Keywords: quartz sand purification, acid washing, special adsorption materials, wastewater reuse
With the development of industries such as fiber optic communication, microelectronics, and solar energy, the importance of high-purity quartz sand as an important raw material is becoming increasingly prominent. Impurities in quartz sand can significantly affect the performance of quartz products, among which transition metals such as iron can affect the light transmittance and conductivity of quartz products; Excessive content of alkali metal impurities such as potassium and sodium can reduce the high temperature resistance of quartz products, thereby affecting their thermal stability and optical properties. To obtain high-quality quartz sand, it is necessary to purify it. Acid washing is an essential step in the purification of quartz ore. By utilizing the characteristic that quartz is insoluble in acid and other impurity minerals can be dissolved by acid solution, the mineral processing and purification of quartz can be achieved. Commonly used acids include sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and hydrofluoric acid. However, although the removal rate of impurities in acid washed quartz sand is higher, improper treatment of the removed wastewater can have serious impacts on the environment, soil, and other factors. There are a large amount of H+and F - ions remaining in the pickling waste liquid. If discharged directly without treatment, it can easily cause serious consequences such as fluorine pollution, underground pipeline corrosion, and groundwater pollution.
Below are several common processes for treating quartz sand pickling waste liquid:
(1) Neutralization+precipitation process
The quartz acid pickling waste liquid enters the regulating tank through the drainage pipeline, fully regulating the water quality and quantity of the acid pickling waste liquid. The regulated wastewater is lifted to the acid-base reaction tank by a water pump, and alkaline substances (caustic soda, sodium bicarbonate, lime, etc.) are added to neutralize the acid pickling waste liquid while stirring. After a period of acid-base neutralization, the clear liquid on the upper layer of the reaction tank overflows to the sedimentation tank, and the water quality is tested after sedimentation. After reaching the standard, it is discharged or recycled.
(2) Neutralization+precipitation+flocculation+pressure filtration dehydration process
The acid washing wastewater is directly discharged into the regulating tank, which is equipped with perforated aeration pipes to homogenize and mix the wastewater. Wastewater is lifted from the regulating tank to the batch treatment tank by a lift pump for primary neutralization reaction, removing the majority of pollutants from the wastewater. The wastewater sludge that has undergone neutralization reaction settles in the batch treatment tank, and the settled wastewater continues to undergo secondary coagulation reaction in the batch treatment tank to thoroughly remove pollutants from the wastewater and ensure compliance with discharge standards. After the coagulation reaction, soluble pollutants are completely removed from the wastewater, and suspended solids are intercepted during the sand filtration process.
(3) Neutralization+pressure filtration dehydration+multi-stage filtration+reverse osmosis process
The quartz pickling wastewater first enters the regulating sedimentation tank, and lime water is added to adjust the pH to 8.5-9.5. After a period of reaction, a flocculant is added to coagulate impurities and sludge in the water, achieving better solid-liquid separation. The separated sludge then enters the sludge tank and is dehydrated by a plate and frame filter press before being transported outside.
The clear liquid on the regulating sedimentation tank is lifted by the raw water pump, then passes through the quartz sand filter, activated carbon filter, and then enters the security filter. After being pressurized by the high-pressure pump, it enters the reverse osmosis membrane group, and the concentrated water produced returns to the regulating sedimentation tank. The product water then enters the reuse water tank for reuse or discharge.
(4) Haipu Special Adsorption Technology
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in Suzhou Industrial Park. It is a national high-tech enterprise that uses special adsorbents and catalysts as its core technology, supporting the development of application processes, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to solve related environmental problems for customers. Haipu's technical team won the Suzhou Industrial Park Leading Talent Award in 2013 and 2015, and the Gusu Leading Talent Award in 2015. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. was rated as a national high-tech enterprise twice in 2015 and 2018, and was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalytic Functional Nanomaterial Engineering Technology Research Center in 2018. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has a leading technological level in the treatment of adsorption materials. The supporting adsorption treatment process is efficient and stable, and has solved multiple environmental problems for many leading domestic enterprises in the industry.
The basic principle of the Haipu special adsorption technology treatment process is to utilize the adsorption performance of special adsorption materials to adsorb and enrich iron, calcium, and magnesium ions in waste acid into the adsorption material, reducing the content of adsorbed acid ions and meeting customer requirements. After adsorption saturation, the adsorbent material is subjected to desorption treatment to regenerate and resume adsorption, and this process is continuously repeated.
Technological process
The process flow is shown in Figure 1-1. The wastewater is first filtered to intercept suspended solids and fine particles, preventing impurities from entering the adsorbent material and affecting its adsorption performance. The filtered wastewater is then sent to an adsorption tower equipped with special adsorption materials for adsorption. After adsorption saturation, the adsorption materials are subjected to desorption and regeneration treatment, and can be reused after regeneration. The adsorbed acid is recycled by the customer, and the high concentration desorption solution is treated by the customer.
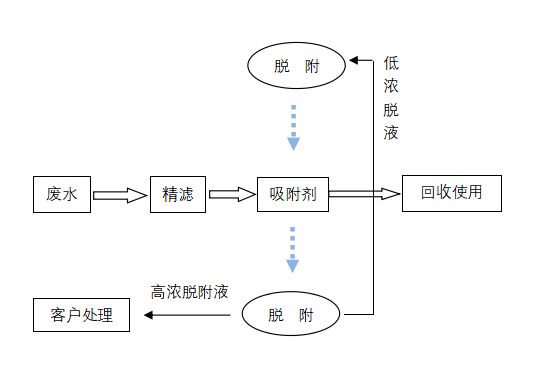
Figure 1-1 Process Flow Diagram
Scope of application
Quartz sand acid washing wastewater
Adsorption treatment case
Our company conducted multiple batches of adsorption and desorption experiments on sampled materials from a certain project site. The specific experimental results and comparison chart before and after processing are as follows:
Case 1 Adsorption of inlet and outlet water data
| Indicator | Acid content (m³/d) | Iron (mg/L) | Calcium (mg/L) | Magnesium (mg/L) |
| Adsorption into acid | 100 | 2410 | 445 | 314 |
| Adsorb acid 1 | 100 | 820 | 74 | 10 |
| Adsorb acid 2 | 100 | 902 | ~43 | ~16 |
| Adsorb acid 3 | 100 | 908 | ~34 | ~16 |
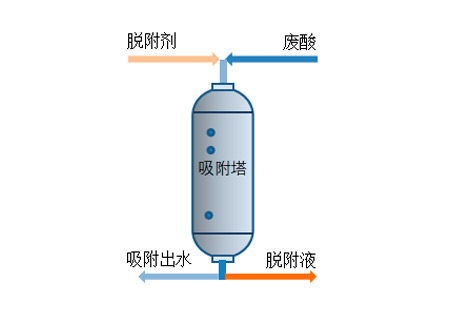
Figure 2-1 Principle of Waste Acid Adsorption Figure
Advantage
Solve the problem of waste acid treatment in enterprises, adsorb acid for recycling, ensure sustainable development of enterprises, and have significant economic and environmental benefits;
Special adsorbent materials have high absorption capacity and high concentration ratio, low equipment investment, and low operating costs;
Automated control, easy operation, convenient maintenance, and long service life;
The process flow is simple, reliable, and occupies a small area.




 CN
CN




