Anthraquinone is an important raw material in industrial production, used as an intermediate in dye synthesis, a delignification agent in the paper-making process, and a desulfurization agent in the fertilizer industry. However, the synthesis of anthraquinone produces a large amount of waste sulfuric acid, which contains a significant amount of organic matter and has a high color intensity. Direct discharge of this waste sulfuric acid would not only waste resources but also cause severe pollution. Therefore, treating and recycling industrial waste sulfuric acid from anthraquinone production is a major industry challenge and an urgent need for many enterprises. Below, Haipu provides detailed information on the decolorization solution for wastewater in the anthraquinone waste acid industry, hoping to be of help.
Currently, most enterprises in China treat anthraquinone waste sulfuric acid by removing the organic matter that causes the color. Common methods include activated carbon adsorption, oxidative cracking, concentration, or the simplest method, incineration. However, these methods often fail to achieve the desired results.
1. Current Status and Challenges of Anthraquinone Wastewater:
Anthraquinone is a compound with multiple benzene rings, an important industrial raw material widely used in the chemical and dyeing industries, and is also a carcinogen. Anthraquinone wastewater is complex, containing a large amount of benzene ring compounds that are not biodegradable, characterized by high COD concentration, high color intensity, and toxicity. Conventional water treatment technologies struggle to manage it, making it a difficult problem in industrial wastewater treatment.
Anthraquinone wastewater is highly acidic and has a high color intensity, making it difficult to remove using general methods.
Anthraquinone compounds have a stable structure due to the presence of benzene rings, making them difficult to degrade.
In recent years, the country has increasingly emphasized ecological and environmental protection, with stricter standards and total control over wastewater discharge. To ensure the sustainable development of industries related to anthraquinone, new approaches to anthraquinone waste acid water treatment have emerged. Recent methods include activated carbon adsorption, oxidation, and incineration.
Activated Carbon Adsorption Method:
The activated carbon adsorption method uses the adsorptive properties of activated carbon to adsorb and concentrate the colored substances in anthraquinone waste acid water, achieving decolorization. This method has good decolorization effects but is a one-time consumable, making it costly and unable to reuse valuable components, as the treated activated carbon is incinerated.
Oxidation Method:
The oxidation method involves adding strong oxidants and catalysts to the wastewater, forming an oxidation system that generates organic radicals in the aqueous solution, breaking down the structure of hard-to-degrade organic matter and ultimately oxidizing and decomposing it. This method effectively removes hard-to-degrade organic matter that traditional wastewater treatment technologies cannot. However, it has some drawbacks:
High oxidant consumption when treating high-concentration pollutants, leading to high treatment costs.
Limited applicable pH range, requiring specific pH conditions.
Conventional oxidation systems can introduce metal ions, necessitating subsequent treatment to recover catalysts, which is costly and complex, potentially causing secondary pollution.
Special Adsorbent Adsorption Method:
The adsorption method uses special adsorbent materials to selectively adsorb specific pollutants in the wastewater, reducing their concentration and purifying the wastewater. After saturation, the adsorbent material is regenerated using a desorbent, allowing for reuse. This simple and direct wastewater treatment technology can remove anthraquinone and other organic matter from anthraquinone waste acid water, resulting in colorless effluent and enabling secondary recovery of sulfuric acid. The adsorption method has strong adsorption capacity, is easy to regenerate, has low operating costs, and is a mature technology, making it an effective method for treating pyridine wastewater.
Incineration Method:
The incineration method is straightforward, involving direct incineration or incineration after concentration, with the need to treat the flue gas. Many enterprises use this method to treat anthraquinone waste acid water. However, the high cost of incineration charged by local solid waste treatment centers, typically around thousands of yuan per ton, makes it unsustainable and economically unviable for enterprises.
Among the above methods, the activated carbon adsorption method is technically mature for industrial applications but too costly and unable to recycle valuable components. The oxidation method is effective but cannot completely oxidize and decompose organic matter and may cause secondary pollution. The high cost of incineration also makes it an unsustainable wastewater treatment method. The adsorption method efficiently removes anthraquinone and other organic matter from wastewater, making it an economical and effective solution for treating anthraquinone waste acid water.
