Pyridine compounds are high value-added fine chemical products. At present, most enterprises in China usually adopt a simple pretreatment+biochemical treatment method for pyridine containing wastewater. Biochemical technology is relatively mature and the treatment cost is low. However, due to the high toxicity of wastewater and the presence of many organic compounds that are difficult to biodegrade, it is often difficult to achieve ideal results in wastewater treatment. It is necessary to strengthen the pretreatment of pyridine containing wastewater, thoroughly degrading or converting highly toxic and difficult to biodegrade pollutants into easily degradable substances during the pretreatment stage, and then subjecting them to biochemical treatment to achieve the desired treatment effect. Below, Haipu will provide a detailed introduction to the characteristics and treatment methods of pyridine wastewater, hoping to be helpful to you.
Current situation and dilemma of pyridine wastewater
Pyridine is an important industrial raw material widely used in chemical, pharmaceutical, wood preservation, printing and dyeing, pesticide production, and other industries. It is also an environmental pollutant that can cause cancer, deformity, and mutation. Pyridine wastewater has complex water quality and contains a large amount of heterocyclic non biodegradable substances. It has the characteristics of high COD concentration, high organic nitrogen content, and high toxicity. Conventional water treatment techniques are difficult to treat and have become a challenge in industrial wastewater treatment.
In recent years, the country has attached increasing importance to ecological environment protection, and the standards for wastewater discharge and the total control of regional wastewater discharge have become increasingly strict. In order to ensure the sustainable development of industries related to the application of pyridine, new ideas have emerged for the treatment of pyridine containing wastewater. In recent years, the main methods for treating pyridine wastewater include photocatalytic oxidation, Fenton oxidation, adsorption, microelectrolysis, incineration, etc.
Photocatalytic oxidation method:
The photocatalytic oxidation method usually uses ultraviolet lamps to generate a certain wavelength range of ultraviolet light to catalyze the degradation of organic matter in water, and accelerates the photochemical reaction through the participation of catalyst (TiO2). The photocatalytic method can form hydroxyl radicals on the surface of specific materials, and highly oxidizing hydroxyl radicals can oxidize and decompose organic matter in wastewater, generating harmless carbon dioxide and water.
The method has certain limitations, mainly manifested in the high cost of catalysts, low catalytic efficiency and stability, and low light conduction efficiency in high concentration wastewater. Moreover, sometimes the rate of complete oxidation of organic matter is relatively slow, and it is still in the early exploration stage.
Fenton oxidation method:
The Fenton oxidation method involves adding H2O2 and Fe2+catalyst to wastewater to form an oxidation system, which generates highly oxidative hydroxyl radicals. These radicals react with recalcitrant organic compounds in aqueous solution to break down their structure and undergo oxidative decomposition, effectively removing recalcitrant organic compounds that cannot be removed by traditional wastewater treatment techniques. For wastewater containing pyridine, the Fenton oxidation method can only break the chemical bonds between multiple pyridine rings, but cannot cause bond breaking within the pyridine rings, resulting in incomplete decomposition of organic matter in the wastewater. The Fenton oxidation method does not require high temperature and pressure, has a fast speed, mild reaction conditions, and relatively simple equipment. However, this method also has some drawbacks:
The high consumption of H2O2 in the treatment of high concentration pollutants results in higher wastewater treatment costs.
The applicable pH range is small, and it must be carried out under conditions where the pH is below 3. The treated water still exhibits strong acidity.
Conventional Fenton reagents belong to homogeneous catalytic systems, and the effluent contains a large amount of iron ions, which require subsequent treatment to recover the catalyst. The recovery cost is high, the process is complex, and it is prone to secondary pollution.
Adsorption method:
By utilizing the special adsorption function of adsorbent materials, specific pollutants in wastewater can be adsorbed and recovered, thereby reducing the concentration of pollutants in wastewater. After adsorption saturation, the adsorbent material is desorbed using a desorption agent to regenerate the adsorbent material, which can be reused. Adsorption method is a very simple and direct wastewater treatment technology that can remove toxic pyridine and benzene from pyridine wastewater. The content of pyridine in the adsorbed water can reach the first level discharge standard of the "Wastewater Discharge Standards", improving the biodegradability of the wastewater. Adsorption method has strong adsorption capacity, easy regeneration, low operating cost, mature process technology, and has become an effective method for treating pyridine wastewater.
