Abstract: Phosphorus is one of the most difficult indicators to solve in the treatment of electroplating wastewater. If the discharge of phosphorus cannot be effectively controlled, it will damage the ecological environment and cause serious environmental pollution. The main methods for phosphorus removal from wastewater include chemical phosphorus removal, biological phosphorus removal, and adsorption phosphorus removal. The composition of electroplating wastewater is complex, and phosphorus exists in various forms. Based on the principles of chemical phosphorus removal, biological phosphorus removal, and adsorption phosphorus removal methods, a comprehensive application of chemical and adsorption phosphorus removal methods is proposed. Through experiments on different types of electroplating wastewater, a solution is proposed to reduce the total phosphorus of electroplating wastewater to the standard (TP ≤ 0.5mg/L). The treatment of phosphorus in electroplating wastewater not only requires end of pipe treatment to meet standards, but also requires control from the source, implementing the principle of prevention first and combining prevention and control, and implementing clean production.
Keywords: electroplating phosphorus containing wastewater; Chemical phosphorus removal; Biological phosphorus removal; Adsorption based phosphorus removal process
0 Preface
Phosphorus is one of the main elements that constitute life in the Earth system. In chemical production, if phosphorus emissions are not scientifically controlled, it will damage the ecological environment and cause serious environmental pollution. For electroplating wastewater, the "Emission Standards for Electroplating Pollutants" (GB21900-2008) stipulate that "in areas where the land development density is already high, the environmental carrying capacity is beginning to weaken, or the environmental capacity is small, the ecological environment is fragile, and serious environmental pollution problems are prone to occur and special protection measures need to be taken", the "Table 3 Special Emission Limits for Water Pollutants" standard shall be implemented, and the TP discharge limit for the total discharge outlet of enterprise wastewater shall be 0.5mg/L.
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is committed to the research and industrialization of high-performance adsorbents and catalysts. Through years of independent research and development, we have achieved international leading levels in ion exchange technology and adsorption technology, nano inorganic adsorption materials, and hybrid technology preparation. We have successfully serialized adsorption and catalytic products and applied them in the fields of environmental protection and resource recycling. For the phosphorus containing wastewater in the electroplating industry, Jiangsu Haipu has a complete set of electroplating phosphorus containing wastewater treatment processes developed with special adsorbents as the core. Independent modular treatment units can be customized according to different water quality types to achieve standard discharge.
1. Methods for phosphorus removal from wastewater
The main methods for removing phosphorus from wastewater are chemical phosphorus removal, biological phosphorus removal, and adsorption phosphorus removal. Chemical phosphorus removal is fast, but costly. Biological phosphorus removal has low cost but long cycle. It is difficult to achieve ideal results using a single phosphorus removal process. If a combined process and process optimization are adopted, the phosphorus in the wastewater can be stabilized and meet the discharge standards.
1.1 Principle of Chemical Phosphorus Removal
Chemical phosphorus removal is the process of converting soluble phosphorus containing substances in wastewater into insoluble phosphorus containing substances through chemical methods, and transferring them from the liquid phase to the solid phase. The commonly used method is to add inorganic metal salt agents such as iron salts, aluminum salts, or calcium salts, which react with soluble phosphates to produce compounds with low solubility products such as iron phosphate, aluminum phosphate, and calcium phosphate. These small insoluble solids are aggregated into larger insoluble solids through the addition of coagulants and flocculants, which precipitate out. After concentration and pressure filtration, solid-liquid separation is achieved, and phosphorus enters the sludge. It is necessary to treat the subsequently produced sediment sludge with higher water content, resulting in higher operating costs.
With the continuous advancement of technology, some new phosphorus removal agents have emerged, especially those for treating non orthophosphate. Some wastewater treatment chemical companies have developed hypophosphite removal agents. The principle is to capture and adsorb hypophosphite in wastewater through bridging, and then precipitate it to remove phosphorus, which still exists in the form of hypophosphite in sludge.
