In industries such as steel, metallurgy, and electroplating, surface treatment of metals is essential. In the steel industry, if the steel is left for too long, rust and oxide scale will form on its surface. In order to carry out further processing such as cold rolling, surface coating, and surface coating on the steel, the oxide scale and rust on the surface need to be removed. The main components of oxide scale and rust include iron oxide, iron oxide, and ferrous oxide. The methods for removing iron oxide scale and rust mainly include mechanical treatment, neutral electrolysis descaling, and acid washing. Due to the easy reaction between iron oxide and acid, acid washing is the most commonly used treatment method. During the pickling process, the acid reacts with iron oxides and the matrix iron, gradually being consumed. At the same time, the concentration of ferrous and iron ions in the acid gradually increases. When the concentration of ferrous and iron ions in the pickling solution reaches a certain value, the pickling efficiency becomes very poor, and the pickling solution can no longer be used, thus becoming pickling waste liquid. Acid pickling waste liquid not only comes from the steel industry, but also is used in industrial production processes such as metal product processing, electroplating, metallurgy, etc. Therefore, these industries generate a large amount of acid pickling waste liquid every year. The commonly used acid pickling agents currently include hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, and hydrofluoric acid. Depending on the object of pickling, the type of pickling solution, and the requirements for the product, the composition, acidity, and metal ion concentration of the pickling waste liquid may also vary. The pickling waste liquid mainly contains H+, Cl -, SO4 2-, Fe2+, Fe3+, Cu2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+ions. With the development of the economy and people's increasing demand for materials, the demand for metals and metal processing products is also constantly increasing, which has driven the development of industries such as steel, electroplating, and metal processing. Therefore, the amount of acid pickling waste generated every day is still increasing.
The characteristics of acid pickling waste liquid are large waste liquid volume, high concentration of acid and metal ions, and direct discharge can cause great harm. Firstly, when the acid pickling waste liquid is discharged into the sewer, it will damage the pipeline structure due to its strong acidic corrosiveness; Secondly, when the acid pickling waste liquid enters the water body, the heavy metal ions in the waste liquid will contaminate the water source, and the residual acid will react with the calcium carbonate in the water to disrupt the acid-base balance of the water body, which is not conducive to the survival of fish and other animals; Finally, when the acid pickling waste liquid seeps into the soil, it will damage the soil and affect the growth of crops. In summary, direct discharge of acid pickling waste liquid not only poses serious environmental hazards, but also wastes the recyclable resources in the acid pickling waste liquid, which does not meet the strategic requirements of sustainable green development in China.
1. Conventional acid pickling waste liquid treatment technology
Due to the hazards of acid pickling waste liquid, it needs to be properly and carefully treated. Currently, there are several conventional methods for treating acid pickling waste liquid, including the following:
(1) Neutralization precipitation method
The neutralization precipitation method refers to the process of adding alkaline reagents such as quicklime to waste acid, neutralizing it with free acid in the acid washing waste liquid, and precipitating metal ions. After multi-stage precipitation separation, the pH value of the waste liquid is adjusted to between 5.6 and 6.5 with acid, and then discharged after reaching the national standard. The chemical reactions involved mainly include the following:
2HCl+Ca(OH)2=CaCl2+2H2O
2FeCl2+2Ca(OH)2+H2O+1/2O2=2Fe(OH)3+2CaCl2
The neutralization precipitation method for treating waste acid has the advantages of simple principle and convenient operation, but it still has some shortcomings. On the one hand, the treatment process requires a large amount of alkaline neutralizing agent, and a large amount of free acid in the waste acid is neutralized and consumed, wasting resources. On the other hand, the treatment process also produces a lot of sludge, causing secondary pollution. Therefore, secondary treatment is needed, usually by sending the sludge to the waste site for landfill or to the recycling station for processing and reuse, which requires a lot of resources.
(2) High temperature roasting method
High temperature roasting method is a resource utilization method for treating waste acid, mainly used for the treatment of hydrochloric acid pickling waste liquid. It can simultaneously recover resources such as hydrochloric acid and iron in the waste acid. The principle is that the residual hydrochloric acid in the pickling waste liquid evaporates into steam at high temperature, while the ferrous salt quantitatively hydrolyzes to produce iron oxide and hydrogen chloride in an atmosphere with sufficient water vapor and appropriate oxygen at high temperature. The reaction equation is as follows:
4FeCl2+O2+H2O→Fe2O3+8HCl
The high-temperature roasting method for treating waste acid has the advantages of large waste liquid treatment capacity, low waste generation, and high resource recovery rate. It can not only recover high concentration acid and directly reuse it in the acid washing process, but also recover the metals in the waste acid to obtain iron oxide, which can be used for smelting and the production of magnetic materials and pigments. However, the high-temperature roasting method for treating waste acid still has some drawbacks, such as complex treatment processes, the need for a large number of equipment, high requirements for equipment corrosion resistance, high equipment investment costs, and high operating expenses. It is more suitable for large steel enterprises, but limits its application in some small and medium-sized enterprises.
(3) Evaporation method
Evaporation method is a waste acid treatment method that can separate acids and metal salts, mainly used for the recovery of volatile acids (such as hydrochloric acid). Its principle is to heat the acid to evaporate into steam and then condense it to obtain acid solution, while the metal salts remain in the mother liquor and are separated from it by cooling crystallization.
The evaporation method can effectively recover metal salts and free acids from waste acid, but the process of treating waste acid by evaporation method requires high temperature, and the acid pickling waste liquid has strong acid corrosion resistance, so it requires high corrosion resistance of the equipment. In addition, the acid concentration obtained by evaporation method is relatively low, and the equipment maintenance cost is high, so it still has certain limitations in practical applications.
