In recent years, China's rapid socio-economic development has generated a huge demand for mineral resources. China has included ammonia nitrogen in the binding control indicators for environmental pollutants during the 12th Five Year Plan period, and has formulated stricter standards for the discharge of wastewater from the smelting industry. The direct discharge standard for ammonia nitrogen in wastewater from the lead and zinc industry needs to be controlled below 8mg/L. So, how to choose efficient and economical methods to handle it? Below, Haipu will provide a detailed introduction to the characteristics and treatment methods of ammonia nitrogen wastewater, hoping to be helpful to you.
Current situation of ammonia nitrogen wastewater:
At present, the main methods for treating industrial ammonia nitrogen wastewater include physical and chemical methods and biological methods. Among them, commonly used methods such as blow off, adsorption, membrane technology, chemical precipitation, and chemical oxidation belong to physical and chemical methods. Biological methods can be divided into traditional nitrification denitrification methods, new short-range nitrification denitrification methods, simultaneous nitrification denitrification methods, anaerobic ammonia oxidation methods, etc.
However, due to differences in water quality indicators and limitations in process conditions, there are significant differences in the treatment techniques used for different types of wastewater. For example, in the treatment of high concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater, methods such as blow off biological method, blow off breakpoint chlorination method, chemical precipitation biological method, etc. are often used. In the treatment of low concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater, adsorption and biological methods are often used to consider cost and benefit issues. We will analyze and summarize different treatment technologies and their effects on wastewater containing ammonia nitrogen, providing reference.
High concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater treatment technology refers to wastewater with a mass concentration of ammonia nitrogen greater than 500mg/L. With the development of industries such as petroleum, chemical, metallurgical, food, and pharmaceutical, as well as the continuous improvement of people's living standards, the content of ammonia nitrogen in industrial wastewater and urban domestic sewage has sharply increased, showing the characteristics of multiple sources of ammonia nitrogen pollution, large emissions, and increased concentration of emissions. At present, the treatment technologies for high ammonia nitrogen wastewater mainly use methods such as blow off and chemical precipitation.
Blow off method: The process of treating wastewater by introducing air into the wastewater to transfer dissolved gases and volatile solutes from the liquid phase to the gas phase. Adjust the pH of ammonia nitrogen wastewater to alkaline. At this point, ammonium ions are converted into ammonia molecules, and then gas is introduced into the water to fully contact the liquid. Dissolved gases and volatile ammonia molecules in the wastewater pass through the gas-liquid interface and enter the gas phase, thereby achieving the goal of removing ammonia nitrogen.
Although the efficiency of air stripping method is lower than that of steam method, it has low energy consumption, simple equipment, and convenient operation. When the total amount of ammonia nitrogen is not high, using air stripping method is more economical. At the same time, sulfuric acid can be used as an absorbent to absorb the stripped ammonia nitrogen, and the generated ammonium sulfate can be made into fertilizer. However, in the large-scale production process of ammonia stripping tower, the generation of scale is a challenging issue. Installing a sprinkler system can effectively solve the problem of soft scale, but it cannot eliminate hard scale even with sprinkler devices. In addition, the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen is low at low temperatures, and the blown off gas forms secondary pollution. Although the blow off method can remove most of the ammonia nitrogen, the ammonia nitrogen in the treated wastewater still exceeds 100mg/L and cannot be directly discharged, requiring further deep treatment.
Chemical precipitation method (magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitation method):
It is also a method of adding reagents containing Mg2+and PO43- to ammonia nitrogen wastewater to precipitate ammonia nitrogen and phosphorus in the form of guano stone (magnesium ammonium phosphate), while recovering nitrogen and phosphorus from the wastewater.
Its process design operation is relatively simple, the reaction is stable, it is less affected by external environment, has strong impact resistance, high denitrification rate and obvious effect. The generated magnesium ammonium phosphate can be used as inorganic compound fertilizer, thus solving the problems of nitrogen recovery and secondary pollution, and has good economic and environmental benefits. The ammonium magnesium phosphate precipitation method is suitable for treating industrial wastewater with high ammonia nitrogen concentration. The suitable conditions for treating ammonia nitrogen wastewater by the ammonium magnesium phosphate precipitation method are: pH of about 9.0, n (P): n (N): n (Mg) ratio of about 1:1:1.2, and the denitrification rate of the ammonium magnesium phosphate precipitation method can be maintained at a high level, generally reaching over 90%.