2. Industry Customer Needs:
Anthraquinone waste acid water is complex, containing a large amount of benzene ring compounds and having a high color intensity, necessitating treatment before discharge. Current treatment methods cannot achieve both decolorization and recovery of valuable components, making the optimization of treatment effectiveness and economic cost a development direction for anthraquinone waste acid water treatment.
Customers producing anthraquinone waste acid water have the following needs:
Efficient and stable removal of colored substances from wastewater, with the possibility of secondary recovery of sulfuric acid.
Low initial investment, low operating costs, and easy operation and maintenance of equipment.
Advanced, reliable technology with no secondary pollution.
3. Haipu’s Customized Process Overview:
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd., located in Suzhou Industrial Park, is a national high-tech enterprise specializing in special adsorbents and catalysts, providing supporting application process development, technical services, and engineering implementation to solve related environmental problems for customers. Haipu’s technical team won the Suzhou Industrial Park Leading Talent Award in 2013 and 2015, the Gusu Leading Talent Award in 2015, and was recognized as a national high-tech enterprise in 2015 and 2018. In 2018, it was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalysis Functional Nanomaterials Engineering Technology Research Center. Haipu has leading technical expertise in adsorption material treatment, with efficient and stable supporting adsorption treatment processes, solving multiple environmental problems for leading domestic enterprises.
Haipu’s adsorption process uses special adsorbent materials developed by the company to selectively adsorb target components or substances. When the adsorbent is saturated, it is regenerated using a specific desorbent, allowing for continuous recycling. The conventional process flow for wastewater treatment using adsorption is shown in Figure 4-1.
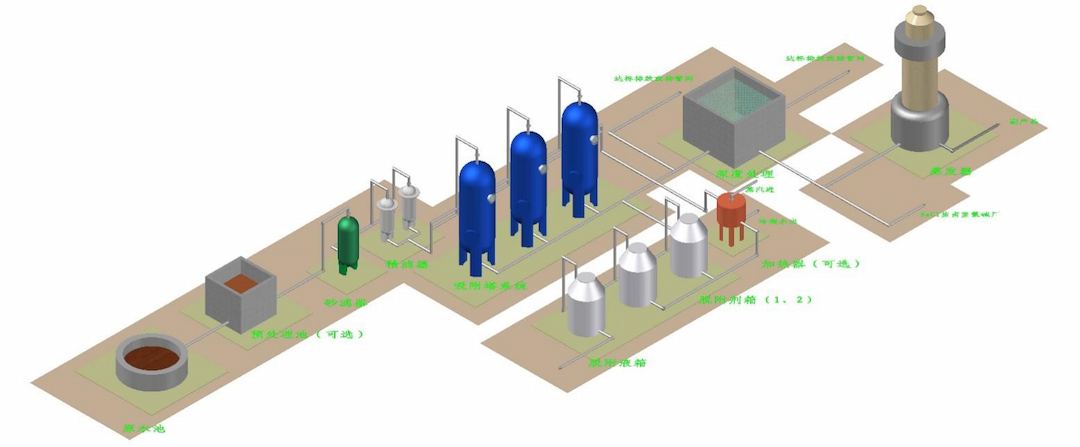
Conventional Process Flow for Wastewater Treatment Using Adsorption
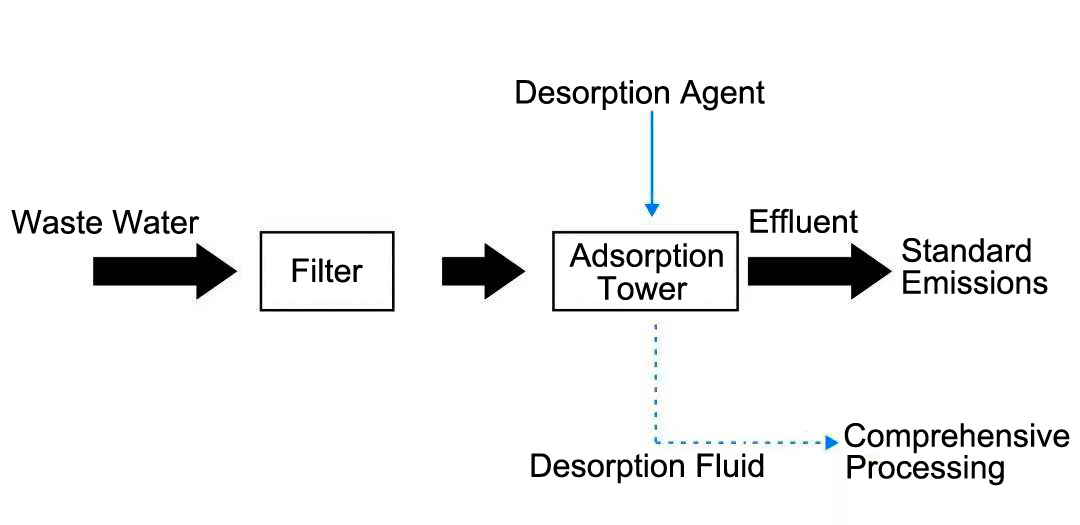
