1 Overview
In August 2017, the SEPS industrial plant with an annual output of 20000 tons was completed and put into operation in the Synthetic Rubber Division of Baling Petrochemical Company, ending the history of China's inability to produce SEPS. The company also became the third SEPS producer in the world, and its SEPS products are mainly used in the fields of fiber optic cable grease, lubricant viscosity index improver, high-performance elastomers, etc. The products have been highly recognized by the market.
The SEPS industrial complete technology process integrates and adopts more than 20 Sinopec patents and proprietary technologies, including the 80m3 polymerization kettle and hydrogenation kettle independently developed by Baling Petrochemical, organic nickel based catalytic hydrogenation technology, gel liquid three kettle coagulation and drying devolatilization post-treatment. This process generates a stream of catalyst wastewater containing heavy metal ions such as nickel, aluminum, lithium, cobalt, as well as citric acid, which needs to be treated for resource utilization.
2 Wastewater treatment processes
Wastewater contains a large amount of heavy metal ions, and the commonly used treatment methods currently include chemical precipitation, adsorption, membrane separation, electrolysis, ferrite, extraction, etc.
Table 2-1 Comparison of Advantages and Disadvantages of Heavy Metal Wastewater Treatment Processes
| Wastewater treatment process | Advantage | Shortcoming |
| Adsorption method | ① Deeply remove metal ions from wastewater, and the concentration of nickel and chromium ions can be controlled below 0.1mg/L;
② Recyclable metal ions in wastewater can achieve resource utilization of wastewater and reduce production costs for enterprises;
③ Nano adsorbent material, with large adsorption capacity, renewable use of adsorbent material, and long service life;
④ It can be implemented in the form of modular components, which can be flexibly adjusted according to production capacity, saving land and having a compact structure;
⑤ High degree of automation, short process flow, simple operation, and low energy consumption. | The composition of wastewater is complex, and adsorption materials exhibit different adsorption abilities for different metal ions. One adsorption material cannot simultaneously remove multiple metal ions. |
|
|
|
|
| Chemical precipitation method | ① At present, the most widely used method both domestically and internationally has a simple process that can simultaneously remove metal ions from multiple types of wastewater;
② Low equipment investment, cheaper prices of alkaline consumables such as lime, and relatively low operating costs. | ① Generate a large amount of heavy metal waste residue, which cannot be directly dumped or buried, and needs to be reprocessed;
② The concentration of metal ions in the effluent of neutralization method is still high and does not meet the discharge standards;
③ Unable to recycle metals from wastewater and consume a large amount of alkali, which is not conducive to the resource utilization production of enterprises. |
|
|
| Membrane separation method | Easy to operate, except for pumping liquids, the dialysis process does not consume electricity and has low energy consumption; | ① The membrane processing capacity is not large, and the equipment volume is huge;
② The equipment investment is large, and the membrane needs to be cleaned regularly and replaced frequently;
③ There is a lot of concentrated liquid that needs to be treated to meet standards and cannot be directly discharged. |
|
|
| Electrolytic method | The device has a small volume and does not require additional chemical agents, resulting in minimal secondary pollution; | ① High energy consumption and cost, with side reactions such as hydrogen and oxygen evolution, resulting in energy waste;
② Long term continuous operation can easily lead to electrode surface passivation, low efficiency, and high power consumption. |
|
| Ferrite method | Ferrous sulfate has a low price, wide sources, simple process, good treatment effect, and large processing capacity | ① Heating (about 70 ℃) is required during the ferrite process, which consumes a lot of energy and increases processing costs;
② The amount of sludge generated is large, and the reaction conditions are difficult to control; ③ After treatment, the salinity is high, and there is an inability to treat wastewater containing Hg and complexes. |
|
| Extraction method | Good separation and removal effect through liquid-liquid contact | Highly selective extractants have strong specificity, but the solvent is severely lost during the extraction and regeneration processes. The energy consumption during the regeneration process is high, and they do not have the ability to treat general wastewater. |
Introduction to Haipu Adsorption Process
The principle of the Haipu adsorption process is to use the special adsorption materials developed by our company to selectively adsorb the components or substances to be removed. When the adsorption is saturated, a specific desorption agent is used to desorb the adsorption material, allowing it to be regenerated. This process is continuously repeated. The conventional process of treating wastewater by adsorption method is shown in the following figure.