Low concentration ammonia nitrogen industrial wastewater treatment technology:
Due to technical and processing cost reasons, many enterprises only perform deep treatment on COD when discharging wastewater, often neglecting the treatment of low concentration ammonia nitrogen. There are two main types of ammonia nitrogen in wastewater, one is ammonia nitrogen formed from ammonia water, and the other is ammonia nitrogen formed from inorganic ammonia, mainly ammonium sulfate, ammonium chloride, etc.
Ammonia nitrogen is one of the important factors causing eutrophication of water bodies. When recycling and reusing such wastewater, it can also corrode metals in pipelines, shorten the lifespan of equipment and pipelines, and increase maintenance costs. At present, the technologies commonly used in industry to treat low concentration ammonia nitrogen mainly include adsorption method, breakpoint chlorination method, biological method, membrane technology, etc.
Adsorption method: Adsorption is the process in which the concentration of one or several substances (called adsorbates) automatically changes on the surface of another substance (called adsorbent), and its essence is a mass transfer phenomenon from the liquid or gas phase to the solid surface.
Adsorption method is one of the promising methods for treating low concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater. Adsorption method often uses porous solids as adsorbents, and ion exchange adsorption is ideal for treating low concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater. It belongs to a type of exchange adsorption method, which uses the exchangeable ions on the adsorbent to exchange with NH4+in the wastewater and adsorb NH3 molecules to remove ammonia from the water. It is a reversible process, and the concentration difference between ions and the affinity of the adsorbent for ions provide the driving force for the adsorption process.
Generally only applicable to low concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater, while for high concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater, the use of adsorption method may cause operational difficulties due to frequent replacement of adsorbents, so it is necessary to combine other processes to complete the denitrification process in synergy.
Fold point chlorination method:
The breakpoint chlorination method is a commonly used denitrification process in sewage treatment engineering. Its principle is to introduce chlorine gas into ammonia nitrogen wastewater to reach a critical point, which is a chemical process that oxidizes ammonia nitrogen into nitrogen gas. Its processing efficiency is high and the effect is stable, with a removal rate of up to 100%; This method is not affected by salt content, is not affected by water temperature, and is easy to operate. The lower the organic matter content, the better the ammonia nitrogen treatment effect. It does not produce precipitation, requires less initial investment, and has a rapid reaction, fully capable of sterilizing and disinfecting water bodies.
But the breakpoint chlorination method is only suitable for the treatment of low concentration wastewater, so it is mostly used for the deep treatment of ammonia nitrogen wastewater. The disadvantages of this method are: high consumption of liquid chlorine, high cost, and high safety requirements for storage and use of liquid chlorine. The by-products of the reaction, chloramine and chlorinated organic compounds, can cause secondary pollution to the environment.
Biological Law:
Ammonia nitrogen in wastewater is removed through a series of reactions such as nitrification and denitrification under the action of various microorganisms, ultimately generating nitrogen gas. For highly biodegradable wastewater (BOD/COD>0.3), ammonia nitrogen can be removed by biological methods.
When using biological methods to treat wastewater containing ammonia nitrogen, the relative concentration of organic carbon is the main factor to consider.
The biological method has the advantages of simple operation, stable effect, no secondary pollution, and economy. However, its disadvantages include a large footprint, treatment efficiency that is easily affected by temperature and toxic substances, and high requirements for operation and management. At the same time, the inhibitory effects of certain substances on microbial activity and reproduction should be considered in industrial applications. In addition, high concentrations of ammonia nitrogen have an inhibitory effect on the biological nitrification process. Therefore, when the initial mass concentration of ammonia nitrogen wastewater is less than 300mg/L, the use of biological methods has a better effect.
Short range nitrification denitrification technology of new biological denitrification technology:
Compared with traditional biological denitrification, short-range nitrification denitrification has the following advantages: for activated sludge process, it can save 25% of oxygen supply, reduce energy consumption, save carbon sources, improve total nitrogen removal rate under certain conditions, increase reaction rate, shorten reaction time, and reduce reactor volume. However, due to the close relationship between nitrifying bacteria and nitrifying bacteria, changes in each influencing factor simultaneously affect both types of bacteria, and there is also a mutual influence between various factors, which makes it difficult to control the conditions of short-range nitrification and denitrification.
