1 What are VOCs
The definition of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) varies among countries, with the United States defining it as any organic compound that can participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions. In China, VOCs refer to organic compounds with a saturated vapor pressure greater than 70Pa at room temperature and a boiling point below 260 ℃ at atmospheric pressure. VOC waste gas treatment includes various organic compounds, usually referring to organic compounds that are easily volatile at room temperature and pressure, such as benzene, toluene, xylene, acetone, styrene, etc. VOCs mainly come from petrochemicals, electronic manufacturing, and automobile exhaust. Some VOCs have strong toxicity or carcinogenicity, posing a serious threat to human life and health. At present, VOCs are increasingly becoming an important component of air pollution, causing significant damage to the environment. Next, we will introduce the VOCs waste gas treatment method - adsorption method
2 Adsorption method for removing VOCs
There are various methods for removing VOCs, and adsorption has the advantages of high efficiency, low energy consumption, simple operation, and recyclability, making it the most effective technology for removing VOCs.
2.1 Adsorption mechanism
The forces exerted on molecules within a substance are symmetrical, therefore they are in equilibrium with each other. But the force field of molecules at the interface is unsaturated, and the surface of liquid or solid substances can adsorb these molecules at the interface. The process and phenomenon of one or several substances accumulating on the surface of another substance is called adsorption. The fundamental reason for adsorption is the mutual attraction between the molecules inside the substance and the surrounding molecules.
2.2 Adsorbents
The key to VOCs adsorption technology is the adsorbent, and the ideal adsorbent should usually have the advantages of large specific surface area, suitable surface structure, easy regeneration, and low cost. Adsorbents can generally be divided into two categories: inorganic and organic adsorbents, with inorganic adsorbents being more common in practical applications. Usually, VOCs adsorbents mainly include the following categories: activated carbon, molecular sieves, clay, metal organic framework materials, and organic adsorbents.
2.2.1. Activated carbon
Activated carbon is the most widely used type of adsorbent, with loose and porous properties, high specific surface area, and large pore volume. It has strong adsorption capacity for VOCs, especially for large molecule VOCs such as benzene derivatives, but poor adsorption performance for small molecules such as formaldehyde.
The surface functional group structure of activated carbon has a significant impact on its adsorption performance. The surface acidity, alkalinity, and pore structure of activated carbon are often adjusted by adjusting the types and quantities of functional groups such as nitrogen and oxygen on its surface, in order to improve its ability to adsorb VOCs.
2.2.2 Molecular Sieve
Molecular sieve is one of the excellent VOCs adsorbents, with a large specific surface area and micropore volume, and strong adsorption ability for polar molecules such as water. Currently, commonly used adsorbents include NaY, H β, ZSM-5, SBA-15, MCM-41, etc. Generally speaking. Molecular sieve materials have been widely used for the adsorption of VOCs. Different types of molecular sieves have different adsorption effects on VOCs, which requires chemical modification and modification of molecular sieves to improve their removal efficiency for VOCs.
2.2.3 Clay
Clay is widely used due to its large specific surface area, pore structure, and low cost. Clay minerals with relatively large specific surface areas such as sepiolite and palygorskite can be directly applied for gas adsorption. Bentonite is a clay mineral mainly composed of montmorillonite, with a large specific surface area and cation exchange capacity. The adsorption performance of organic pollutants by surface active modified organic bentonite is significantly improved, and organic bentonite prepared by different surface active agents has selectivity for adsorbates.
2.3.4. Metal organic framework materials
Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) are a new type of material developed in the past decade. Due to its high specific surface area and stable chemical properties, its application in the adsorption of harmful organic gases in the environment has been widely studied by researchers. The materials that have been extensively studied for the adsorption of VOCs by MOFs include MOF-5, MIL-101, and MOF-177.