1.2 Principle of Biological Phosphorus Removal
1.2.1 PAO principle
The principle of biological phosphorus removal is generally believed to be that during the treatment of wastewater with activated sludge, the polyphosphate accumulating organisms (PAOs) in the sludge release phosphorus in an anaerobic state, and excessively uptake phosphorus in an aerobic state. By discharging excess phosphorus rich sludge, the phosphorus in the wastewater is removed.
1.2.2 DPB principle
Denitrifying Phosphorus Removal Bacteria (DPB) has a similar phosphorus removal principle to polyphosphate accumulating bacteria (PAO), except that the electron acceptor for oxidizing PHB stored in cells is different. PAO is O2, while DPB is NOx -- N. Denitrifying phosphorus removal bacteria DPB can uptake phosphorus in anaerobic environments (without molecular oxygen but with nitrate). Denitrifying phosphorus removal bacteria DPB use nitrate as an electron acceptor to produce biological phosphorus uptake. At the same time as biological phosphorus uptake, nitrate is reduced to nitrogen, which enables the two different biological processes of phosphorus uptake and denitrification to be completed using the same type of bacteria and in the same environment.
In addition, there are artificial wetlands for phosphorus removal. It is a wastewater phosphorus removal technology that focuses on phosphorus removal through a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes, based on the general artificial wetland system, artificially controlled and optimized by the interaction between the wetland substrate, aquatic plants, and microorganisms. Its advantages are: high efficiency, low investment, low energy consumption, simple operation, flexible settings, and low maintenance and operation costs. But this method takes up a large area of land.
1.3 Principle of phosphorus removal by adsorption method
Adsorption based phosphorus removal is a wastewater phosphorus removal process that utilizes the affinity of certain porous or high specific surface area solid substances for phosphate ions in water. Phosphorus can be separated from wastewater through physical adsorption, ion exchange, or surface precipitation processes on the adsorbent surface, and further phosphorus resources can be recovered through desorption treatment. The adsorption method for phosphorus removal is simple and reliable, and can be used as a supplement to biological phosphorus removal methods or as a standalone method for phosphorus removal. The selection requirements for phosphorus removal adsorbents are: 1) high adsorption capacity; 2) High selectivity; 3) Fast adsorption speed; 4) Strong resistance to interference from other ions; 5) No harmful substances dissolved out; 6) Adsorbent regeneration is easy and its performance is stable; 7) The raw materials are easy to obtain and the cost is low. Phosphorus removal adsorbents are generally divided into two categories: natural adsorbents and synthetic adsorbents. Natural adsorbents include fly ash, steel slag, zeolite, sepiolite, activated alumina, etc; Another type is synthetic adsorbents, which expand the selection range of adsorbent materials for phosphorus removal.
Haipu has developed a series of special phosphorus removal adsorbents based on the properties of electroplating phosphorus containing wastewater, which can selectively adsorb phosphorus and greatly remove phosphorus from the wastewater. The effluent can be directly discharged to meet the standard, or used as a pretreatment to remove the vast majority of total phosphorus, and then combined with subsequent conventional treatment (such as biochemistry) to achieve standard discharge. The specific process flow chart is as follows:
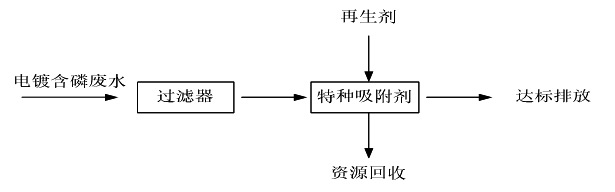
Figure 1 Adsorption phosphorus removal process flow
2 Practical Cases of Phosphorus Removal from Electroplating Wastewater
The phosphorus containing substances in electroplating wastewater include phosphoric acid, phosphate, hypophosphite, hypophosphite, pyrophosphate, phytic acid, etc. Orthophosphate is relatively easy to remove, while non orthophosphate and organic phosphate are difficult to remove. Most electroplating wastewater plants in large electroplating industrial parks adopt a classification treatment method, which involves treating wastewater containing orthophosphate into pre-treatment wastewater and non orthophosphate wastewater into chelating wastewater (wastewater containing chelating agents).