(4) Solvent extraction method
The solvent extraction method utilizes the different distribution coefficients of each component in the acid pickling waste liquid in immiscible solvents to extract metal ions from the acid pickling waste liquid, thereby achieving the separation of acid and metal ions. The solvent extraction method for treating waste acid has some advantages, such as being able to be carried out at room temperature and low energy consumption. However, efficient extractants are generally toxic organic solvents, and the treatment process requires the use of a large amount of extractants, resulting in high costs.
2. Introduction to Haipu customized process:
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is located in Suzhou Industrial Park. It is a national high-tech enterprise that uses special adsorbents and catalysts as its core technology, supporting the development of application processes, technical services, engineering implementation, etc., to solve related environmental problems for customers. Haipu's technical team won the Suzhou Industrial Park Leading Talent Award in 2013 and 2015, and the Gusu Leading Talent Award in 2015. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. was rated as a national high-tech enterprise twice in 2015 and 2018, and was approved as the Suzhou Adsorption and Catalytic Functional Nanomaterial Engineering Technology Research Center in 2018. Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. has a leading technological level in the treatment of adsorption materials. The supporting adsorption treatment process is efficient and stable, and has solved multiple environmental problems for many leading domestic enterprises in the industry.
The principle of the Haipu adsorption process is to use the special adsorption materials developed by our company to selectively adsorb the components or substances to be removed. When the adsorption is saturated, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to be regenerated. This process is continuously repeated. The conventional process for treating waste acid by adsorption method is shown in the following figure.
Process diagram for adsorption treatment of waste acid
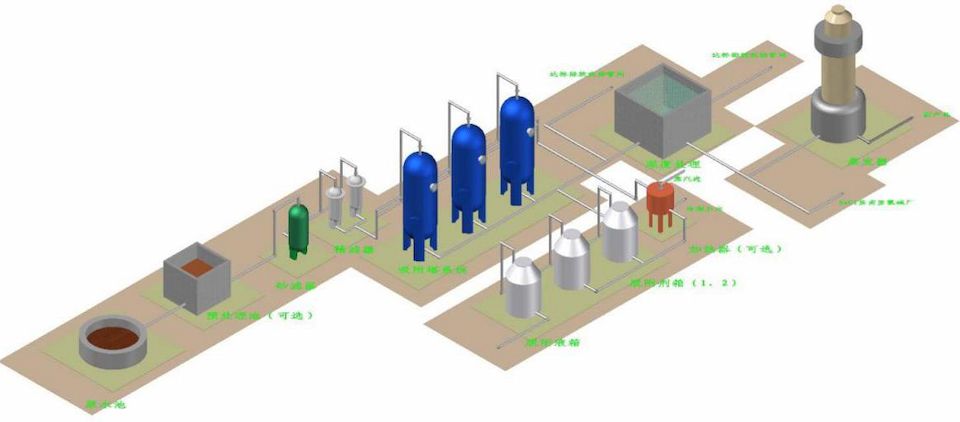
Adsorption treatment process for waste acid
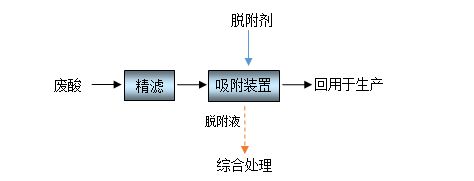
When using Haipu's adsorption process to treat waste acid, the waste acid first passes through a fine filtration system to intercept fine suspended solids and particles in the waste acid, preventing impurities from entering the adsorption material and affecting the adsorption performance. After fine filtration, the waste acid enters the adsorption tower equipped with special adsorption materials for adsorption. After adsorption saturation, the adsorption materials are subjected to desorption and regeneration treatment. The regenerated adsorption materials can be reused, and the adsorbed acid can be recycled by customers.
Process treatment effect: Adsorption technology is used to treat waste acid, and the use of special adsorbents can effectively reduce the concentration of metal ions in the waste acid. After adsorption treatment of waste acid from a certain enterprise in Jiangsu, the treatment effect showed that the metal ions in the waste acid were significantly affected by adsorption treatment, meeting customer requirements. The specific data is shown in the table below.
Table 1 Adsorption in and out acid data
| Index | Iron (mg/L) | Calcium (mg/L) | Magnesium (mg/L) |
| Adsorption into acid | 2410 | 445 | 314 |
| Adsorb acid 1 | 820 | 74 | 10 |
| Adsorb acid 2 | 902 | ~43 | ~16 |
| Adsorb acid 3 | 908 | ~34 | ~16 |

Processing effect image: From left to right are the original acid and adsorbed acid, respectively
Core advantages of craftsmanship:
At present, the methods for recycling waste acid have their own shortcomings in terms of treatment efficiency and operating costs. Compared to adsorption methods, adsorption methods have the following advantages:
(1) Conduct experiments on waste acid sampling samples generated on the enterprise site, based on technology and experiments, to design adsorption processes with a 100% matching degree between processes.
(2) The equipment occupies less land, has a compact structure, and requires less investment in civil engineering and equipment; The desorption agent is applied multiple times and concentrated step by step, resulting in high drug utilization and low operating costs.
(3) It can be implemented in module component form, flexibly adjusted according to production capacity, and easy to install.
(4) Advanced and mature technology, no secondary pollution, strong technical support, and rich engineering application experience.




 CN
CN





