Chemical wastewater refers to the wastewater produced during the production of products in chemical plants, such as oily wastewater from the production of ethylene, polyethylene, rubber, polyester, methanol, ethylene glycol, oil tank areas, air separation and compression stations, etc. After biochemical treatment, it can generally meet the national secondary discharge standard. Due to the shortage of water resources, the water that meets the discharge standard needs to be further treated to meet the requirements of industrial water replenishment and reused.
As a major water user, chemical plants generally consume several million cubic meters of fresh water annually, with low water reuse rates. At the same time, they discharge several million cubic meters of sewage, which not only wastes a large amount of water resources but also causes environmental pollution. Moreover, the shortage of water resources has posed a threat to the production of these industrial water users. To maintain the sustainable development of the enterprise, reduce water waste, lower production costs, and improve the economic and social benefits of the enterprise. Chemical wastewater needs to undergo advanced treatment (tertiary treatment) as makeup water for circulating water or power desalinated water to achieve wastewater reuse.
Due to the fact that impurities in water are mainly suspended particles and fine fibers, mechanical filtration principle is used to remove impurities through microporous filtration technology. The working condition of the filter equipment is controlled by PLC or time relay to achieve automatic backwashing and operation, and the water pump is raised to provide the required water head for the filter. The effluent is directly introduced into the production system.
Main characteristics of chemical wastewater
The composition of chemical wastewater is complex, and the reaction raw materials are often solvents or cyclic compounds, which increases the difficulty of wastewater treatment;
The wastewater contains a large amount of pollutants, mainly due to incomplete reaction of raw materials and the use of a large amount of solvents in raw materials or production.
There are many toxic and harmful substances, and there are many organic pollutants in fine chemical wastewater that are toxic and harmful to microorganisms, such as halogen compounds, nitro compounds, dispersants or surfactants with bactericidal effects, etc;
There are many biologically recalcitrant substances, with B being lower than C and having poor biodegradability.
Wastewater properties
The wastewater generated in the production process of chemical products is characterized by large discharge volume, high toxicity, high concentration of organic matter, high salt content, high chromaticity, high content of difficult to degrade compounds, and difficult treatment. However, at the same time, there are also many available resources in the wastewater. Membrane technology, as a high-tech, plays an important role in the production and processing, energy conservation and consumption reduction, and clean production of the chemical industry.
Chemical wastewater pretreatment physicochemical process
1 Catalytic microelectrolysis treatment technology
Micro electrolysis technology is an ideal process for treating high concentration organic wastewater. This process is used for the treatment of high salt, difficult to degrade, and high color wastewater, which not only significantly reduces COD and color, but also greatly improves the biodegradability of the wastewater. This technology utilizes micro electrolysis fillers filled in micro electrolysis equipment to generate the "primary battery" effect for wastewater treatment without power supply. After the water is supplied, countless "primary batteries" with a potential difference of 1.2V will be formed inside the equipment. The "primary battery" uses wastewater as an electrolyte and generates an electric current through discharge to perform electrolytic oxidation and reduction treatment on the wastewater, in order to achieve the goal of degrading organic pollutants.
This process has the advantages of wide applicability, good treatment effect, low cost, short treatment time, convenient operation and maintenance, and low power consumption. It can be widely used in the pretreatment and deep treatment of industrial wastewater.
2 Multiphase catalytic oxidation treatment technology
This treatment technology is a newly developed technology in the field of environment, mainly using strong oxidants with hydroxyl radicals as the core to quickly, non selectively, and thoroughly oxidize various organic pollutants in the environment. Hydroxyl radicals react with soluble organic compounds in water to form hydroxyl radicals; Under the catalysis of catalysts, hydroxyl radicals oxidize and decompose organic matter in wastewater. This technology has significant effects on CODcr removal, decolorization, and improving the biodegradability of wastewater. Its chromaticity and CODcr removal rate can reach 75% -99%. In the practical application of pesticide wastewater, chemical wastewater, and pharmaceutical wastewater, this technology has demonstrated excellent application effects.
Chemical wastewater treatment methods
1 Chemical treatment methods
Chemical methods are the use of chemical reactions to remove organic and inorganic impurities from water. There are mainly chemical coagulation method, chemical oxidation method, electrochemical oxidation method, etc. The main target of chemical coagulation method is small suspended solids and colloidal substances in water. Through the coagulation and flocculation effects generated by adding chemical agents, the colloids are destabilized to form precipitates and removed. The coagulation method can not only remove fine suspended particles with a particle size of 1-10mm from wastewater, but also remove chromaticity, microorganisms, and organic matter. This method is greatly affected by changes in pH value, water temperature, water quality, water quantity, etc., and has a low removal rate for certain soluble organic and inorganic substances; Chemical oxidation is usually a method of using oxidants to oxidize and remove organic pollutants from chemical wastewater. Through chemical oxidation-reduction, wastewater can transform toxic organic and inorganic substances into non-toxic or less toxic substances, thereby achieving the goal of wastewater purification.