Jiangsu Haipu has developed a series of phosphorus removal special adsorbents and related solutions to address the water quality, diversity, and treatment requirements of phosphorus containing wastewater in the electroplating industry. They have successfully helped multiple enterprises achieve standard treatment of wastewater.
2.1 Phosphorus Removal Treatment Project for Electroplating Enterprise Wastewater
The water samples selected for the experiment were membrane concentrated wastewater discharged from a certain electroplating plant at different times, with a pH of 7.3 ± 0.2, COD of 180-420mg/L, total phosphorus of 10.5-50.2mg/L, orthophosphate of 2.6-10.2mg/L, and total salt of 8300-10400mg/L. It is known that the content of non orthophosphate such as hypophosphite accounts for about 80% of total phosphorus, and the solubility of calcium hypophosphite is 16.7g, which can be converted into easily treatable orthophosphate through oxidation. Jiangsu Haipu has verified through relevant phosphorus removal adsorbent application experiments and designed the process to deeply remove phosphorus from wastewater. The removal rate of phosphate is stable at over 90%, and the phosphorus content in the effluent is far below the requirements and discharge standards of the enterprise.
Table 1 Adsorption treatment effect of phosphorus containing electroplating wastewater
| Raw Water Phosphorus Content (mg/L) | Treated Water Phosphorus Content (mg/L) | Removal Rate |
| 32.5 | 0.375 | 98.80% |
| 32.5 | 0.306 | 99.00% |
| 32.5 | 0.279 | 99.10% |
2.2 Experimental Cases of Phosphorus Removal in Metal Surface Treatment and Heat Treatment Processing Electroplating Enterprises
A electroplating enterprise engaged in metal surface treatment and heat treatment processes generates 200 tons of phosphorus containing wastewater per day. Jiangsu Haipu has conducted application research and process design on this phosphorus containing wastewater, deeply removing phosphorus elements from the wastewater. The total phosphorus content of the adsorbed water can be stabilized below 1mg/L, meeting the requirements of the enterprise. The adsorbed water can be directly discharged, solving the problem of wastewater treatment in the enterprise.
Table 2 Adsorption treatment effect of phosphorus containing wastewater on metal surface treatment
| Raw Water Phosphorus Content (mg/L) | Treated Water Phosphorus Content (mg/L) | Removal Rate |
| 17 | <1 | >94.12% |
2.3 Example of Oxidation Adsorption Treatment of Phosphorus Containing Electroplating Wastewater
After filtering and pretreatment of electroplating phosphorus containing wastewater, ferrous sulfate and hydrogen peroxide are added to the pretreated water to adjust the pH and filter it. The filtrate is then passed through a device filled with phosphorus removal adsorbent for downstream adsorption, reducing the phosphorus content from 100-300mg/L of raw water to below 0.3mg/L. Using this process to treat phosphorus containing production wastewater, the phosphorus removal rate in the wastewater reaches over 98%, with stable operation, good treatment effect, and simple process flow.
Table 3 Oxidation adsorption treatment effect of phosphorus containing electroplating wastewater
| Raw Water Phosphorus Content (mg/L) | Treated Water Phosphorus Content (mg/L) | Removal Rate |
| 100-300 | <0.3 | >99.7% |
3. Summary
The composition of electroplating wastewater is complex, and the forms of phosphorus in the wastewater are diverse. It is difficult to reduce the phosphorus in electroplating wastewater to below 0.5mg/L using a single method of chemical phosphorus removal or biological phosphorus removal. Jiangsu Haipu has rich experience in electroplating wastewater treatment, especially in waste acid treatment, heavy metal standard discharge and recovery, phosphorus removal, etc., with significant treatment efficiency and energy consumption advantages. This article briefly describes a solution for treating phosphorus containing wastewater in the electroplating industry using adsorption technology. Through the adsorption phosphorus removal process, the phosphorus in the wastewater can be greatly removed, and the effluent can be directly discharged in compliance with standards, or used as a pre-treatment to provide guarantees for subsequent standard discharge, providing new ideas and choices for the treatment of phosphorus containing wastewater in electroplating for enterprises.




 CN
CN