Iron carbon microelectrolysis method:
Micro electrolysis, also known as internal electrolysis, is a process in which a primary battery is formed between zero valent iron (Fe0) and carbon powder (C) due to a potential difference. Among them, iron acts as the anode, loses electrons, and is converted into Fe2+and Fe3+. On the other side, carbon acts as the cathode, where hydrogen ions undergo a reduction reaction and are converted into highly active [H]. This new ecology of [H] and Fe2+has strong reducibility and can perform addition and bond cleavage reactions on organic molecules, decomposing large molecules of difficult to degrade organic matter into small molecules of easily degradable organic matter, achieving the decomposition and oxidation of organic matter. Simultaneously, a coagulation reaction centered around Fe3+occurs, and the surface of Fe-C material can further promote the removal of pollutants through adsorption and electrophoresis. The iron carbon microelectrolysis method can effectively remove the chromaticity and suspended solids of mixed wastewater. After comprehensive treatment, various indicators of the wastewater have been greatly improved, reducing the cost and load of subsequent treatment. However, microelectrolysis cannot destroy the pyridine ring or further decompose pyridine chloride. The treatment effect of microelectrolysis on pyridine wastewater is limited, and the filler needs to be regularly updated, resulting in a large amount of waste filler solid slag and causing secondary pollution.
Burning method:
The incineration method is convenient and can be directly incinerated or concentrated before incineration. The flue gas must be treated, which is a method used by many enterprises to treat pyridine containing wastewater. At present, solid waste treatment centers in various regions charge high incineration costs for this type of wastewater, generally around thousands of yuan per ton of water. With the increasing environmental requirements, the cost of incinerating pyridine wastewater may also increase, which is difficult for enterprises to afford.
The industrial application technology of photocatalytic oxidation in the above-mentioned pyridine wastewater treatment methods is not mature, and the pyridine oxidation effect is not obvious. Incineration method is not a long-term and economical wastewater treatment method due to high commission costs. Adsorption method can efficiently remove pyridine and benzene from wastewater, making it an economical and effective method for treating pyridine wastewater.
Industry customer demand
The composition of pyridine wastewater is complex and contains a large amount of toxic and harmful substances, which cannot be directly subjected to biochemical treatment. Pre treatment of the wastewater is necessary, and various pyridine wastewater can be treated by combining traditional biochemical treatment techniques. Wastewater treatment needs to meet the following requirements:
1. Efficiently and stably removing toxic substances such as pyridine and benzene from wastewater, the treated effluent can enter the biochemical tank for biochemical treatment without affecting the activity of biochemical bacteria.
2. Low investment cost, low operating cost, and convenient equipment operation and maintenance.
3. Advanced and reliable technology, with no secondary pollution.
Introduction to Haipu customized process
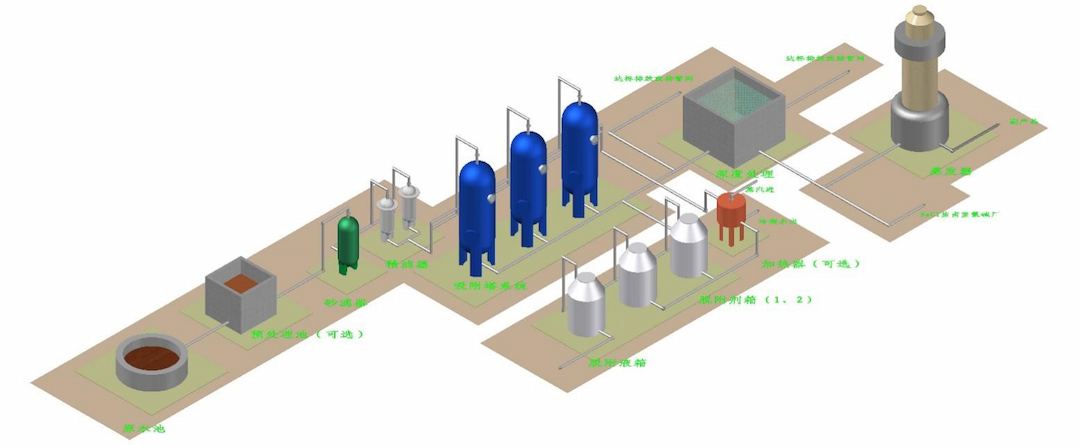
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in Suzhou Industrial Park. It is a national high-tech enterprise that uses special adsorbents and catalysts as its core technology, supporting the development of application processes, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to solve related environmental problems for customers. Haipu's technical team won the Suzhou Industrial Park Leading Talent Award in 2013 and 2015, and the Gusu Leading Talent Award in 2015. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. was rated as a national high-tech enterprise twice in 2015 and 2018, and was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalytic Functional Nanomaterial Engineering Technology Research Center in 2018. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has a leading technological level in the treatment of adsorption materials. The supporting adsorption treatment process is efficient and stable, and has solved multiple environmental problems for many leading domestic enterprises in the industry.