Anaerobic ammonia oxidation technology: Anaerobic ammonia oxidation refers to the process in which microorganisms use NH4+as an electron acceptor and NO2- or NO3- as an electron donor to convert NH4+, NO2-, or NO3- into N2 under anaerobic or anaerobic conditions.
Anaerobic ammonia oxidation technology can significantly reduce the oxygenation energy consumption of nitrification reactions, eliminate the need for external electron donors in denitrification reactions, save the neutralizing reagents required in traditional nitrification denitrification processes, and produce less sludge. But so far, the reaction mechanism, participating strains, and various operating parameters are not clear.
Reverse osmosis technology of membrane technology: Reverse osmosis technology is a technology that separates solutes from solvents by using the selective retention effect of semi permeable membranes on solutes under pressure higher than the osmotic pressure of the solution. It has the advantages of low energy consumption, no pollution, advanced process, and easy operation and maintenance.
In the process of using reverse osmosis technology to treat ammonia nitrogen wastewater, the equipment provides sufficient pressure, and the water is separated through a selective membrane, which can be used as industrial pure water. The concentration of ammonia nitrogen solution on the other side of the membrane increases accordingly, becoming a concentrated solution that can be reprocessed and utilized again. In practical operation, the applied reverse osmosis pressure is directly proportional to the concentration of the solution. As the concentration of ammonia nitrogen increases, the energy consumption required for the reverse osmosis device increases, while the efficiency decreases.
Electrodialysis method: It is the process of separating ions from an electrolyte solution by utilizing the selective permeability of an ion exchange membrane under the action of an external direct current electric field. Electrodialysis can efficiently separate ammonia nitrogen from wastewater, with low initial investment, low energy and chemical consumption, simple operation, high water utilization rate, and no secondary pollution by-products.
Industry customer demand: The composition of ammonia nitrogen wastewater is complex and cannot be directly discharged, therefore pre-treatment of the wastewater is necessary. Wastewater treatment should include the following three points:
1. Efficiently and stably removing ammonia nitrogen from wastewater, the treated effluent can meet discharge standards without causing water pollution.
2. Low investment cost, low operating cost, and convenient equipment operation and maintenance.
3. Advanced and reliable technology, with no secondary pollution.
Introduction to Haipu customized process:
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in Suzhou Industrial Park. It is a national high-tech enterprise that uses special adsorbents and catalysts as its core technology, supporting the development of application processes, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to solve related environmental problems for customers. Haipu's technical team won the Suzhou Industrial Park Leading Talent Award in 2013 and 2015, and the Gusu Leading Talent Award in 2015. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. was rated as a national high-tech enterprise twice in 2015 and 2018, and was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalytic Functional Nanomaterial Engineering Technology Research Center in 2018. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has a leading technological level in the treatment of adsorption materials. The supporting adsorption treatment process is efficient and stable, and has solved multiple environmental problems for many leading domestic enterprises in the industry.
The principle of the Haipu adsorption process is to use the special adsorption materials developed by our company to selectively adsorb the components or substances to be removed. When the adsorption is saturated, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to be regenerated. This process is continuously repeated. The conventional process of treating wastewater by adsorption method is shown in the following figure.
Conventional process diagram for adsorption treatment of wastewater
When using Haipu's adsorption process to treat ammonia nitrogen wastewater, the wastewater is pre filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, and then enters the adsorption tower for adsorption. The special adsorption material filled in the adsorption tower can adsorb ammonia nitrogen in the wastewater on the surface of the material, achieving the removal of ammonia nitrogen from the water body. After adsorption saturation, use a desorption agent to desorb, and the process flow of ammonia nitrogen wastewater adsorption treatment is shown in the following figure.