2 Physical Processing Method
The commonly used physical methods for chemical wastewater include filtration, gravity precipitation, and air flotation. The filtration method uses a layer of granular particles with pores to intercept impurities in water, mainly to reduce suspended solids in the water. In the filtration treatment of chemical wastewater, commonly used are frame filter machines and microporous filter machines. The microporous tubes are made of polyethylene, and the pore size can be adjusted for easy replacement; Gravity precipitation method is a process that utilizes the precipitable properties of suspended particles in water to naturally settle under the action of gravity field, in order to achieve solid-liquid separation; The air flotation method is a method of bringing suspended particles out of the water surface by generating adsorbed microbubbles. These three physical methods have simple processes and convenient management, but they are not suitable for the removal of soluble wastewater components and have significant limitations.
3 Photocatalytic oxidation technology
Photocatalytic oxidation technology combines oxidants such as O2 and H2O2 with light radiation through photoexcited oxidation. The main light used is ultraviolet light, including processes such as UV-H2O2 and UV-O2, which can be used to treat recalcitrant substances such as CHCl3, CCl4, and polychlorinated biphenyls in wastewater. In addition, in the Feton system with ultraviolet light, there is a synergistic effect between ultraviolet light and iron ions, which greatly accelerates the rate of hydroxyl radicals generated by the decomposition of H2O2 and promotes the oxidation and removal of organic matter.
It can generally be divided into two types: homogeneous and multiphase. Homogeneous photocatalytic degradation mainly uses Fe2+or Fe3+and H2O2 as media, and pollutants are degraded through photo Fenton reaction assisted by light, which can directly utilize visible light; Multiphase photocatalytic degradation is the process of adding a certain amount of photosensitive semiconductor material to a polluted system, combined with a certain amount of energy of light radiation, to excite the photosensitive semiconductor to produce electron hole pairs under light irradiation. Dissolved oxygen, water molecules, etc. adsorbed on the semiconductor react with the electron hole pairs, producing highly oxidizing free radicals such as • OH. Then, through hydroxyl addition, substitution, electron transfer, etc. with pollutants, the pollutants are completely or almost completely mineralized, ultimately generating CO2, H2O, and other ions such as NO3-, PO4 3-, SO4 2-, Cl -, etc. Compared with photocatalytic degradation without catalysts, the application research of photocatalytic degradation in environmental pollution control is more active.
4 Magnetic Separation Method
Magnetic separation method is a process of adding magnetic seeds and coagulants to chemical wastewater. By utilizing the residual magnetism of the magnetic seeds and the simultaneous action of the coagulants, particles are attracted to each other and agglomerate, accelerating the separation of suspended solids. Then, organic pollutants are removed using a magnetic separator. High gradient magnetic separation technology has been applied from the laboratory abroad.
There are three methods for applying magnetic separation technology to wastewater treatment: direct magnetic separation, indirect magnetic separation, and microbial magnetic separation. The use of magnetic technology to treat wastewater mainly relies on the cohesiveness of pollutants and their additive properties. Agglomeration refers to pollutants with ferromagnetism or paramagnetism, which condense into particles with increased surface diameter under the action of a magnetic field and are then removed. Additive seeding refers to the use of external magnetic seeds to enhance the magnetic properties of weak paramagnetic or non-magnetic pollutants, making it easier to remove them using magnetic separation methods; Alternatively, external microorganisms can be utilized to adsorb paramagnetic ions from wastewater, followed by magnetic separation to remove ion paramagnetic pollutants.
5 Adsorption method
The water quality of chemical wastewater containing heavy metals is complex and the composition is difficult to control. The heavy metal ions such as nickel, zinc, copper, cadmium, chromium, etc. contained in it are highly toxic, some of which are carcinogenic and highly toxic substances, posing great harm to humans.
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise dedicated to the research and development of high-performance adsorbents, catalysts, and their process applications. With a series of independently developed high-performance adsorbents and catalysts as the core, combined with independently developed process technology, Haipu has become a professional solution provider in the fields of environmental governance and resource recycling. At the same time, taking it as our responsibility to help industrial enterprises meet environmental standards and achieve sustainable development through resource utilization, we adopt modular lean production and develop engineering solutions based on research and development data.