The principle of the Haipu adsorption process is to use the special adsorption materials developed by our company to selectively adsorb the components or substances to be removed. When the adsorption is saturated, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to be regenerated. This process is continuously repeated. The conventional process of treating wastewater by adsorption method is shown in the following figure.
Conventional process diagram for adsorption treatment of wastewater
When using Haipu's adsorption process to treat pyridine wastewater, the wastewater is pre filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, and then enters the adsorption tower for adsorption. The special adsorption material filled in the adsorption tower can adsorb pyridine and benzene in the wastewater on the surface of the material, achieving the removal of toxic and difficult to grow substances. After adsorption saturation, specific desorption agents are used to desorb the adsorbent material, allowing it to regenerate, and this process is continuously repeated. The adsorbed water is used to remove pyridine and benzene from wastewater, which can be directly treated in the biochemical system. The adsorption treatment process for pyridine containing wastewater is shown in the following figure.
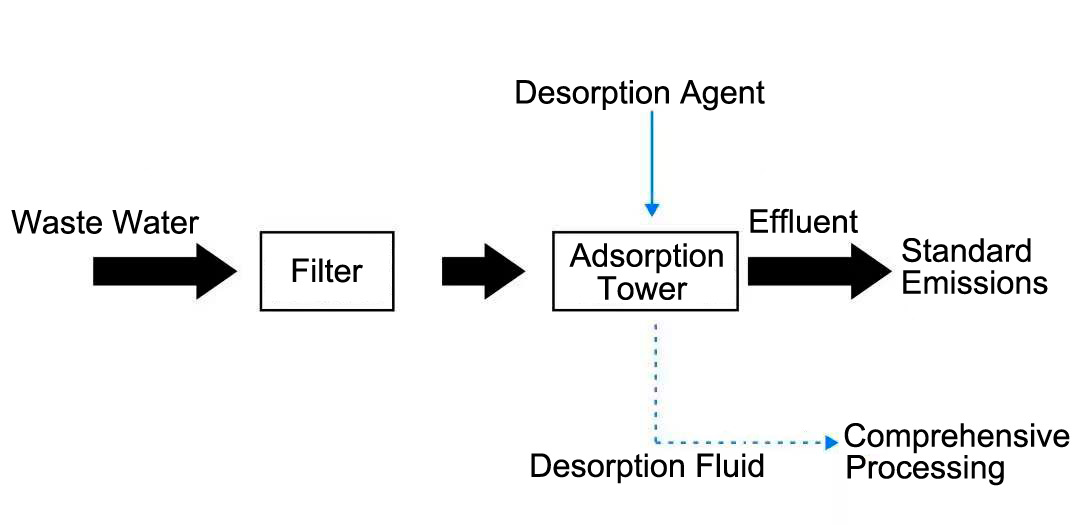
Process treatment effect: Adsorption process is used to treat pyridine containing wastewater, which can effectively remove pyridine and benzene from the wastewater
Data on pyridine removal by wastewater adsorption
| Pyridine content in raw water | Pyridine content in effluent | Removal rate |
| 656 mg/L | 0.68 mg/L | 99.90% |
| 656 mg/L | 0.59 mg/L | 99.91% |
| 656 mg/L | 0.81 mg/L | 99.88% |
The enterprise requires the pyridine content in the treated wastewater to be less than 2mg/L. Experimental treatment results show that using adsorption treatment, the pyridine removal rate in the wastewater is stable at over 99%, and the pyridine content in the effluent can be controlled below 1mg/L. While ensuring compliance with customer requirements, a certain safety margin is left to effectively prevent water quality fluctuations in the incoming wastewater from causing effluent to fail to meet standards. The treatment effect is shown in the following figure.

