hydrochloric acid generated by a certain metal surface treatment enterprise can be purified and used to produce the water purification agent ferrous chloride.
Table 3
| Index | Pb/ppm | Hydrochloric acid content |
| Original acid | 2500 | 10% |
| Purification acid | <30 | 10% |
4.2 Waste acid COD removal and decolorization
4.2.1 COD removal
The by-product hydrochloric acid produced in the production process of a certain fine chemical enterprise contains organic compounds that need to be purified before use. After being processed by Haipu customized technology, it can meet the requirements for use.
Table 4
| Index | Organic compound | Hydrochloric acid content |
| Original acid | 70000 | 30% |
| Purification acid | <10000 | 30% |
| Removal rate | >85% | —— |
4.2.2 Discoloration
The waste sulfuric acid generated in the production process of a certain chemical enterprise contains a large amount of COD and high chromaticity. After treatment by the Haipu adsorption system, its COD and chromaticity can be greatly reduced, ensuring that it meets the requirements for reuse after concentration.
Table 5
| 指标 | COD | Appearance | Sulfuric acid content |
| 原酸 | 50000 | Oxblood red | 30% |
| 净化酸 | <2500 | Colourless | 30% |
| 去除率 | >95% | —— | —— |
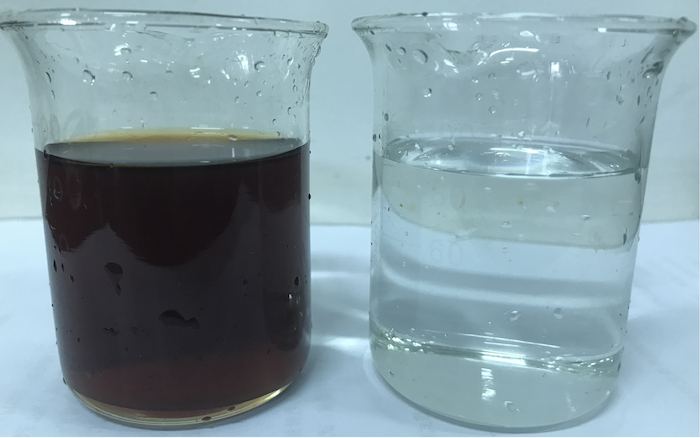

Figure 2. Processing effect diagram, with the original acid on the left and the purified acid on the right
5 Summary
Applying adsorption technology to the purification and impurity removal of waste acid can improve the quality of acid without reducing its concentration, thereby providing support for the direct reuse of waste acid and the resource utilization of by-products in production. From a societal perspective, it has reduced the environmental pressure of waste acid emissions and saved resources; From the perspective of enterprises, reducing production costs and increasing profits. In the future, with the introduction of various new adsorbents, adsorption methods will make more contributions in purifying waste acid.




 CN
CN