2.3.5 Organic adsorbents
Organic adsorbents mainly refer to high polymer adsorption resins. Polymer adsorption resin refers to a type of porous, highly cross-linked polymer that is characterized by adsorption and has the ability to concentrate and separate organic matter. Adsorption resins are mainly divided into gel type and macroporous type. Macroporous adsorption resins are widely used at present. With the emergence of macroporous ion exchange resins, macroporous adsorption resins have been developed. Adsorption resin is very similar to activated carbon in terms of adsorption performance, and most of them can be quantitatively adsorbed and reused. Although activated carbon has good adsorption performance, regeneration is often difficult. There are currently over 200 brands of adsorption resin products, and they are constantly increasing. According to the surface properties of resins, adsorption resins are generally divided into four categories: non-polar, medium polar, polar, and strongly polar.
2.3.6 Haipu Organic Waste Gas Treatment Solution
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise dedicated to the research and development of high-performance adsorbents, catalysts, and their process applications. With a series of independently developed high-performance adsorbents and catalysts as the core, combined with independently developed process technology, Haipu has become a professional solution provider in the fields of environmental governance and resource recycling. At the same time, taking it as our responsibility to help industrial enterprises meet environmental standards and achieve sustainable development through resource utilization, we adopt modular lean production and develop engineering solutions based on research and development data.
According to the "Technical Specification for Industrial Organic Waste Gas Treatment by Adsorption Method", the process of adsorption regeneration recovery can be used for recyclable organic waste gas, and the process of adsorption concentration combustion can be used for non recyclable organic waste gas. Based on the characteristics of these organic waste gases, a series of special adsorption materials and application processes have been developed to achieve effective treatment and resource recovery of various VOCs.
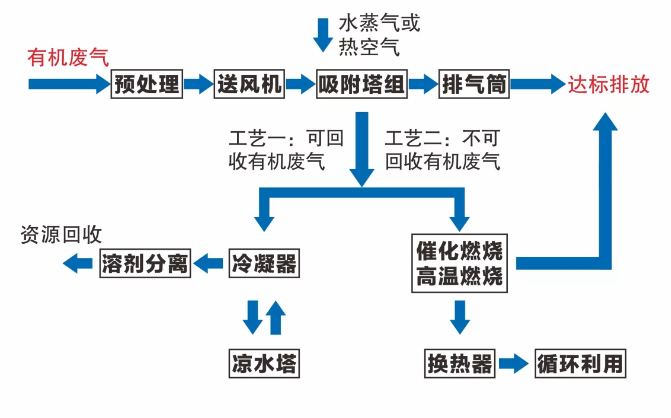
Figure 1 Process flow of organic waste gas treatment
The technological advantage lies in: 1. It can flexibly combine relevant processes according to the characteristics and treatment requirements of different organic waste gases, achieving efficient resource utilization and treatment of waste gases; 2. The adsorbent material has a high specific surface area, large adsorption capacity, high mechanical strength, and can be repeatedly regenerated and used.
The solution is applied to the treatment and recovery of volatile organic gases generated in chemical plants, electronics plants, printing plants, spray painting workshops, coating plants, etc. For example, in the treatment of exhaust gas generated by a pharmaceutical plant using dichloromethane as a solvent, the exhaust gas emission is 500 cubic meters per hour, and the dichloromethane content is about 90%. After treatment, the effective recovery of dichloromethane exhaust gas is achieved, providing protection for subsequent RTO systems; The recovery efficiency of dichloromethane reaches 95%, and the annual value of recovered resources is about 500000 yuan.
3 Conclusion
The harm of VOCs to the environment and the threat to human health have attracted widespread attention from the public, and their governance is urgent. In the technology of VOCs pollution control, adsorption is one of the effective and economical technologies, and adsorbents are the key to treating VOCs pollution. However, current adsorbents still have disadvantages such as low adsorption efficiency at high temperatures and inhibition of VOCs adsorption at high humidity. Therefore, further improving the adsorption capacity and efficiency of existing adsorption materials through surface modification, adjusting pore structure, and composite of various materials to develop more efficient and green adsorption materials is the future research direction.




 CN
CN