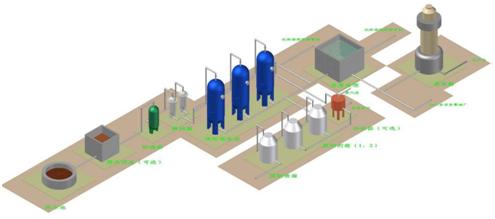
Figure 1 Conventional Process Diagram for Adsorption Treatment of Wastewater
When using Haipu's adsorption process to treat wastewater containing heavy metal ions, the wastewater is pre filtered to remove suspended and particulate matter, and then enters the adsorption tower for adsorption. The special adsorption material filled in the adsorption tower can adsorb heavy metals in the wastewater on the surface of the material, and the heavy metals in the effluent meet the requirements. Citric acid can be recovered from the effluent. After adsorption saturation, specific desorption agents are used to desorb the adsorbent material, allowing it to regenerate, and this process is continuously repeated. A large amount of heavy metal ions are enriched in the desorption solution, which can be returned to the front-end precipitation system for treatment.
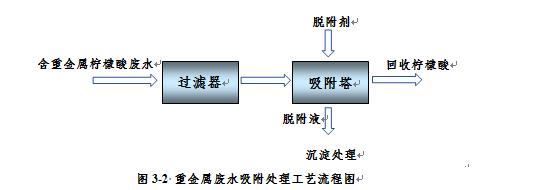
Figure 2 Process Flow Diagram for Adsorption Treatment of Heavy Metal Wastewater
4 Application Cases
Jiangsu Haipu Functional Materials Co., Ltd. is committed to the research and industrialization of high-performance adsorbents and catalysts. Through years of independent research and development, we have achieved international leading levels in ion exchange technology, adsorption technology, nano inorganic material hybridization technology, etc., realizing the serialization of adsorption and catalytic products, and successfully applying them in the fields of environmental protection and resource recycling. With a series of independently developed high-performance adsorbents and catalysts as the core, combined with self-developed process technology, Haipu has become a professional supplier of green and environmental protection solutions.
The application cases of Haipu nano adsorbent technology are as follows:
Citric acid wastewater treatment project of a certain enterprise in Zhejiang Province
A certain synthetic material enterprise has a citric acid wastewater containing metal ions that needs to be treated during the production process. The content of cobalt, aluminum, and lithium ions is high. Our company uses nano adsorption materials to remove cobalt, lithium, and aluminum from the wastewater. The metal ion content in the effluent meets the customer's requirements, making it convenient for customers to tax citric acid resources and promoting the sustainable development of the enterprise.
Table 4-1 Adsorption inlet and outlet water data
| Project | Cobalt(mg/L) | Lithium(mg/L) | Aluminum(mg/L) |
| Raw water | 1150 | 1700 | 770 |
| Water outlet 1 | 0.46 | 8.9 | 220 |
| Water outlet 2 | 0.26 | 8.2 | 203 |
| Water outlet 3 | 0.3 | 8.5 | 214 |

Figure 3 Appearance of Raw Water (Left) and Outlet Water (Right)
Project Highlights:
Efficiently remove metal ions from wastewater, strictly control the concentration of metal ions in the effluent, and be suitable for controlling the end of the wastewater;
Using specially modified adsorption materials, with large adsorption capacity and low equipment investment;
The equipment has a compact structure, occupies a small area, is easy to install, debug, and maintain, and has a short construction period;
Low energy consumption, low operating costs, can achieve the recycling and utilization of citric acid, and improve the economic benefits of enterprises.
High degree of automation, easy operation and maintenance, and stable operational performance.




 CN
CN





