Keywords: special adsorbent material for wastewater treatment, decolorization
High chromaticity waste salt water has a wide range of sources. In various industrial production processes such as chemical, pharmaceutical, printing and dyeing, and papermaking, a large amount of wastewater is discharged. The water not only contains high concentrations of organic pollutants, but also a large amount of calcium, sodium, chlorine, and sulfate ions. These industrial waste salt water often contain deep and persistent colors. The salt after evaporation, concentration, and separation cannot be used as by-product salt due to its high chromaticity, nor can it be treated as conventional garbage. It can only be treated as hazardous waste, which increases the cost of wastewater treatment and causes waste of resources.
The commonly used decolorization methods for wastewater currently include activated carbon decolorization, clay adsorption decolorization, microelectrolysis decolorization, biochemical decolorization, coagulation decolorization, decolorization agent decolorization, etc.
(1) Activated carbon decolorization and clay adsorption decolorization
Activated carbon decolorization and clay adsorption decolorization rely on the adsorption effect of adsorbents to remove chromaticity, which is costly, requires a large amount, and has expensive adsorption regeneration costs. They are generally used for wastewater treatment or deep treatment with small amounts and low concentrations.
(2) Micro electrolysis decolorization
Micro electrolysis decolorization can effectively decolorize wastewater with a certain color, but when the color of the wastewater is higher than 200, it is difficult to achieve good decolorization effect, and sometimes it can even deepen the color of the wastewater.
(3) Biochemical decolorization
Biochemical decolorization is the use of microbial enzymes to oxidize or reduce colored molecules, breaking their unsaturated bonds and chromophores to achieve decolorization. At present, activated sludge, contact oxygen, and bio rotating discs are commonly used. But biochemical methods can only be used for low salinity wastewater, such as when the salt content of the wastewater is less than 8000mg/L, and cannot be used for high salinity wastewater.
(4) Coagulation decolorization
Coagulation decolorization is the process of using coagulants to precipitate color forming substances in wastewater for decolorization. Agglomeration decolorization technology is a widely used decolorization technology with low investment cost, small equipment footprint, and large processing capacity.
(5) Decolorizing agent decolorization
For high salt wastewater, the conventional method currently used is to wash the concentrated and separated salt with organic solvents, and achieve salt decolorization through the principle of similar compatibility. This can achieve the purpose of decolorization, but it will produce a large amount of organic products. These organic products also need to be separated and reused through distillation, which consumes a lot of energy and is not conducive to energy conservation and emission reduction, further increasing the investment and operating costs of enterprises. And currently, almost all difficult to remove chromaticities are caused by organic compounds, which are colored by the presence of one or several functional groups in these organic compounds. These chromaticities are extremely difficult to handle using conventional methods.
(6) Haipu Special Adsorption Technology
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is committed to the research and industrialization of high-performance adsorbents and catalysts. In 2018, it was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalytic Functional Nanomaterials Engineering Technology Research Center. Through years of independent research and development, it has significant advantages in ion exchange technology, adsorption technology, and nano inorganic material hybridization technology, achieving the serialization of adsorption and catalytic products and successfully applying them in the fields of environmental protection and resource recycling.
The basic principle of the Haipu special adsorption technology treatment process is to utilize the adsorption performance of special adsorption materials to adsorb and enrich organic matter in wastewater into the adsorption materials. The color of the adsorbed water is reduced, meeting the requirements of the effluent index, and the effluent evaporated salt is white. After adsorption saturation, the adsorbent material is subjected to desorption treatment to regenerate and resume adsorption, and this process is continuously repeated.
Technological process
The process flow is shown in the figure. The wastewater is first filtered to intercept suspended solids and fine particles, preventing impurities from entering the adsorbent material and affecting its adsorption performance. The filtered wastewater is then sent to an adsorption tower equipped with special adsorption materials for adsorption. After adsorption saturation, the adsorption materials are subjected to desorption and regeneration treatment. The regenerated adsorption materials can be reused, and the adsorbed water is sent to the subsequent evaporation system. The high concentration desorption solution is treated by the customer.
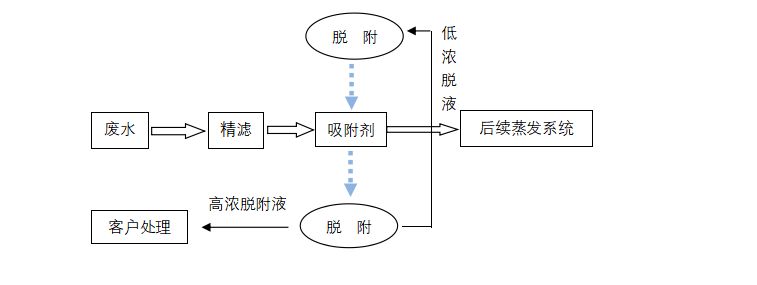
Figure 1 Process Flow Diagram
Scope of application
Decolorization of waste saltwater
Advantage
Solve the problem of wastewater decolorization, ensure sustainable development of enterprises, and have significant economic and environmental benefits;
Special adsorbent materials have high absorption capacity and high concentration ratio, low equipment investment, and low operating costs;
Automated control, easy operation, convenient maintenance, and long service life;
The subsequent steamed salt turns white and can be used as a byproduct to achieve resource recovery.
Adsorption processing data
Case 1 Adsorption of inlet and outlet water data
| Indicator | Chroma | Steamed salt |
| Absorb incoming water | Brown | Grey |
| Adsorbed water 1 | Canary yellow | White |
| Adsorbed water 2 | Canary yellow | White |
| Adsorbed water 3 | Canary yellow | White |

Figure 2-1 Appearance of raw water (left) and effluent (right)




 CN
CN