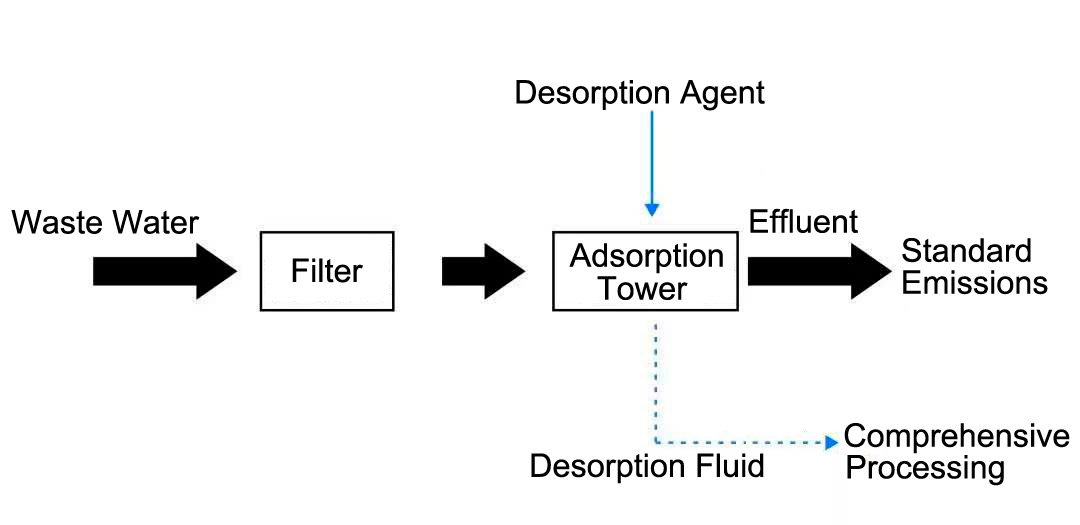
Process flow of ammonia nitrogen wastewater adsorption treatment
Process treatment effect:
The use of adsorption technology to treat ammonia nitrogen wastewater can effectively remove ammonia nitrogen from the wastewater, as shown in the following figure:
Wastewater adsorption and removal of ammonia nitrogen data
| Raw Water Ammonia Nitrogen Content | Treated Water Ammonia Nitrogen Content | Removal Rate |
| 112.1 mg/L | 7.2 mg/L | 93.58% |
| 112.1 mg/L | 7.8 mg/L | 93.76% |
| 112.1 mg/L | 7.8 mg/L | 93.76% |
The enterprise requires that the ammonia nitrogen content in the treated wastewater be less than 20mg/L. Experimental treatment results show that adsorption treatment can stabilize the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen in the wastewater at over 90%, and the ammonia nitrogen content in the effluent can be controlled below 10mg/L. While ensuring compliance with customer requirements, a certain safety margin can be left to effectively prevent water quality fluctuations in the incoming wastewater from causing the effluent to fail to meet standards. The treatment effect is shown in the following figure.

Core advantages of craftsmanship:
At present, the treatment methods for high concentration ammonia nitrogen in industrial wastewater mainly use physical and chemical methods for pretreatment, and other methods for subsequent treatment. Although good treatment effects can be achieved, there are still problems of scaling and secondary pollution.
In addition, high concentrations of ammonia nitrogen have inhibitory effects on the biological nitrification process. The use of adsorption method to treat ammonia nitrogen wastewater can efficiently remove ammonia nitrogen from the wastewater, ensuring that the treated wastewater content is below 20mg/L to meet the requirements of enterprises and reduce the pressure of subsequent wastewater treatment. The advantages of adsorption method include:
1. Efficiently remove ammonia nitrogen from wastewater, strictly control the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the treated wastewater, and keep the content below 20mg/L.
2. Greatly reducing the cost of wastewater treatment for enterprises, the treatment cost of adsorption method is generally 100-200 yuan/ton.
3. Conduct experiments on the sampling samples of waste acid generated on the enterprise site, based on technology, and design adsorption processes based on experiments. The matching degree between wastewater and processes is 100%.
4. The equipment occupies less land, has a compact structure, and requires less investment in civil engineering and equipment; The desorption agent is applied multiple times and concentrated step by step, resulting in high drug utilization and low operating costs.
5. It can be implemented in module component form, flexibly adjusted according to production capacity, and easy to install.
6. Advanced and mature technology, no secondary pollution, strong technical support, and rich engineering application experience.




 CN
CN