When using Haipu’s adsorption process to treat anthraquinone waste acid water, the wastewater is pre-filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, then enters the adsorption tower. The special adsorbent materials in the adsorption tower adsorb anthraquinone and other colored substances from the wastewater, achieving decolorization. After saturation, the adsorbent is regenerated using a specific desorbent, allowing for continuous recycling. The treated effluent is almost pure sulfuric acid water, suitable for secondary reuse. The process flow is shown in Figure 4-2.
Considering the variability of anthraquinone waste acid water and the need for continuous operation, ensuring stable treatment effectiveness, the industrial adsorption solution requires three adsorption towers in a two-series-one-desorption configuration. Two towers operate in series for adsorption, while one tower undergoes desorption. The front tower undergoes desorption, and the desorbed tower is connected in series for subsequent adsorption. The three towers cycle through different operational states via pipeline valve switching, ensuring each tower alternates between desorption, front tower, and rear tower roles. The process is illustrated in Figure 4-3, with each adsorption tower rotating roles according to the arrow sequence during different operational periods.
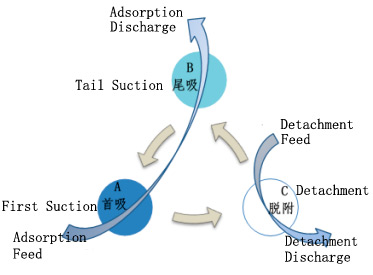
Diagram of the Operation Process of Series Adsorption (2 Adsorption and 1 Desorption)
Process Treatment Effectiveness:
Using the adsorption process to treat anthraquinone waste acid water effectively removes colored substances. Specific treatment data are shown in the table below:
Wastewater Adsorption Decolorization Data
| Raw Water Color | Water Color |
| Oxblood Red | Transparent and Colorless |
| Oxblood Red | Transparent and Colorless |
| Oxblood Red | Transparent and Colorless |
The enterprise requires the treated waste acid water to be colorless. Experimental results show that the adsorption treatment achieves a high removal rate of colored substances, resulting in transparent, colorless effluent, meeting customer requirements. The treatment effectiveness is shown in the image below.