Appearance of raw water (left) and adsorbed effluent (right)
Data on the adsorption of pyridine and benzene from wastewater
| Name | COD | Pyridine class | Benzene class | Ammonia nitrogen |
| Absorb incoming water | 70000mg/L | 130mg/L | 600mg/L | 300mg/L |
| Adsorbed water | 2680mg/L | 1.6mg/L | 1.8mg/L | 25mg/L |
| Removal rate | 96.20% | 98.80% | 99.70% | 91.70% |
The pyridine wastewater generated during the production process of the enterprise contains pyridine, benzene, ammonia nitrogen, etc., with a COD of up to 35000mg/L. In order to meet the requirements of the subsequent treatment process, it is hoped to separate and remove most of the biochemical recalcitrant substances. The production wastewater of the enterprise requires a pyridine content of less than 2mg/L and benzene content of less than 2mg/L after treatment. The experimental results show that adsorption can remove the vast majority of pyridine and benzene from the wastewater, meeting the requirements of the enterprise. At the same time, it also has a high removal rate for COD and ammonia nitrogen in the wastewater, which reduces the pressure for the subsequent treatment of the enterprise's wastewater. The adsorption treatment effect diagram is shown below.

The left image shows raw water, and the right image shows adsorbed effluent
Core advantages of craftsmanship
At present, the treatment methods for pyridine wastewater have their own shortcomings in terms of treatment efficiency and operating costs. Many companies outsource the incineration treatment of pyridine wastewater, and at the current commission fee of 1000 yuan/ton, the treatment of wastewater is particularly high, which brings great pressure to the production of enterprises. Therefore, it is urgent to find a cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and efficient treatment method, which is also the focus of the current pyridine wastewater treatment industry.
Using adsorption method to treat pyridine wastewater can efficiently remove pyridine and benzene from the wastewater, ensuring that the pyridine and benzene content in the treated wastewater is below 2mg/L. Toxic and difficult to degrade substances in the wastewater are almost removed. Its advantages include:
(1) Efficiently remove pyridine and benzene from wastewater, while reducing COD and ammonia nitrogen content, with high removal efficiency. Strictly control the concentration of pyridine and benzene in the treated wastewater, with pyridine and benzene content below 2mg/L.
(2) Greatly reducing the cost of wastewater treatment for enterprises, the treatment cost of adsorption method is generally 100-200 yuan/ton, much lower than the cost of incineration treatment+1000 yuan/ton.
(3) Conduct experiments on the sampling samples of waste acid generated on the enterprise site, based on technology, and design adsorption processes based on experiments. The matching degree between wastewater and processes is 100%.
(4) The equipment occupies less land, has a compact structure, and requires less investment in civil engineering and equipment. The desorption agent is repeatedly applied and concentrated step by step, resulting in a high utilization rate of the agent and low operating costs.
(5) It can be implemented in module component form, flexibly adjusted according to production capacity, and easy to install.
(6) Advanced and mature technology, no secondary pollution, strong technical support, and rich engineering application experience.
Case Introduction: A 350t/d Pyridine Containing Wastewater Treatment Project of a Chemical Enterprise in Shandong Province:
The company uses our adsorption process to treat the pyridine wastewater generated during its production process. Experiments have shown that the pyridine content in the wastewater has decreased from the original 656mg/L to below 2mg/L. The removal rate of pyridine in the wastewater is over 99%. The treated pyridine content is particularly low and can be directly sent to the biochemical system for further treatment. The wastewater after biochemical treatment can achieve water reuse and reduce the amount of water consumed in production. The "adsorption method+biochemistry" treatment of pyridine wastewater has an annual treatment cost of 5.3856 million yuan, which can save enterprises~110 million yuan in treatment costs annually and has significant economic benefits.

On site application of adsorption tower
300t/d Pyridine containing Wastewater Treatment Project of a Chemical Enterprise in Anhui Province:
The production project generates~300t/d pyridine containing wastewater, which is treated by incineration at a cost of+1000 yuan/water. The annual production time is 330 days, and the annual wastewater treatment cost is as high as 99 million yuan. After using adsorption method for treatment, the pyridine content in the wastewater decreased from 130mg/L to 1.6mg/L, the benzene content decreased from 600mg/L to 1.8mg/L, and the COD content of the wastewater decreased from~55000mg/L to~4500mg/L. The adsorption effluent was treated by biochemical treatment, and the comprehensive treatment cost of "adsorption method+biochemical" wastewater treatment was about 10 million yuan/year, which can save the enterprise 89 million yuan in wastewater treatment costs in one year.




 CN
CN