The Haipu team targets the characteristics of specific heavy metal ions and utilizes the special functional groups of chelating resin adsorption materials to form complexes with heavy metal ions, achieving the recovery and utilization of heavy metal ions. This type of resin adsorbent material has high selectivity for heavy metal ions, and the treated wastewater can meet the discharge standards. Has a large material adsorption capacity, low operating costs, easy regeneration, and long service life; The adsorption treatment technology is widely used in the treatment of wastewater generated in processes such as non-ferrous metal production, electroplating, mining, and petrochemical catalysis due to its technical advantages of low operating costs, low maintenance costs, and simple operation. The process flow is as follows:
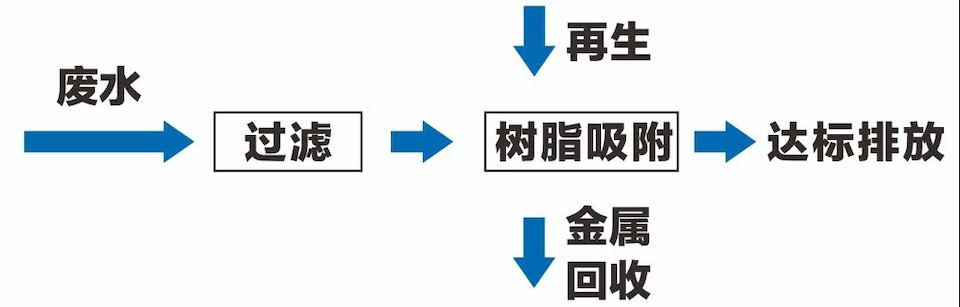
Figure 1 Process Flow
5.1 Technical advantages
Can meet environmental protection requirements and meet emission standards (nickel content ≤ 0.1ppm, copper content ≤ 0.5ppm);
The material has a large adsorption capacity, low operating cost, easy regeneration, and long service life;
The equipment has low operating costs, low maintenance expenses, and simple operation.
5.2 Application Cases
We have implemented nickel containing wastewater treatment and resource utilization in a petrochemical enterprise, achieving citric acid reuse and nickel concentration recovery, with an annual recovery value of about 5 million yuan.
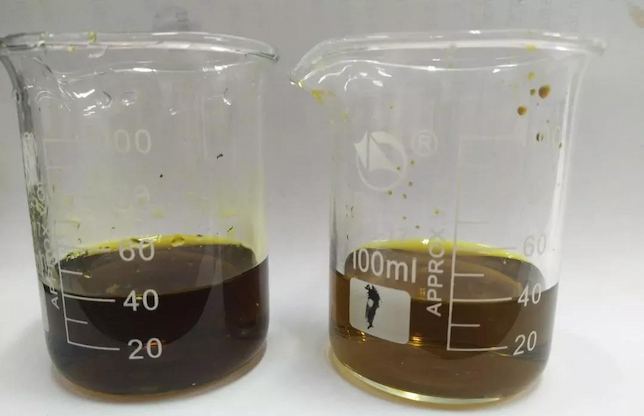

Figure 2 Comparison of nickel containing wastewater raw water and effluent (raw water 1700mg/L, effluent ≤ 0.1mg/L).
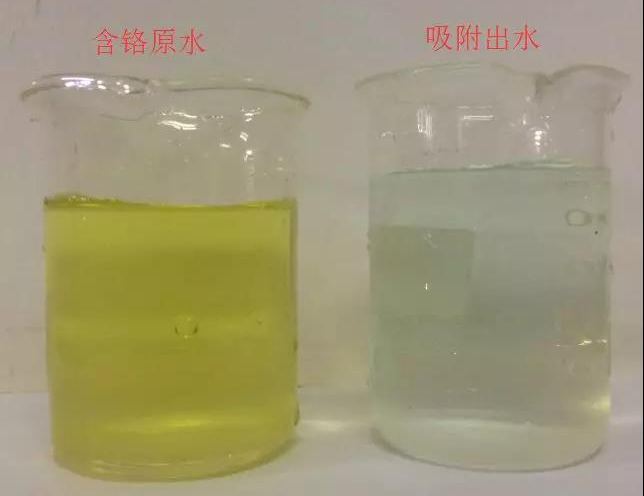

Figure 3 Comparison of chromium containing wastewater raw water and effluent (raw water 1300mg/L, effluent ≤ 0.1mg/L).
Conclusion
The treatment of chemical wastewater is a major challenge for the development of the chemical industry and is of great significance to the economic and social development of the country. Relying solely on the basic treatment methods mentioned above is far from enough. In the process of chemical production, it is necessary to greatly reduce the discharge of wastewater and minimize pollution from the source. At the same time, we should also strive to explore new processes for wastewater treatment to promote the development of wastewater treatment technology.




 CN
CN