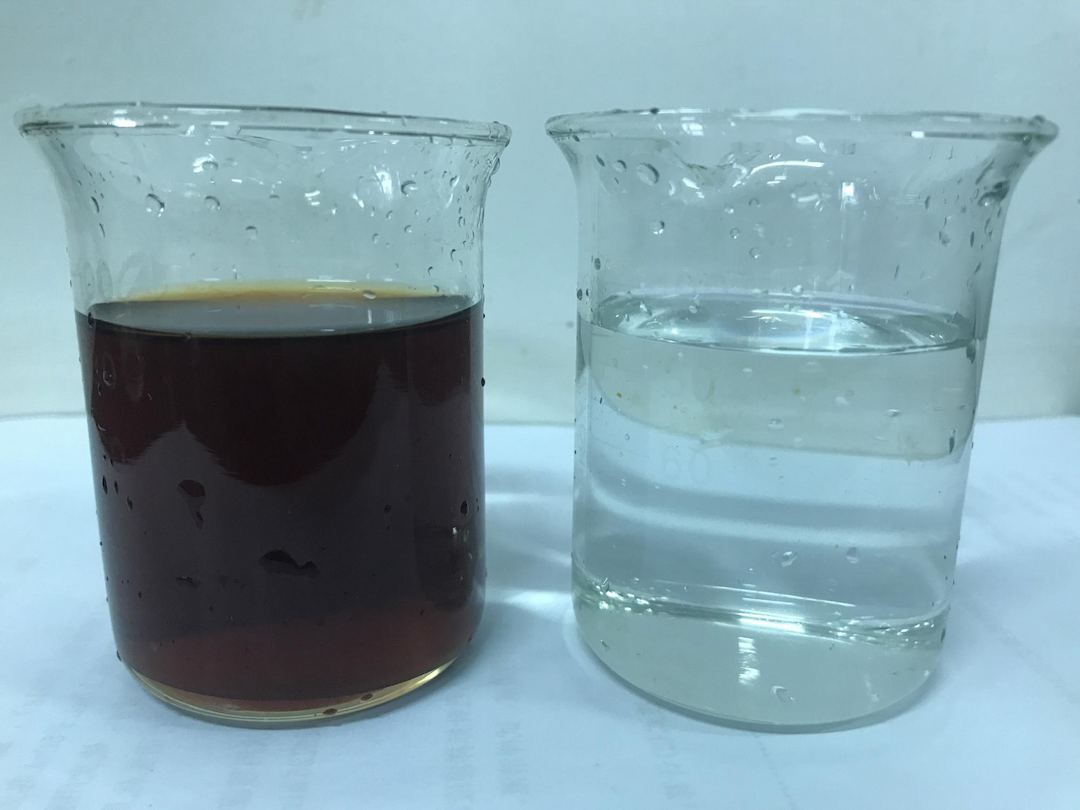

Appearance of Raw Water (Left) and Adsorption Effluent (Right)
The enterprise requires the recovery of sulfuric acid from the wastewater. Experimental results show that the adsorption treatment removes over 99% of anthraquinone and colored substances, resulting in transparent, colorless effluent, which is almost pure sulfuric acid water, suitable for secondary reuse in production, improving resource utilization and reducing production costs.
4. Core Advantages of the Process:
Current methods for treating anthraquinone waste acid water have various drawbacks in terms of treatment effectiveness and operational costs. The special adsorbent adsorption method efficiently removes colored substances from wastewater, ensuring transparent, colorless effluent that meets enterprise requirements. The advantages of the adsorption method include:
Efficient removal of colored substances and recovery of sulfuric acid from wastewater.
Significantly reduced wastewater treatment costs, with adsorption treatment costs generally between 15-25 yuan/ton, much lower than incineration costs.
Experimental design of the adsorption process based on theoretical and scientific principles, ensuring 100% compatibility between wastewater and process.
Space-saving equipment with a compact structure, low civil engineering and equipment investment; high reagent utilization rate with multiple reuse of desorbents, resulting in low operating costs.
Modular component design, allowing flexible adjustment based on production capacity and easy installation.
Advanced, mature technology with no secondary pollution, supported by strong technical expertise and extensive engineering application experience.
Economic Benefits of the Adsorption Method for Anthraquinone Waste Acid Water Decolorization:
According to our company’s design for the anthraquinone waste acid water treatment project, using the adsorption method to remove colored substances from anthraquinone waste acid water, with a treatment scale of 110 tons/day, the annual wastewater treatment cost is 6.2075 million yuan. Additionally, 100 tons of 30% sulfuric acid can be recovered daily, making the investment cost much lower than 6.2075 million yuan.
If the wastewater is not treated with special adsorbents to remove anthraquinone and colored substances, the incineration cost is +800 yuan/ton. With a daily treatment capacity of 110 tons and an annual operation time of 330 days, the annual operating cost is 29.04 million yuan. Comparing the costs of the two wastewater treatment methods, our company’s adsorption process can save enterprises over 22.8325 million yuan annually, with the savings in treatment costs far exceeding the investment cost of the entire wastewater treatment system within one year.




 CN
CN






